Figure 4-5. sequential decoder block diagram – Comtech EF Data SDM-100A User Manual
Page 126
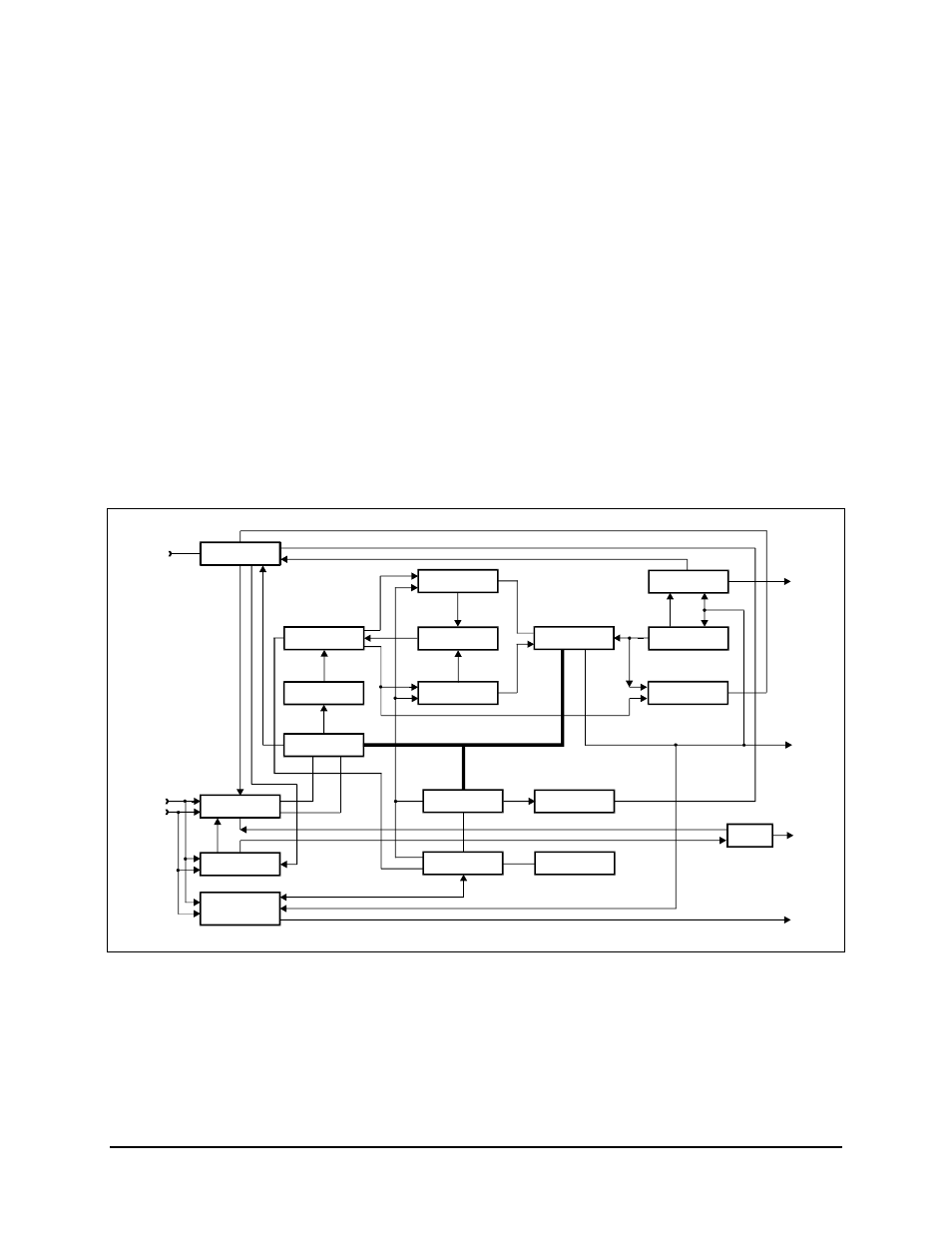
Theory of Operation
SDM-100A Satellite Modem
4–10
Rev.
0
The syndrome input generator converts the 2-bit soft decision data into a single bit per
channel, and simultaneously corrects some isolated bit errors. The data is then shifted
through the syndrome shift registers, which allows the parity generator to detect bit
errors. The resulting error signal provides the feedback to the timing and control circuitry
to allow it to direct the data along the path of the highest cumulative metric.
The corrected data is buffered through the output RAM and retiming circuit, which
provides a data stream to the differential decoder and descrambler at the constant rate of
the data clock. The data and the clock are then output from the card.
The sequential decoder also provides a lock detect signal to the M&C when the error rate
has dropped below a threshold level. The M&C monitors these signals and takes
appropriate action.
The raw BER count is made by comparing the input and output decoder data. Because the
input data contains many more errors than the output, differences in the two can be
counted to yield the raw BER. The raw BER is sent to the M&C for further processing.
MICRO-
COMPUTER
BUS
MICROCOMPUTER
INTERFACE
SYNDROME SHIFT
REGISTER A
DESCRAMBLER
V.35
RECEIVE
DATA
DECODER
DETECTOR
DIFFERENTIAL
CHANNEL BER
OUTPUT
BUFFER
PARITY
GENERATOR
SYNDROME SHIFT
REGISTER B
AMBIGUITY
RESOLVER
SYNDROME INPUT
GENERATOR
INPUT
BUFFER
RECEIVE
CLOCK
RCVR
DDS
LOCK
DETECT
ADDRESS
GENERATOR
COSTAS
PROCESSOR
I CHANNEL
Q CHANNEL
VCXO
SWEEP
TIMING AND
CONTROL
PROCESS
CLOCK
IF
AGC
CONTROL
CLOCK
RECOVERY
Figure 4-5. Sequential Decoder Block Diagram
