Port trunking – D-Link DES-3624 User Manual
Page 34
Stackable NWay Ethernet Switch User’s Guide
34
Switch Management Concepts
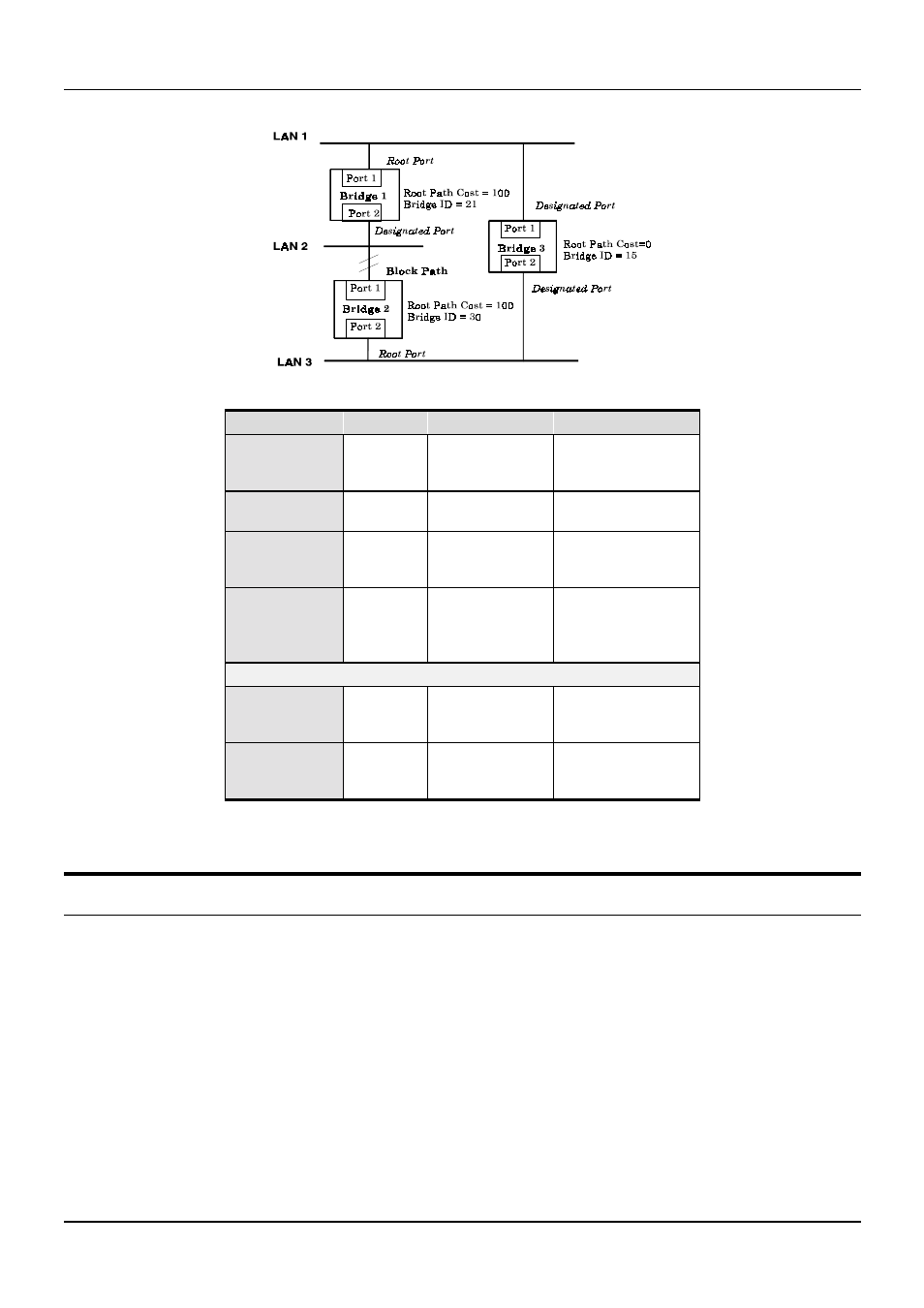
Figure 5-2. After Applying the STA Rules
STA parameters
Settings
Effects
Comment
Bridge Priority
lower the #,
higher the
priority
Increases chance of
becoming the Root
Bridge
Avoid, if the switch is
used in workgroup level
of a large network
Hello Time
1 - 10 sec.
No effect, if not
Root Bridge
Never set greater than
Max. Age Time
Max. Age Time
6 - 40 sec.
Compete for Root
Bridge, if BPDU is
not received
Avoid low number for
unnecessary reset of
Root Bridge
Forward Delay
4 - 30 sec.
High # delays the
change in state
Max. Age
≤
2 x
(Forward Delay - 1)
Max. Age
≥
2 x (Hello
Time + 1)
Port Level STA parameters
Enable / Disable
Enable /
Disable
Enable or disable
this LAN segment
Disable a port for
security or problem
isolation
Port Priority
lower the #,
higher the
priority
Increases chance of
become Root Port
Table 5-1. User-selective STA parameters
Port Trunking
Port trunking is used to combine a number of ports together to make a single high-bandwidth data pipeline.
The participating parts are called members of a trunk group, with one port designated as the anchor of the
group. Since all members of the trunk group must be configured to operate in the same manner, all settings
changes made to the anchor port are applied to all members of the trunk group. Thus, when configuring the
ports in a trunk group, you only need to configure the anchor port.
The Switch supports 3 trunk groups, which may include from 2 to 8 switch ports each, except for the third
trunk group which consists of the 2 ports of the Slot 1, 100BASE-TX or 100BASE-FX front-panel module. The
anchor port for the first group is preset as port 5, the anchor port for the second group is port 13 and the
anchor port for the third group is the first port (1x) on the 2-port module.
