Titration theory – Hanna Instruments HI 903 User Manual
Page 204
12
TITRATION THEORY
Figure 3 shows a traditional titration curve. The curve is obtained by plotting the pH value
against the volume of NaOH added.
2.2.3 Argentometric Titrations
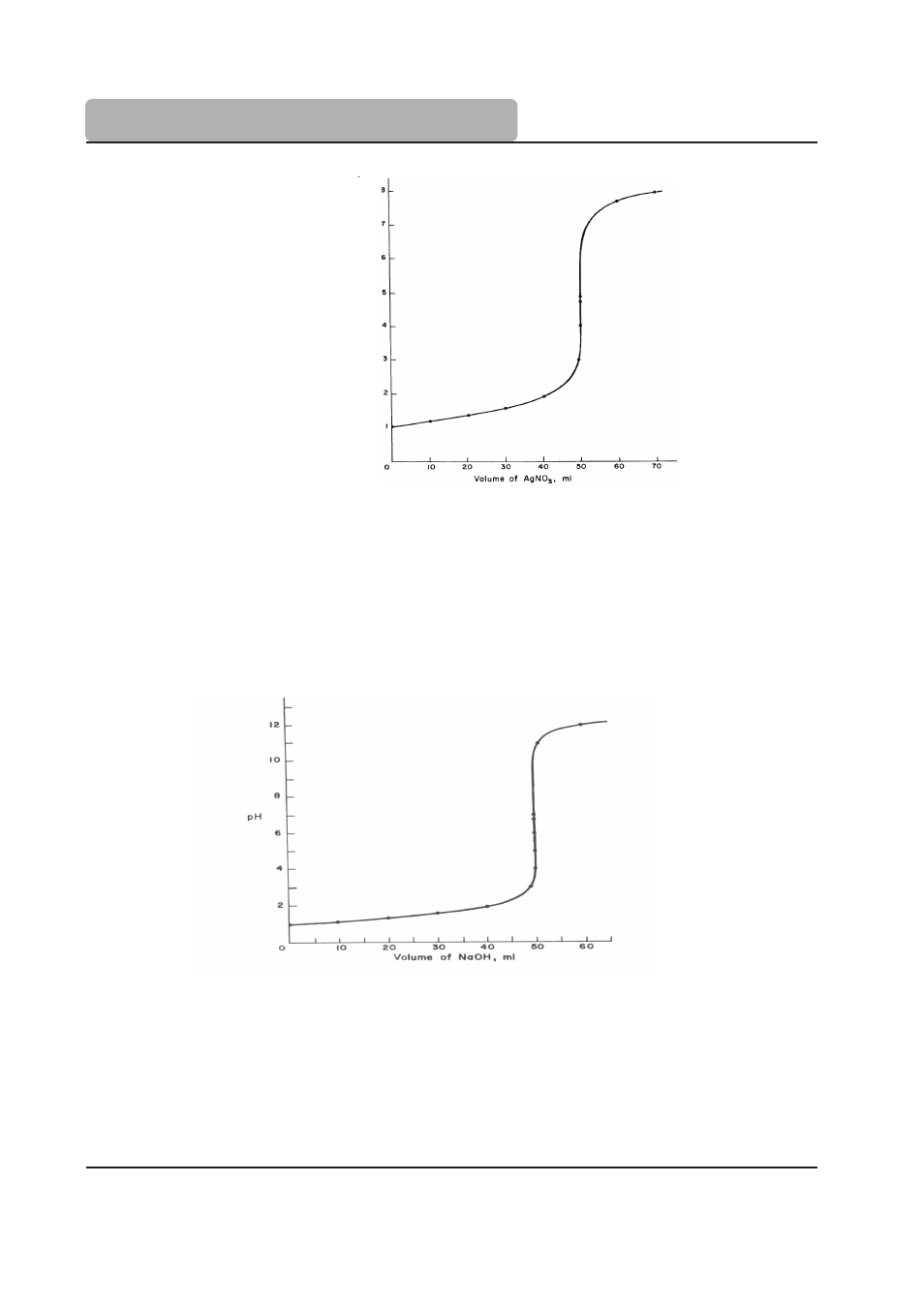
Argentometric titrations use silver (nitrate) as the titrant and are generally precipitation titrations,
as many silver salts are insoluble. These titrations are commonly used to titrate and determine
the concentration of bromide, chloride, cyanide, iodide, and sulfide.
Argentometric titrations can be done with Mohr’s indicator, when all of the chloride has reacted,
a red silver chromate precipitate is formed or the titration can be easily followed with a silver ISE
(or chloride ISE for chloride titrations) and a reference electrode.
Figure 4
shows the titration of 50 mL of 0.1N NaCl with 0.1N AgNO
3
. The potentiometric
signal is from a chloride ISE, and is plotted as pCl (- log [Cl-]).
2.2.4 Complexometric Titrations
A complex is a species where a central metal ion is covalently bonded to one or more electron
donating groups called ligands. In a complexometric titration, metal ions are titrated using a
p
C
l
Figure 3
Figure 4
