Panasonic 7 User Manual
Page 126
Attention! The text in this document has been recognized automatically. To view the original document, you can use the "Original mode".
126 Chapter 6 Configuring branch office tunnels
A DNS server will be aware of all the IP addresses that correspond to a particular
domain name. When a user requests a lookup for that domain, the DNS will
provide all the known addresses in a random order. The user can pick one of the
addresses to communicate with the service. The Nortel VPN Router always uses
the first address provided. If the first address is unresponsive, the Nortel VPN
Router performs a new query.
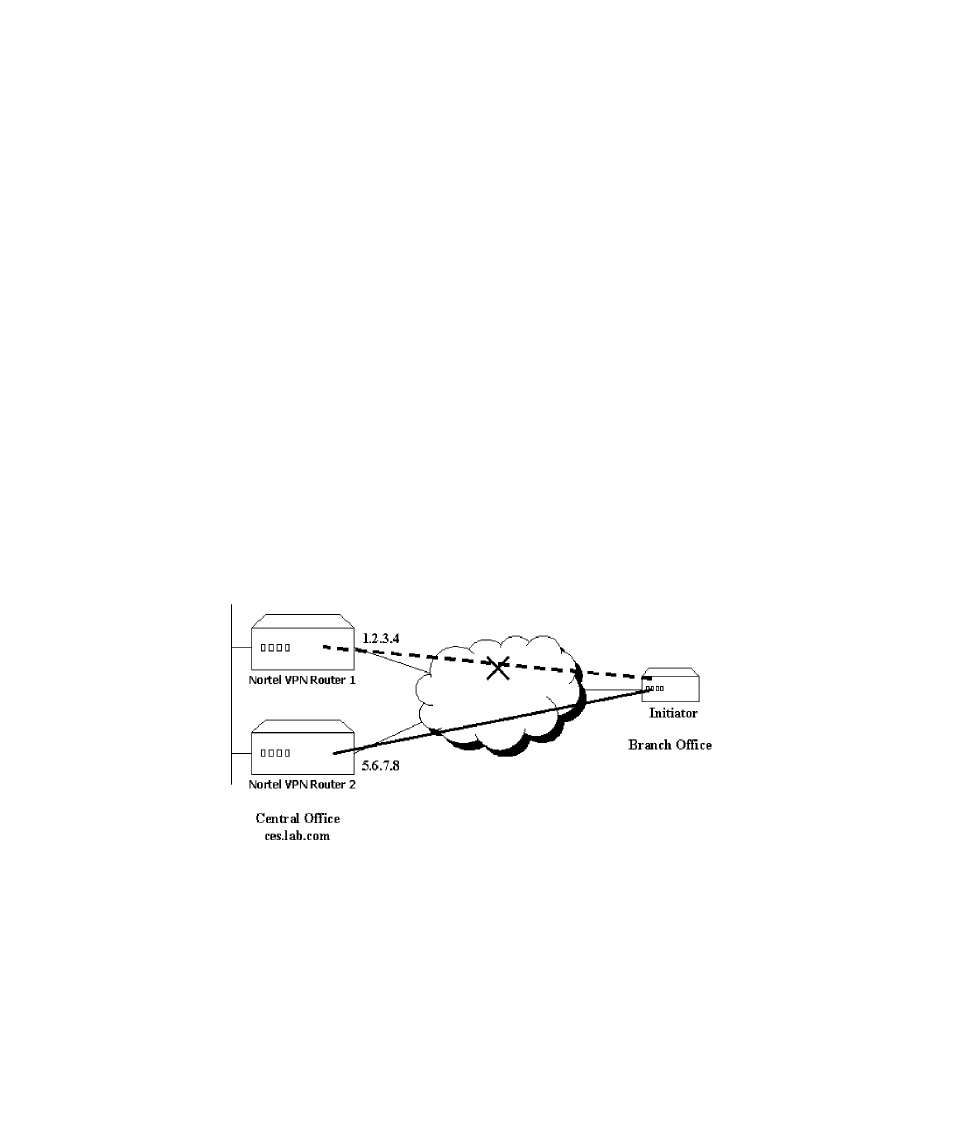
Round Robin DNS can be used to achieve failover. Figure 23 shows a central
office that has two Nortel VPN Routers. The first VPN Router has a public IP
address 1.2.3.4 and the second has public IP address 5.6.7.8. Both addresses have
been mapped to the same DNS name ces.lab.com. The initiator is configured with
the remote endpoint set to the domain name of the responder ces.lab.com. When
the initiator performs a DNS query, the DNS server returns IP addresses 1.2.3.4
and 5.6.7.8. The initiator selects 1.2.3.4 because it is first in the list of addresses
and establishes a tunnel. If 1.2.3.4 goes down, the initiator must reestablish the
tunnel and send a new DNS query. The DNS server returns addresses 5.6.7.8 and
1.2.3.4 because of the Round Robin operation. The initiator selects address 5.6.7.8
because it is the first in the list and establishes a tunnel with the second Nortel
VPN Router, achieving a failover.
Figure 23
Failover example
Round Robin DNS can be used to achieve a simple load balancing between Nortel
VPN Routers. Figure 24 on page 127 shows a central office that has two Nortel
VPN Routers. The first VPN Router has public IP address 1.2.3.4 and the second
has public IP address 5.6.7.8. Both addresses are mapped to the same DNS name,
such as ces.lab.com. There are multiple branch offices and the initiators at the
NN46110-500
