Change tracking – Dell PowerVault DP600 User Manual
Page 95
95
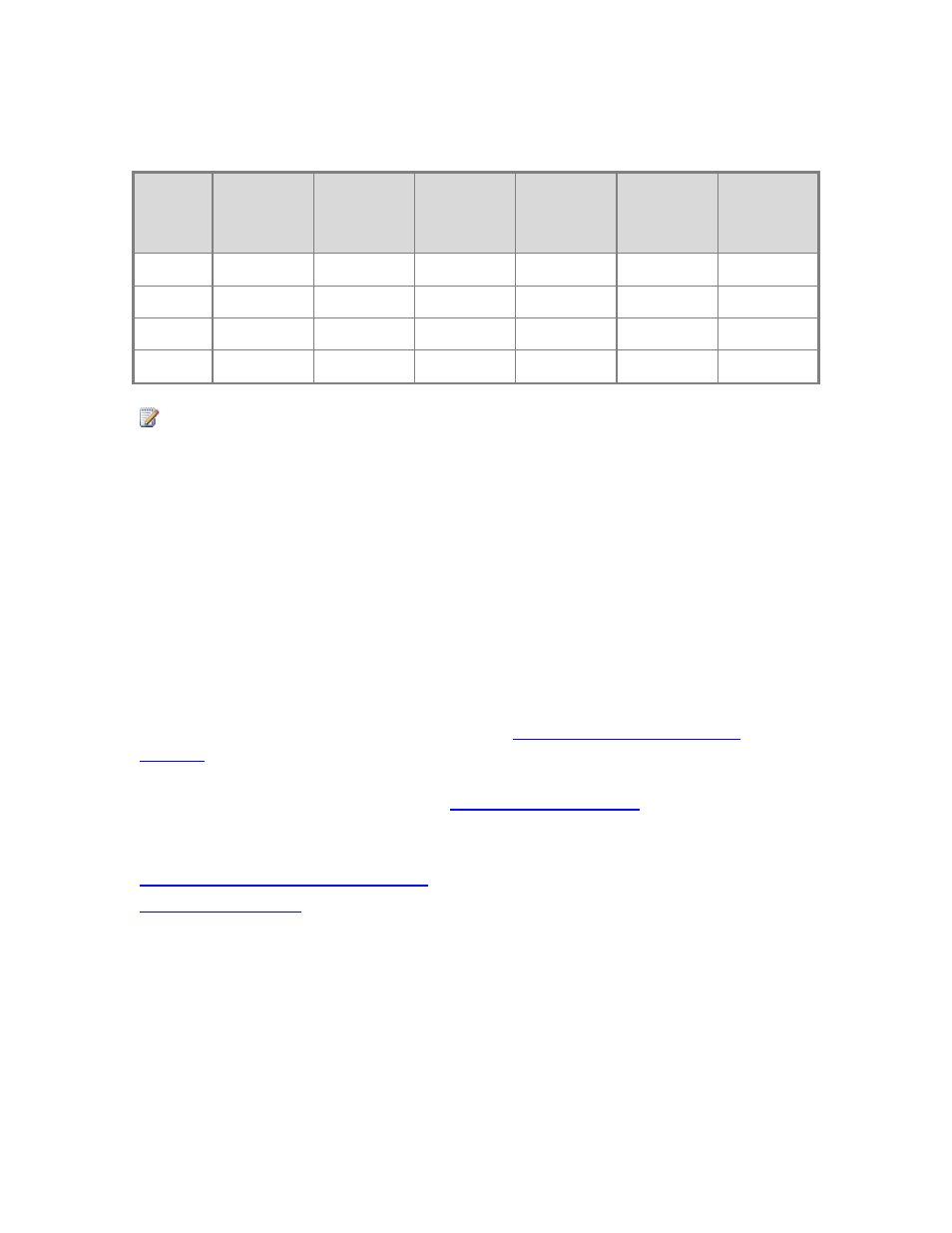
Time Required to Transmit Data over a Network at Various Speeds
Data size
Network
speed
1 Gbps
Network
speed
100 Mbps
Network
speed
32 Mbps
Network
speed
8 Mbps
Network
speed
2 Mbps
Network
speed
512 Kbps
1 GB
< 1 minute
< 1 hour
< 1
< 1
1.5
6
50 GB
<10 minutes 1.5 hour
5
18
71
284
200 GB
<36 minutes 6 hours
18
71
284
1137
500 GB
<1.5 hours
15
45
178
711
2844
Note
• In the preceding table, Gbps = gigabits per second, Mbps = megabits per second, and
Kbps = kilobits per second. The figures for a network speed of 1 Gbps assume that the
disk speed on the DPM server and the protected computer are not a bottleneck.
Typically, the time to complete initial replica (IR) creation can be calculated as follows:
• IR: hours = ((data size in MB) / (.8 x network speed in MB/s)) / 3600
• Note 1: Convert network speed from bits to bytes by dividing by 8.
• Note 2: The network speed is multiplied by .8 because the maximum network efficiency is
approximately 80%.
On an extremely fast network, such as a gigabit connection, the speed of replica creation will be
determined by the disk speed of the DPM server or that of the protected computer, whichever is
slower.
The impact of replica creation on network performance can be reduced by using network
bandwidth usage throttling. For more information, see
To avoid the network load of replica creation, you can create replicas manually from tape or other
removable media. For more information, see
See Also
How DPM Operations Affect Performance
Change Tracking
After the replica is created, the DPM protection agent on the computer begins tracking all
changes to protected data on that computer. Changes to files are passed through a filter before
being written to the volume. This process is similar to the filtering of files through antivirus
software, but the performance load of DPM tracking changes is less than the performance load of
antivirus software.
