Transmig 175i – Tweco 175i Transtig User Manual
Page 24
TRANSMIG 175i
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
3-6
Manual 0-5143
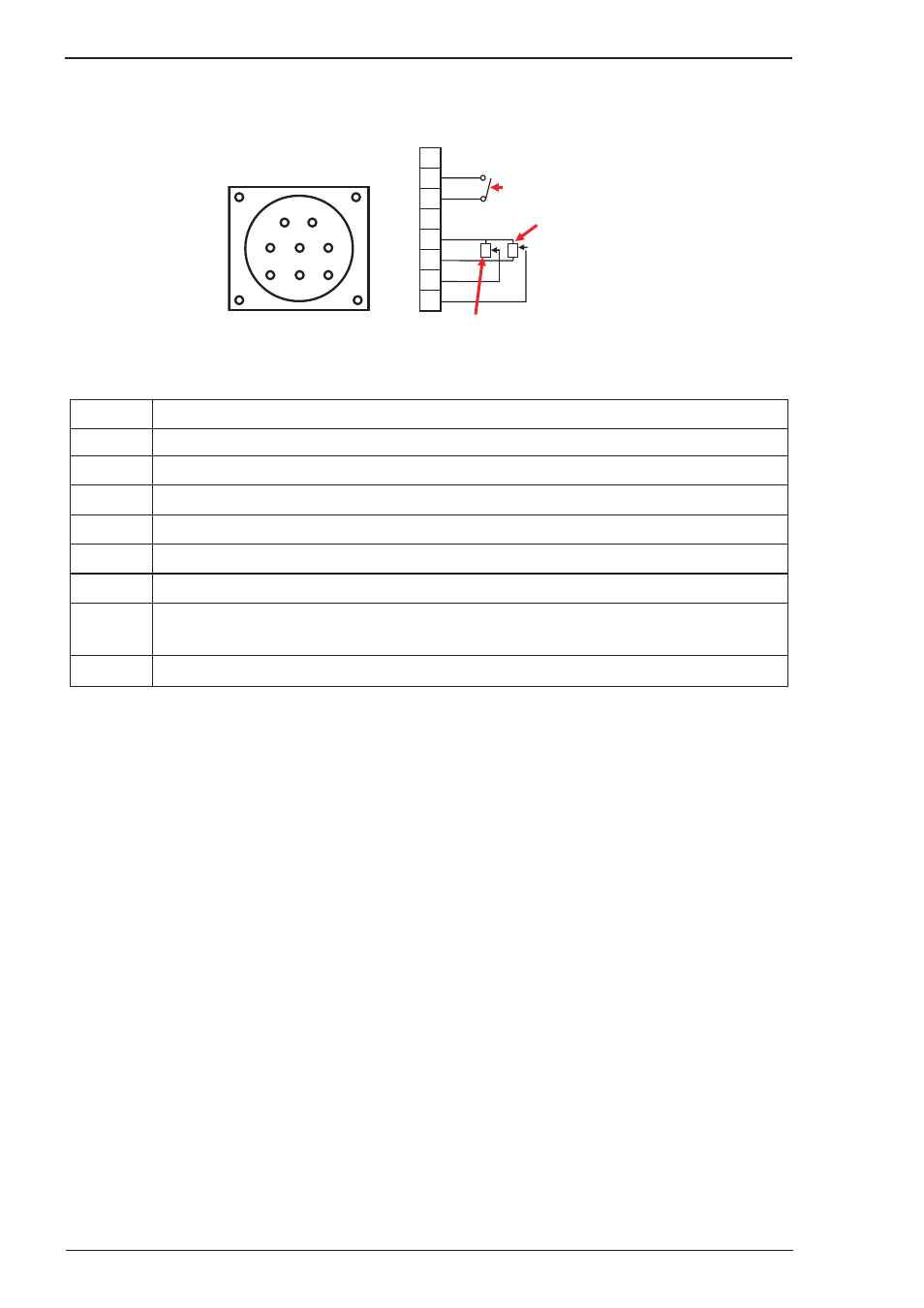
9. Remote Control Socket
The 8 pin Remote Control Socket is used to connect remote control devices to the welding power source.
To make connections, align keyway, insert plug, and rotate threaded collar fully clockwise.
2
1
8
7
6
3
4
5
Trigger Switch
Remote Wirespeed in GMAW mode
Remote Amps in GTAW mode
Remote Volts in
GMAW Mode
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
W
V
A-09594
Figure 3-4: Remote Control Socket
Socket Pin
Function
1
Not connected
2
Trigger Switch Input
3
Trigger Switch Input
4
Not connected
5
5k ohm (maximum) connection to 5k ohm remote control potentiometer.
6
Zero ohm (minimum) connection to 5k ohm remote control potentiometer.
7
Wiper arm connection to 5k ohm remote control Wirespeed GMAW (MIG) mode potentiometer.
Wiper arm connection to 5k ohm remote control Amps GTAW (TIG) mode potentiometer.
8
Wiper arm connection to 5k ohm remote control Volts GMAW (MIG) mode potentiometer.
Table 3-1
Note that the remote local switch (item 18) located in the wirefeed compartment should be set to remote
for the amperage/voltage controls to be operative.
10. Multifunction Control - Voltage, Down Slope & Arc Force
The multifunction control knob is used to adjust three main parameters depending on the welding mode
selected.
When GMAW/FCAW (MIG) Mode is Selected
In this mode the control knob is used to adjust the output voltage of the unit. The welding voltage is
increased by turning the knob clockwise or decreased by turning the knob anti-clockwise. The optimum
voltage level required will dependent on the type of welding application. The setup chart on the inside
of the wire feed compartment door provides a brief summary of the required output settings for a basic
range of MIG welding applications.
When MMAW (Stick) Mode is Selected
In this mode the multifunction control knob is used to adjust arc force. Arc force control provides an
adjustable amount of welding force (or “dig”) control. This feature can be particularly beneficial in
providing the operator the ability to compensate for variability in joint fit-up in certain situations with
particular electrodes. In general increasing the arc force control toward ‘10’ (maximum arc force) allows
greater penetration control to be achieved. Arc force is increased by turning the control knob clockwise
or decreased by turning the knob anti-clockwise
