Application information, Theory of operation – Powers 596 Series Flowrite II Heavy Duty Control Valves - Type MI Mixing User Manual
Page 2
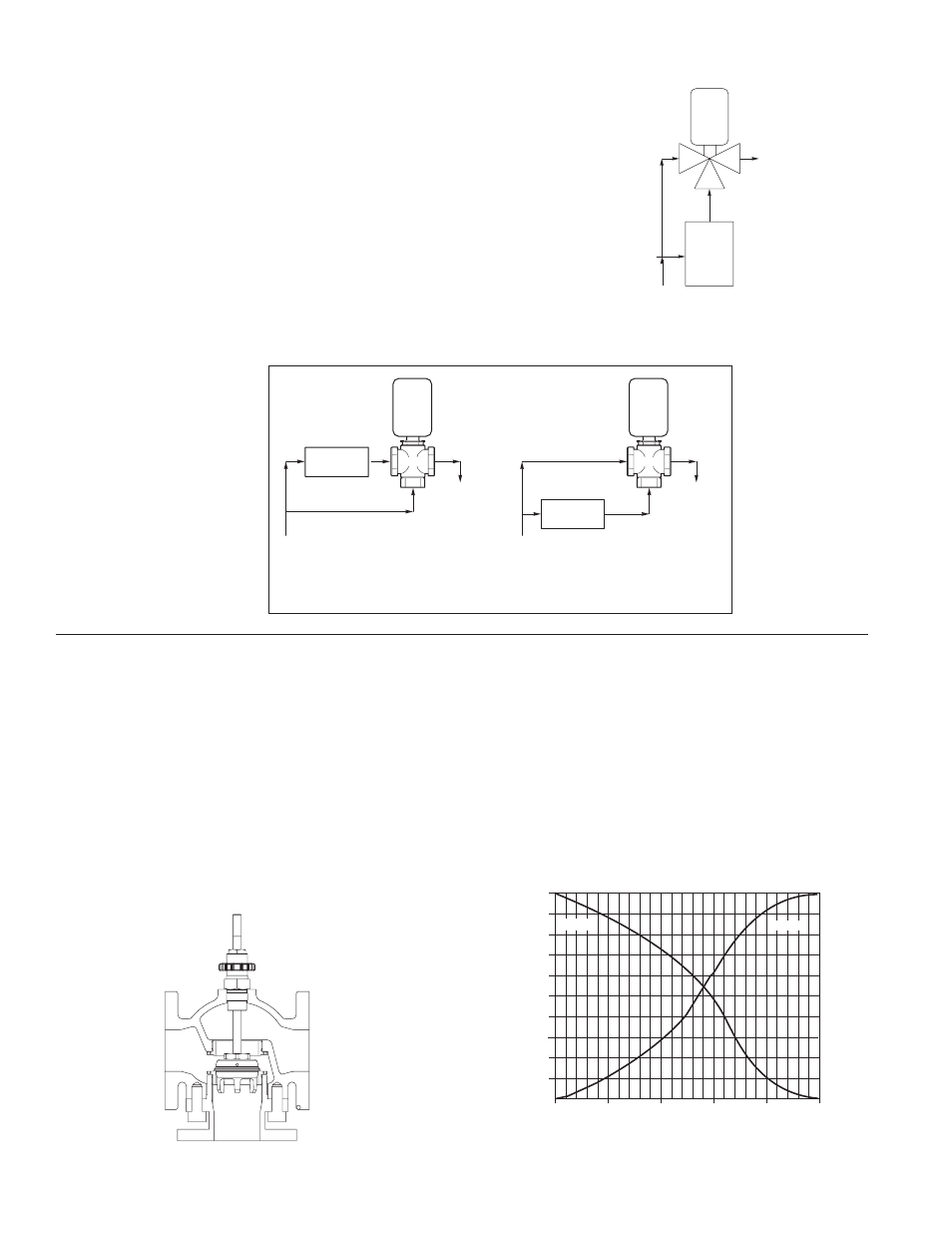
Flowrite II 596MI Valves are used for mixing hot and cold-water
streams or bypassing flow with the valve in the return line. The
controlling instrument positions the mixing valve to obtain the
approximate mixture temperature.
Figure 1 shows an example of a mixing application, a typical
boiler hot water control system. The cold inlet supply is fed to
the upper inlet port (A port) of the valve as well as through the
boiler for production of hot water to be fed into the bottom port
(B port).
Figure 2 shows an example of a bypass application, piping for
control of a heating or cooling coil, with the valve in the return
line. The controlling instrument positions the valve so that the
hot water will bypass the coil when the air is at the proper tem-
perature. A pump is recommended in the coil loop to improve
the heat transfer characteristics of the coil.
Air pressure from the controlling instrument enters the pressure
tight chamber of the actuator between the diaphragm and the
upper housing. An increase in control air pressure causes the
diaphragm to press down on the thrust plate, compressing the
springs and moving the valve stem downward. In the valve, this
reduces the flow through the "B" port and increases the flow
through the "A" port.
Conversely, A decrease in control air pressure reduces the
downward force on the actuator diaphragm, moving the
thrust plate and stem upward. The flow through the "B" port is
increased, and the flow through the "A" port is decreased.
In temperature mixing applications the hot inlet is usually
plumbed to the "A" side port, which will close on loss of signal.
Otherwise, the "B" lower port is used for hot, "A" upper side port
for cold, and the "AB" outlet for the mixed combination (see
Figure 3).
Three-way mixing valves are designed so that the flow from
either of the inlet ports to the outlet is approximately linear,
which means the total flow from the outlet is almost constant
over the stroke of the valve stem. See Figure-4 for typical flow
characteristics of 596 MI.
Application Information
n
Theory of Operation
n
2
Boiler
Hot Water Inlet
Control
Valve
A
AB
B
Cold Water
Supply
Return
Boiler Hot Water Control System
Coil
Valve
Return
Bypass
Supply
Supply
Coil
Bypass
Valve
Return
Stem down flow through coil.
Stem up flow through coil bypass.
Stem up flow through coil.
Stem down flow through coil bypass.
Bypass Piping for Control of a Heating or Cooling Coil
Figure 1
Figure 2
Three-way valve
Rated Flow
Stroke
Stem In
Stem Out
"A" Port
"B" Port
100%
90%
80%
70%
60%
50%
40%
30%
20%
10%
0%
0%
20%
40%
60%
80%
100%
Rated Flow vs Stroke Diagram
A
B
AB
Figure 3
Figure 4
