3 introduction, 1 synchronisation of the drives via a master angle, Introduction – Lenze E94AxHE Technology Application Electronic gearbox User Manual
Page 10: 9400 technology applications | electronic gearbox, 3introduction
9400 Technology applications | Electronic gearbox
Introduction
Synchronisation of the drives via a master angle
10
L
EDS94TA10030xxxx EN 1.2 - 11/2009
3
Introduction
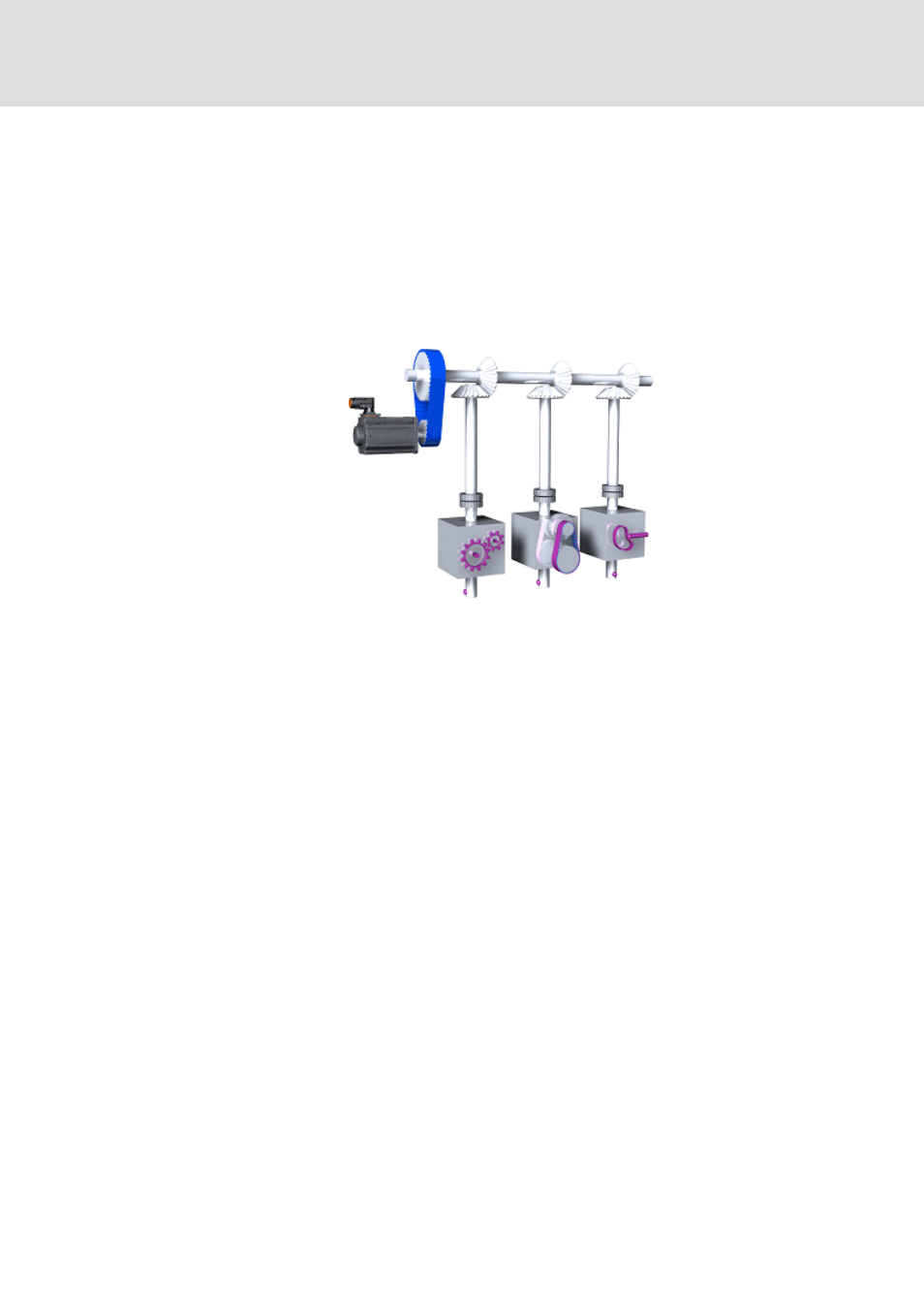
The following subchapters provide information on the electrical shaft.
3.1
Synchronisation of the drives via a master angle
By coupling the drives via a master angle the positions are firmly allocated to each other
like a mechanical shaft.
A drive with a virtual master or a real master (encoder) is able to create the master
angle and transmit this to the other drives which follow this master angle.
Advantages of this type of synchronisation
The communication between the drives is very simple. A time-consuming evaluation of
the status signals of each drive and the control signals to be generated from it for each
single drive is not required.
Due to the flexible electronics trimming functions can be carried out very easily. Thus,
motion sequences in machines can be easily synchronised and optimised.
A variation of the master angle speed changes the number of cycles of the machine.
The drives keep the position allocation.
