Cam sensor – AEM 30-6905 Universal Programmable EMS-4 User Manual
Page 33
Page 33 of 279 EMS-4 Install and Tuning Guide_Rev 1.6
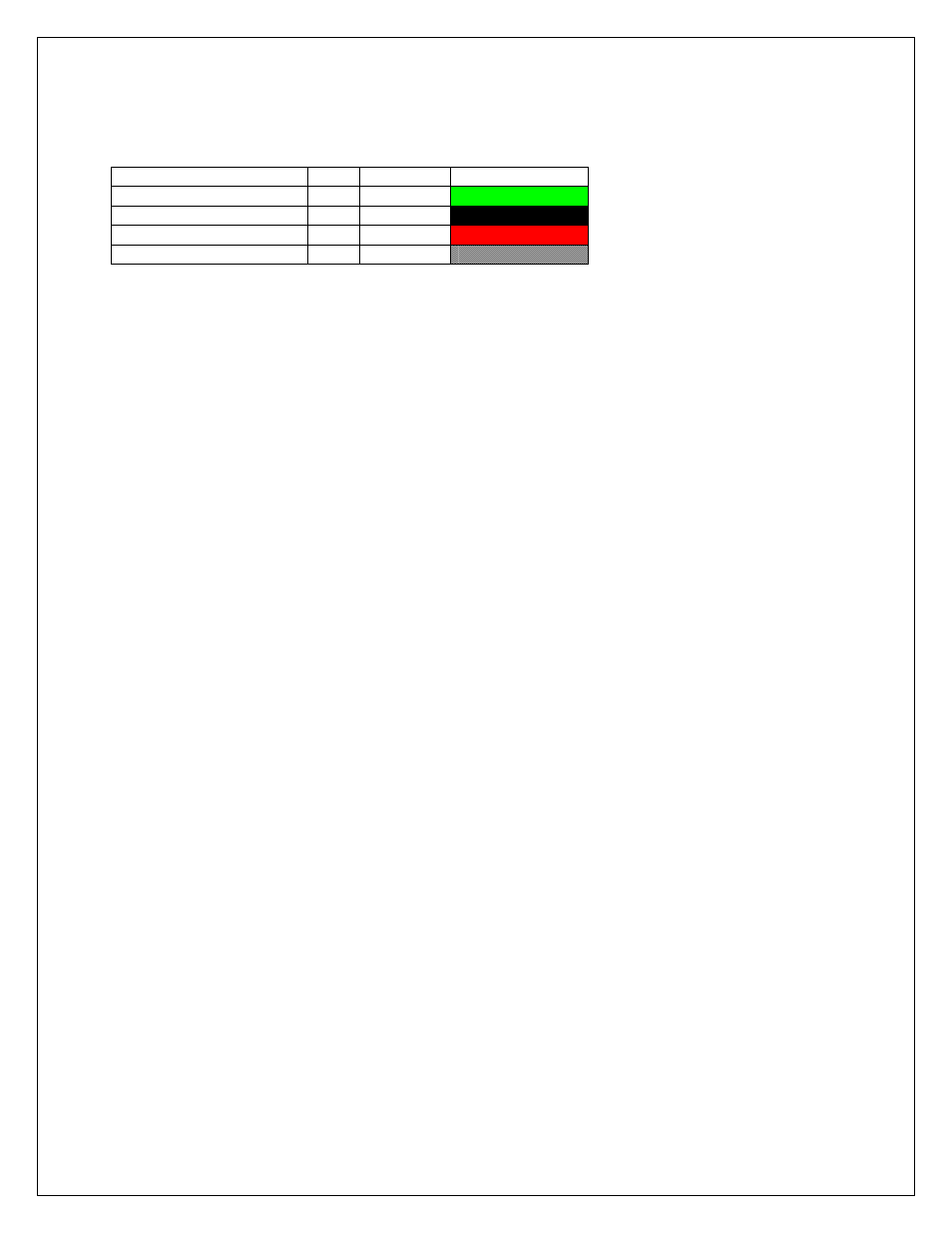
Harness Connections
Crank Sensor Harness Connections
Crank Sensor Ground
28
White
Crank Sensor Mag Input
28
Green
Crank Sensor Hall input
24
Black
+12 volts
24
Red
Cable Shield
---
Crank Sensor Mag Input, Green
– Connect to VR (+) signal (rising edge zero cross). Not used
for Hall sensor configurations.
Crank Sensor Hall input, Black
– Connect to Hall sensor signal. Not used for VR sensor
configurations.
+12 volts, Red
– Connect to Hall sensor reference voltage. Not used for VR sensor
configurations.
Insulate if not using (hot at key-on).
Crank Sensor Ground, White
– Connect to Crank sensor VR (-) or Hall sensor signal ground
Cam Sensor
Cam Sensor Basics
The cam sensor is used to calculate engine position. It is necessary for sequential fuel
calculations. It senses a toothed wheel (reluctor wheel, reluctor ring, etc.) and converts this
pattern into a voltage/frequency signal that the EMS uses for basic calculations. Combined with
the crank position sensor, it is one of the most important inputs to the system. There are two
basic types of cam sensors, variable reluctance (VR or “mag”) and hall-effect.
All VR Cam Sensor inputs to the EMS-4 must be connected such that the rising edge of the raw
sensor signal is the consistent zero crossing edge as shown in the examples above. Failure to
do this could result in misfires or ignition timing inaccuracies. Verify data with an oscilloscope or
contact your sensor manufacturer to verify polarity. The crank inputs to the EMS-4 are
contained within a black shielded cable assembly as shown below. Refer to the EMS-4
System Diagram for more information.
