HP Prime Graphing Wireless Calculator User Manual
Page 65
Geometry
61
Example:
if GA is a point at (1, –2), then affix(GA) returns 1–2i.
barycenter
Calculates the hypothetical center of mass of a set of points,
each with a given weight (a real number). Each point, weight
pair is enclosed in square brackets as a vector.
barycenter([[point1, weight1], [point2,
weight2],…,[pointn, weightn]])
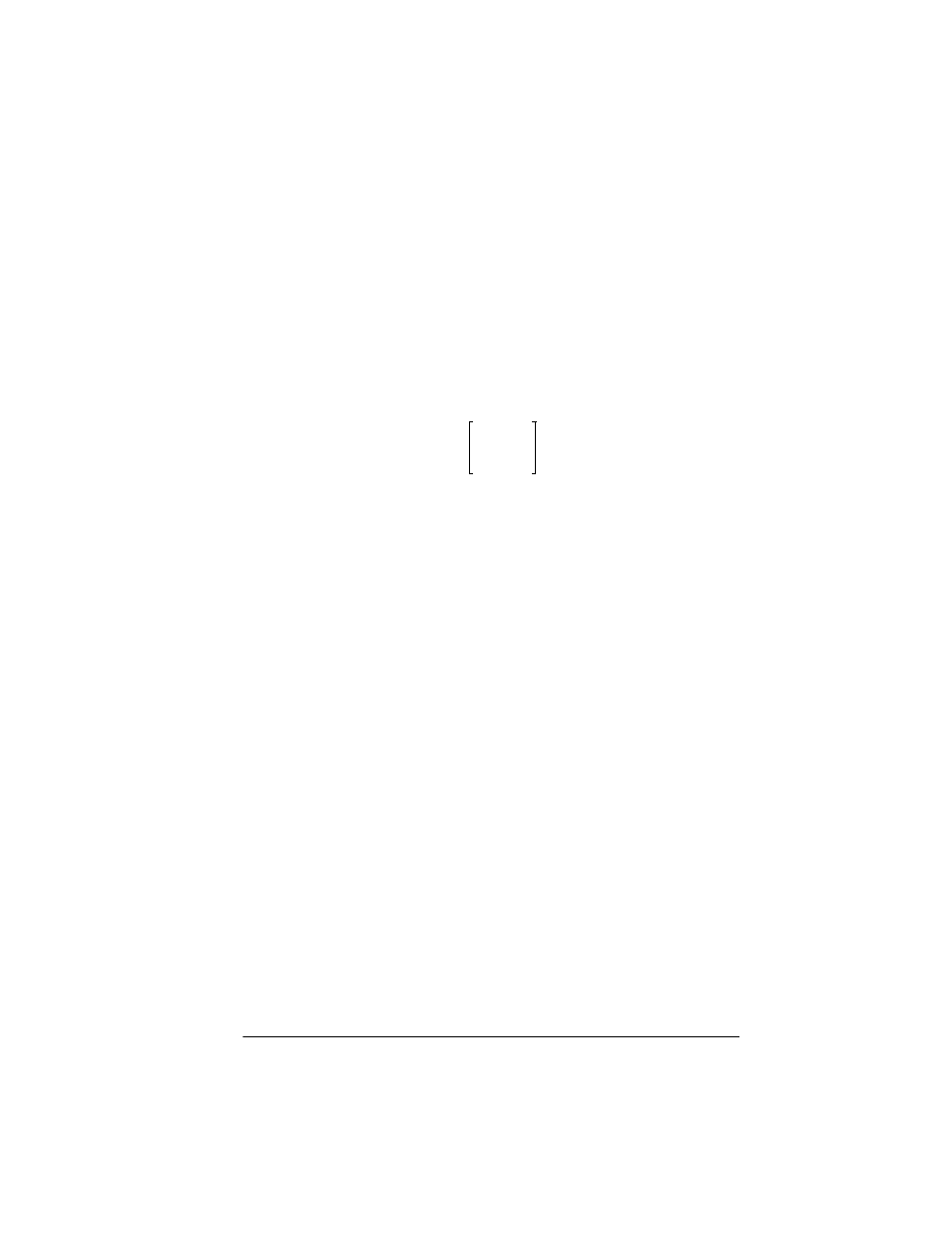
Example:
barycenter
returns point (1/2, 1/4)
convexhull
Returns a vector containing the points that serve as the convex
hull for a given set of points.
convexhull(point1, point2, …, pointn)
Example:
convexhull(0,1,1+i,1+2i,-1-i,1-3i,-2+i)
returns [1-3*i 1+2*i -2+ i -1- i ]
distance2
Returns the square of the distance between two points or
between a point and a curve.
distance2(point1, point2)
or
distance2(point,
curve)
Examples:
distance2(1+i, 3+3i) returns 8.
If GA is the point at (0, 0) and GB is defined as plotfunc(4-
x^2/4), then distance2(GA, GB) returns 12.
division_point
For two points A and B, and a numerical factor k, returns a
point C such that C-B=k*(C-A).
division_point(point1, point2, realk)
Example: division_point(0,6+6*i,4) returns point
(8,8)
point(1) 1
point(1+i) 2
point(1–i) 1
