HP Prime Graphing Wireless Calculator User Manual
Page 196
192
Functions and commands
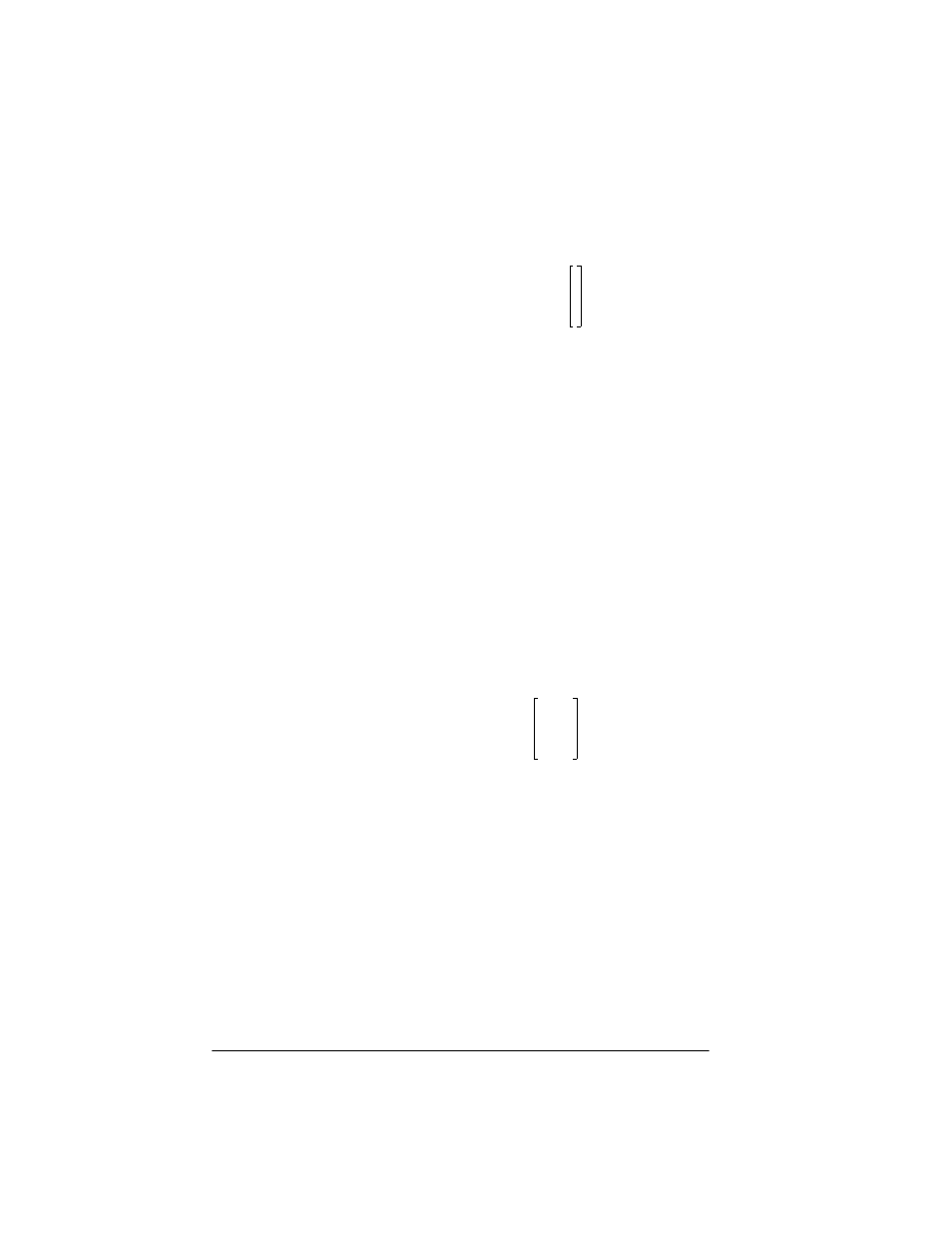
Example:
list2mat({1,8,4,9},1) returns
lname
Returns a list of the variables in an expression.
lname(Expr)
Example:
lname(exp(x)*2*sin(y))
gives
[x,y]
lnexpand
Returns the expanded form of a logarithmic expression.
lnexpand(Expr)
Example:
lnexpand(ln(3*x))
gives
ln(3)+ln(x)
logarithmic_
regression
Given a set of points, returns a vector containing the
coefficients a and b of y=a*ln(x)+b, the natural logarithmic
function which best fits the set of points. The points may be the
elements in two lists or the rows of a matrix.
logarithmic_regression(Matrix) or
logarithmic_regression(List1, List2)
Example:
logarithmic_regression
returns
[6.3299…, 0.7207…]
logb
Returns the logarithm of base b of a.
logb(a,b)
Example:
logb(5,2)
gives
ln(5)/ln(2)
which is approximately
2.32192809489
logistic_
regression
Returns y, y', C, y'max, xmax, and R, where y is a logistic
function (the solution of y'/y=a*y+b), such that y(x0)=y0 and
where [y'(x0),y'(x0+1)...] is the best approximation of the line
formed by the elements in the list L.
logistic_regression(Lst(L),Real(x0),Real(y0))
1
8
4
9
1.0 1.0
2.0 4.0
3.0 9.0
4.0 9.0
