Port fc/ca chip product, Figure 2 16-port chip pair labeling, Host groups – HP StorageWorks XP Remote Web Console Software User Manual
Page 15: 2 16-port chip pair labeling
LUN Configuration and Security Manager XP user guide for the XP1024/XP128
15
If a hardware failure (such as a CHA failure) occurs, there is a chance that some LU paths are disabled
and some I/O operations are stopped. To avoid this, the system administrator can define alternate LU
paths. If one LU path fails, the alternate path takes over the host I/O.
In a Fibre Channel environment, up to 1,024 LU paths can be defined for one host storage domain. Up to
1,024 LU paths can be defined for one port.
NOTE:
You cannot define an LU path to LUN On Demand volumes or volumes reserved by Auto LUN XP.
•
Up to 256 host storage domains can be created for one Fibre Channel port. Up to 57,344 host
storage domains can be created for one disk subsystem. The maximum number of ports per subsystem
is 224.
•
Up to 255 host groups can be created for one Fibre Channel port.
16-Port FC/CA CHIP product
Although there is not a significant performance gain compared to the 8-port FC/CA CHIP product, the
primary advantage of the 16-port FC/CA CHIP product is its increased FC connectivity (or port count).
High-speed mode is currently unavailable on the 16-port FC/CA CHIP product.
Odd/even LUN data path handling through the processor does not exist on the XP1024/XP128. There is
no odd/even LUN mapping issue associated with this product. Each processor of the 16-port CHIP
product handles the data flow of two ports (eight total processors for 16 total ports = two ports per
processor).
For load balancing, the two ports serviced by a processor should be considered as one port. Although
volumes can be mapped to both ports handled by a processor, the I/O will go through one processor. For
redundancy and performance reasons, consider distributing the load across multiple CHIPs.
When deciding whether to map volumes to ports (LUN mapping) for host connectivity, after considering
load balancing across processors, there is no reason to not use all 16 ports immediately. After
considering load balancing among processors, there is no reason not to use both ports in the I/O path of
one processor or to use both ports in the I/O path of a processor.
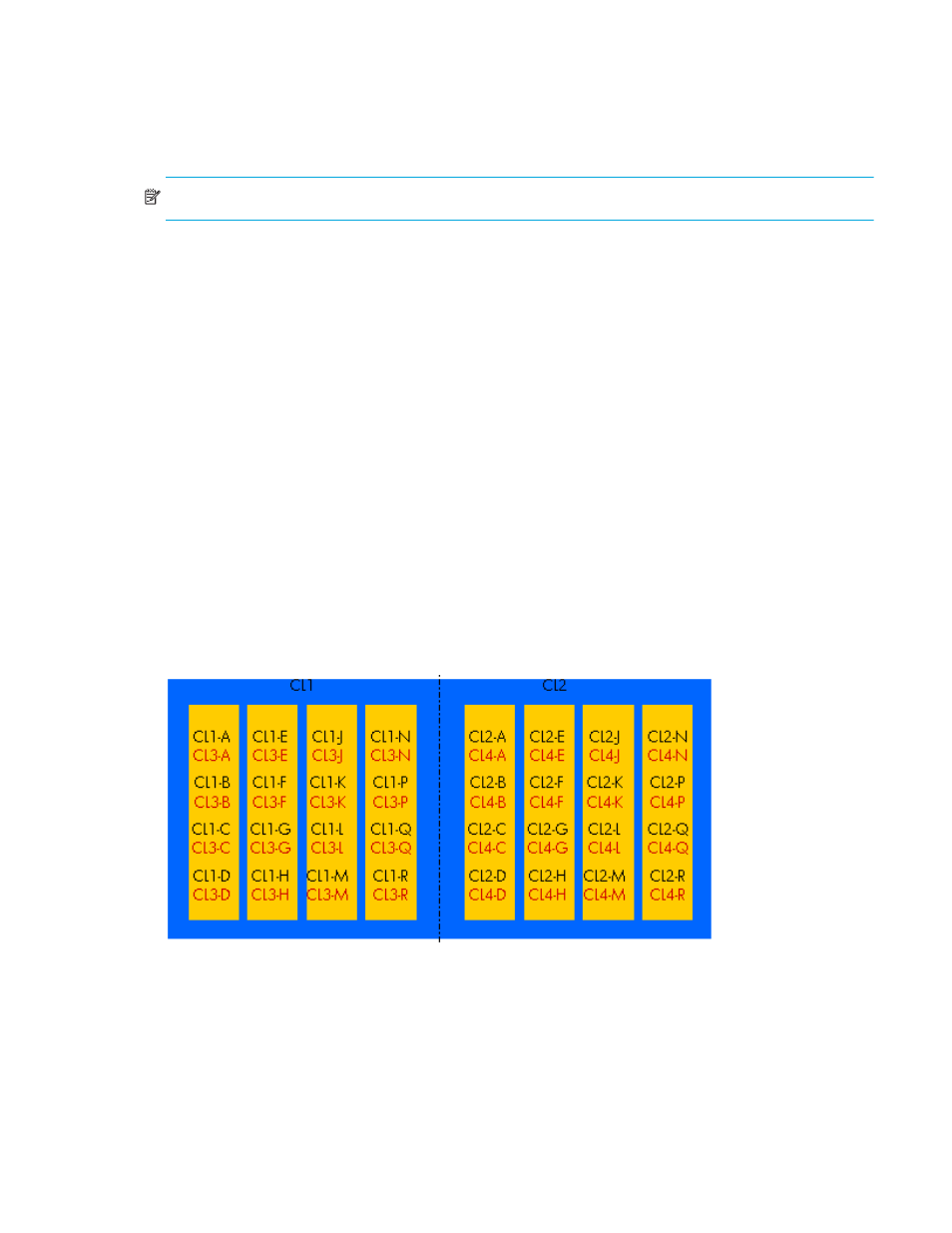
Figure 2
16-Port CHIP pair labeling
Port numbering is as follows: Cluster 1 uses CL1-* and CL3-*, while Cluster 2 uses CL2-* and CL4-*,
where * is an alphabetical character designation of the port such as A, B, C, and so on. Ports A, for
example, CL1-A and CL3-A, share the same processor for I/O purposes.
Host groups
Begin by grouping server hosts into host groups. For example, if HP-UX and Windows hosts are
connected to the disk array, you must create a separate host group for each host type. When this is done,
register the hosts in their corresponding host groups. After hosts are classified into host groups, associate
the host groups with LUs.
