Setting a percent full warning, Setting a percent full warning threshold – HP X1800sb G2 Network Storage Blade User Manual
Page 21
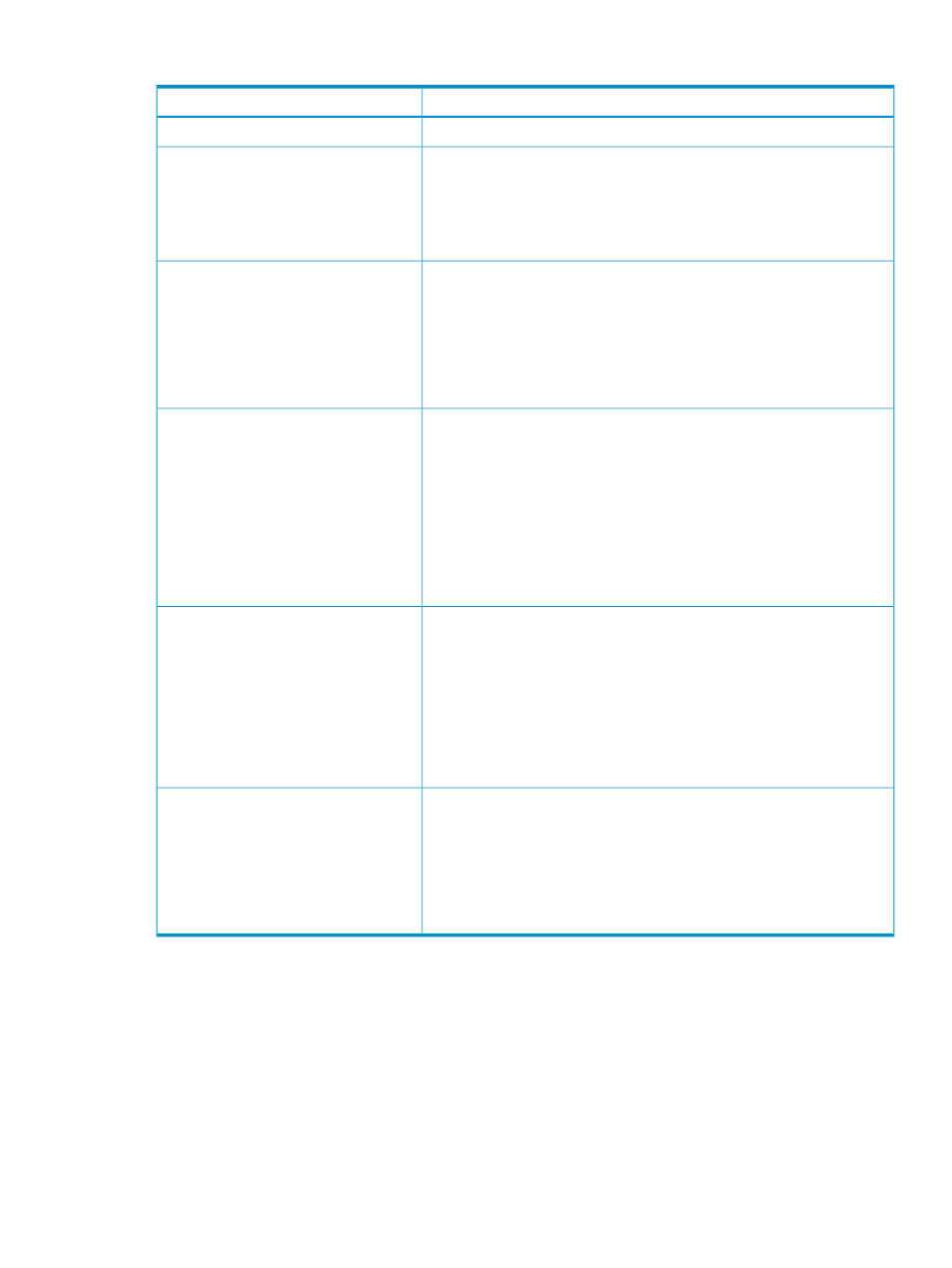
Table 6 Descriptions of RAID levels
Description
RAID level
Offers no protection against disk failure. If a disk drive fails, data is lost.
No RAID
Offers the greatest capacity and performance without data protection. If
you select this option, you will experience data loss if a hard drive that
holds the data fails. However, because no logical drive capacity is used
for redundant data, this method offers the best capacity. This method offers
the best processing speed by reading two stripes on different hard drives
at the same time and by not having a parity drive.
RAID 0 – Striping (No Fault Tolerance)
Offers a good combination of data protection and performance. RAID 1
or drive mirroring creates fault tolerance by storing duplicate sets of data
on a minimum of two hard drives. There must be an even number of drives
for RAID 1. RAID 1 and RAID 1+0(10) are the most costly fault tolerance
methods because they require 50 percent of the drive capacity to store the
redundant data. RAID 1 mirrors the contents of one hard drive in the array
onto another. If either hard drive fails, the other hard drive provides a
backup copy of the files and normal system operations are not interrupted.
RAID 1 – Mirroring
Offers the best combination of data protection and performance. RAID 1+0
or drive mirroring creates fault tolerance by storing duplicate sets of data
on a minimum of four hard drives. There must be an even number of drives
for RAID 1+0. RAID 1+0(10) and RAID 1 are the most costly fault tolerance
methods because they require 50 percent of the drive capacity to store the
redundant data. RAID 1+0(10) first mirrors each drive in the array to
another, and then stripes the data across the mirrored pair. If a physical
drive fails, the mirror drive provides a backup copy of the files and normal
system operations are not interrupted. RAID 1+0(10) can withstand multiple
simultaneous drive failures, as long as the failed drives are not mirrored to
each other.
RAID 1+0 – Mirroring and Striping
Offers the best combination of data protection and usable capacity while
also improving performance over RAID 6. RAID 5 stores parity data across
all the physical drives in the array and allows more simultaneous read
operations and higher performance than data guarding. If a drive fails, the
controller uses the parity data and the data on the remaining drives to
reconstruct data from the failed drive. The system continues operating with
a slightly reduced performance until you replace the failed drive. RAID 5
can only withstand the loss of one drive without total array failure. It requires
an array with a minimum of three physical drives. Usable capacity is N-1
where N is the number of physical drives in the logical array.
RAID 5 – Distributed Data Guarding
Offers the best data protection and is an extension of RAID 5. RAID 6 uses
multiple parity sets to store data and can therefore tolerate up to 2 drive
failures simultaneously. RAID 6 requires a minimum of 4 drives and is
available only if the controller has an enabler. Writer performance is lower
than RAID 5 due to parity data updating on multiple drives. It uses two disk
for parity; its fault tolerance allows two disks to fail simultaneously. Usable
capacity is N-2 where N is the number of physical drives in the logical
array.
RAID 6– Advanced Data Guarding (ADG)
Setting a percent full warning threshold
To receive a warning alert when storage capacity reaches a specified limit, set the percent full
warning threshold. You can set a warning threshold for any application component, user-defined
application, and shared folder that ASM manages. An iSCSI LUN application will not have a
warning threshold.
By default, the warning threshold is set to 80%. To change it, enter a new percent value on the
Advanced window.
After you set a warning threshold, ASM changes the status indicator for the application component,
user-defined application, or shared folder when this threshold has been surpassed. This is a warning
Allocating space for components
21
