Application information, Chlorine chemistry, Chlorine and the effect of ph – Metex 8760CLP Total Free Chlorine & pH Analyzer User Manual
Page 20
AQUAMETRIX INC.
1-800-742-1413 www.aquametrix.com
20
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Chlorine Chemistry
When chlorine gas is dissolved in water, it hydrolyzes rapidly according to equation 1. This reaction
occurs very rapidly, in only a few tenths of a second at 18 °C.
1)
Cl
2 g
H
2
O
aq
—
HOC
l aq
HCl
aq
Since HCl (hydrochloric acid) is a strong acid, the addition of gaseous chlorine to water results in a
lowering of the pH due to the acidic HCl by-product.
The important product of reaction (1) is HOCl or hypochlorous acid. Hypochlorous acid is the
disinfectant form of chlorine in water. Hypochlorous acid is unstable because the chlorine molecule is
weakly bonded and as a result will react quickly.
Hypochlorous acid is also referred to as free available chlorine, or free chlorine. It is taste free and
aggressive against germs and organic compounds.
Chlorine supplied as sodium hypochlorite, calcium hypochlorite, or bleach is in a basic form. When a
base is present, a different reaction sequence occurs:
2)
NaOCl
aq
H
2
O
aq
—
HOCl
aq
Na
1
OH
1
3)
Ca OCl
2 aq
2 H
2
O
aq
—
2 HOCl
aq
Ca
2
2 OH
1
In any hypochlorite solution, the active ingredient is always hypochlorous acid. Then once HOCl and
OH
-
are formed an additional reaction occurs:
4)
HOCl
aq
OH
1
—
OCl
1
H
2
O
aq
The proportion of chlorine, hypochlorous acid, and hypochlorite ion in solution depends primarily on
pH and somewhat on temperature. The different forms of chlorine are named as follows:
Cl
2
chlorine
HOCl
hypochlorous acid
OCl
1
hypochlorite ion
At atmospheric pressure and 20 °C, the maximum solubility of chlorine is about 7,395 mg per liter or
7.395 ppm.
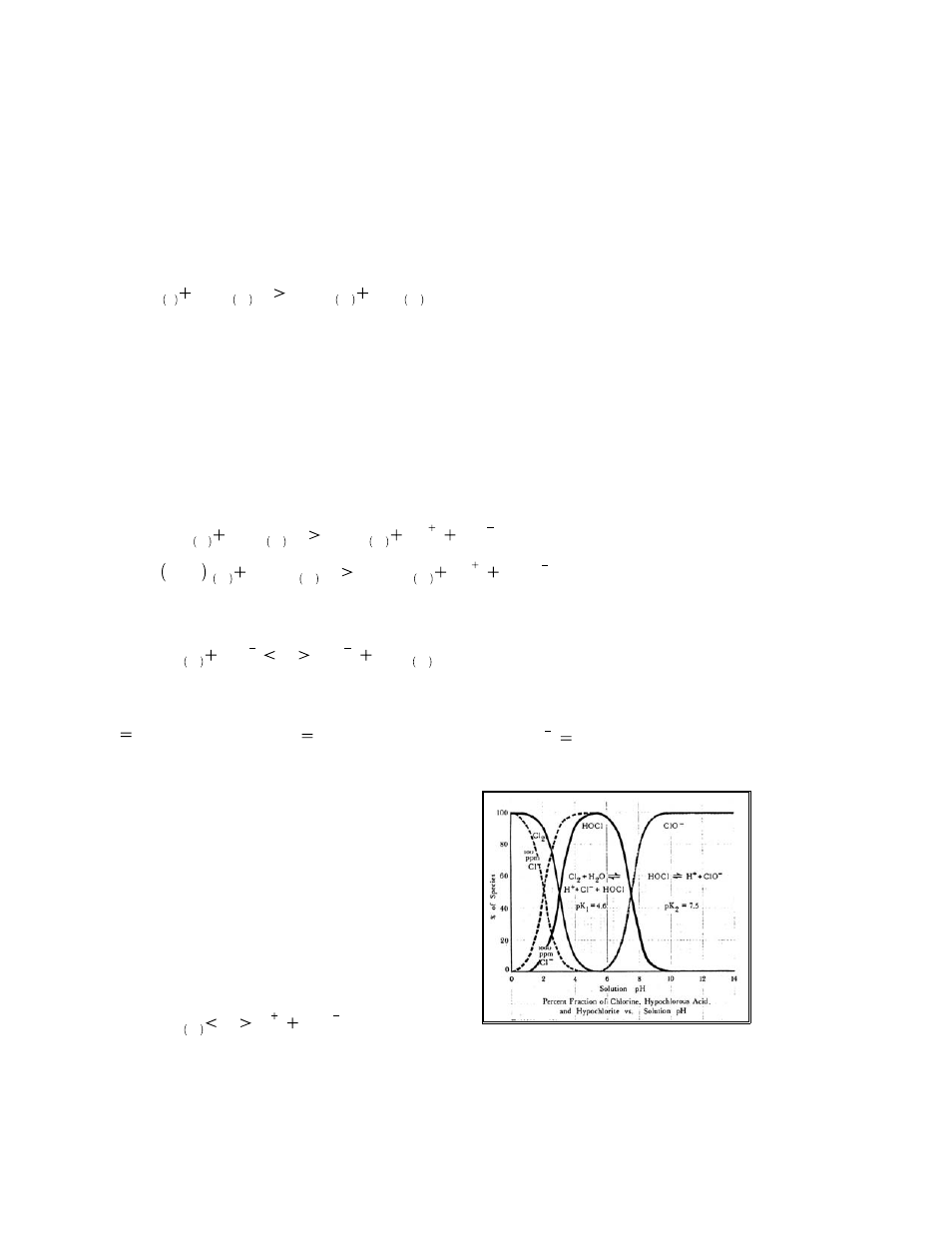
Chlorine and the effect of pH
The most important reaction in the chlorination of an
aqueous solution is the formation of hypochlorous acid.
The hypochlorous acid form of chlorine is very
effective for killing germs. Hypochlorous acid is a
‘weak’ acid, meaning that it tends to undergo partial
dissociation to form a hydrogen ion and a hypochlorite
ion. Once in a water environment, HOCl tends to
dissociate into H
+
and OCl
-
ions.
5)
HOCl
aq
—
H
1
OCl
1
Illustration 14: Chlorine species change vs. pH
