Operation – KROHNE OPTIWAVE 6300C EN User Manual
Page 62
6
OPERATION
62
OPTIWAVE 6300 C
www.krohne.com
03/2014 - 4000547004 - HB OPTIWAVE 6300 R04 en
6.4.7 How to make a filter to remove radar signal interference
If the device measures level in a silo that contains obstructions (ladder, supports etc.), these
objects can cause radar signal interference (parasitic signals). You can use the empty spectrum
function (menu item A.1.3) in the Quick Setup menu to make a filter to remove radar signal
interference.
• Get access to the Main Menu
Main Menu
Main Menu
Main Menu of the supervisor mode.
i
For more data, refer to
How to get access to the supervisor mode
on page 41.
• Go to Main Menu > Quick Setup > Setup Mode > Empty Spectrum
Main Menu > Quick Setup > Setup Mode > Empty Spectrum
Main Menu > Quick Setup > Setup Mode > Empty Spectrum
Main Menu > Quick Setup > Setup Mode > Empty Spectrum.
• Is the tank completely full? Select Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes or No
No
No
No and then push [^
^
^
^].
i
If you select Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes, the device will not do the empty spectrum scan. Empty the tank and repeat
the procedure.
• Are all the moving parts switched on? Select Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes or No
No
No
No and then push [^
^
^
^].
• Is your tank partially filled or completely empty? Select Partially filled
Partially filled
Partially filled
Partially filled or Empty
Empty
Empty
Empty and then push
[^
^
^
^].
• Do you want to use the average value or the maximum value? Select Average
Average
Average
Average or Maximum
Maximum
Maximum
Maximum and
then push [^
^
^
^].
i
Use the maximum for tanks that have moving parts. Use the average value for tanks that do
not have moving parts. The device will do an empty spectrum scan and then display the
results on the signal screen.
INFORMATION!
We recommend that you do an empty spectrum scan when the silo is empty and all the moving
parts are in operation..
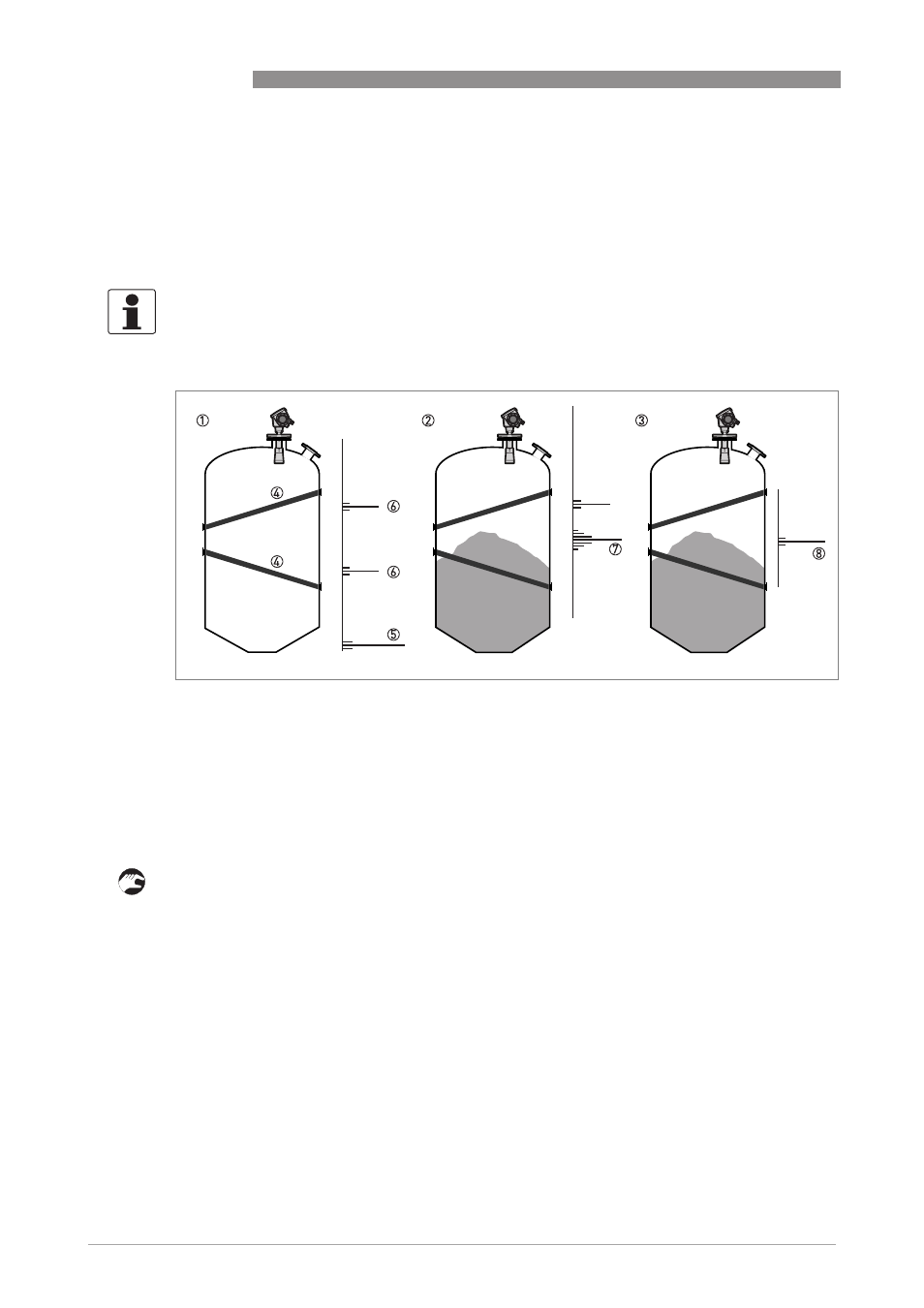
Figure 6-7: How to make a filter to remove radar signal interference
1 Empty silo before the device uses the empty spectrum scan (with a graph of reflections shown)
2 Partially filled silo before the device uses the empty spectrum scan (with a graph of reflections shown)
3 Partially filled silo after the device uses the empty spectrum scan (with a graph of reflections shown)
4 Support beam location
5 Silo bottom signal
6 Support beam signals (interference signals) before the device does the empty spectrum scan
7 Bad quality (mixed) signals of the solid and the support beam before the device does the empty spectrum scan
8 Reflected signal if the device uses the data from the empty spectrum scan. The device only uses the reflection on the
surface of the solid to measure distance.
