Overview of the time and frequency domain, Observation from a different perspective, Verview of the time and frequency domain – GW Instek GRF-1300A User Manual
Page 18
GRF-1300A User Manual and Teaching Materials
O
VERVIEW of the TIME and
FREQUENCY DOMAIN
Observation from a different perspective
When a signal is said to be in the time domain, it means that
the signal is expressed as a function of time. For example, if we
describe a sine wave signal that repeats once each microsecond
(μsec, 10
-6
), it means that the period of the signal is 1
microsecond. Usually we use an oscilloscope to measure these
signal characteristics in the time domain. In addition, when we
talk about the rise and fall time of a square waveform, we also
can observe that in the time domain. Phase delay is also
measured in the time domain. Oscilloscopes are well-known
electrical signal measurement instruments that perform
measurements in the time domain.
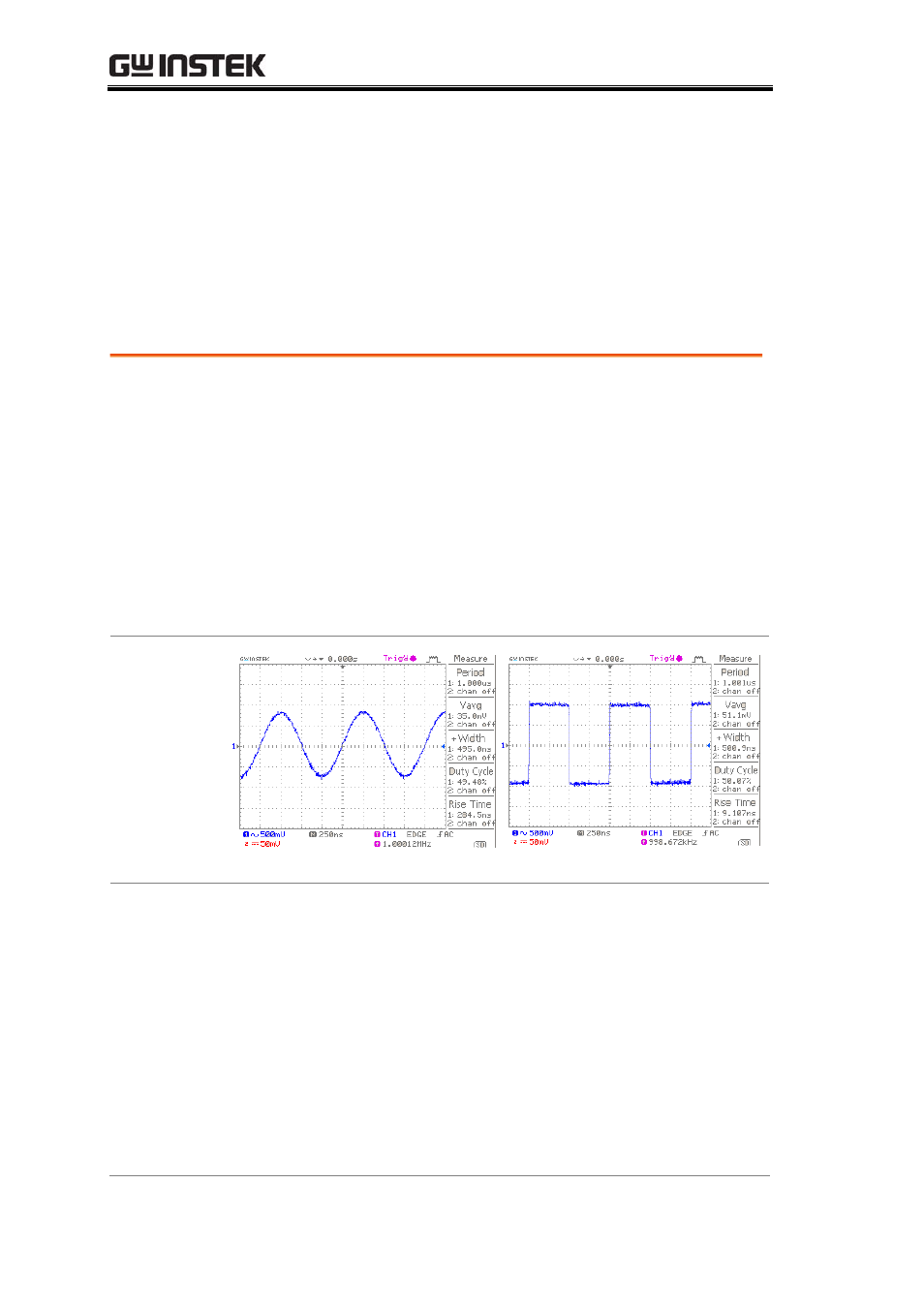
1μsec sine wave
Square wave with the same period
However, when we observe a sine wave and a square wave
with the same amplitude and period, is there a way to describe
the difference between them? Frequency domain measurements
just provide a different view point.
First we will explain what frequency domain means.
Frequency domain means to observe the frequency composition
of a signal. If we add a sine wave signal that has a 1 microsecond
period to a spectrum analyzer, we will see an obvious signal on
the scale at 1 megahertz (MHz). We know that frequency is the
inverse of period. Therefore, a sine wave with a period of
microsecond has a frequency of 1MHz. You can measure voltage
16
