Rainbow Electronics MAX7033 User Manual
Page 13
filter output. Both comparator inputs are accessible off-
chip to allow for different methods of generating the
slicing threshold, which is applied to the second com-
parator input.
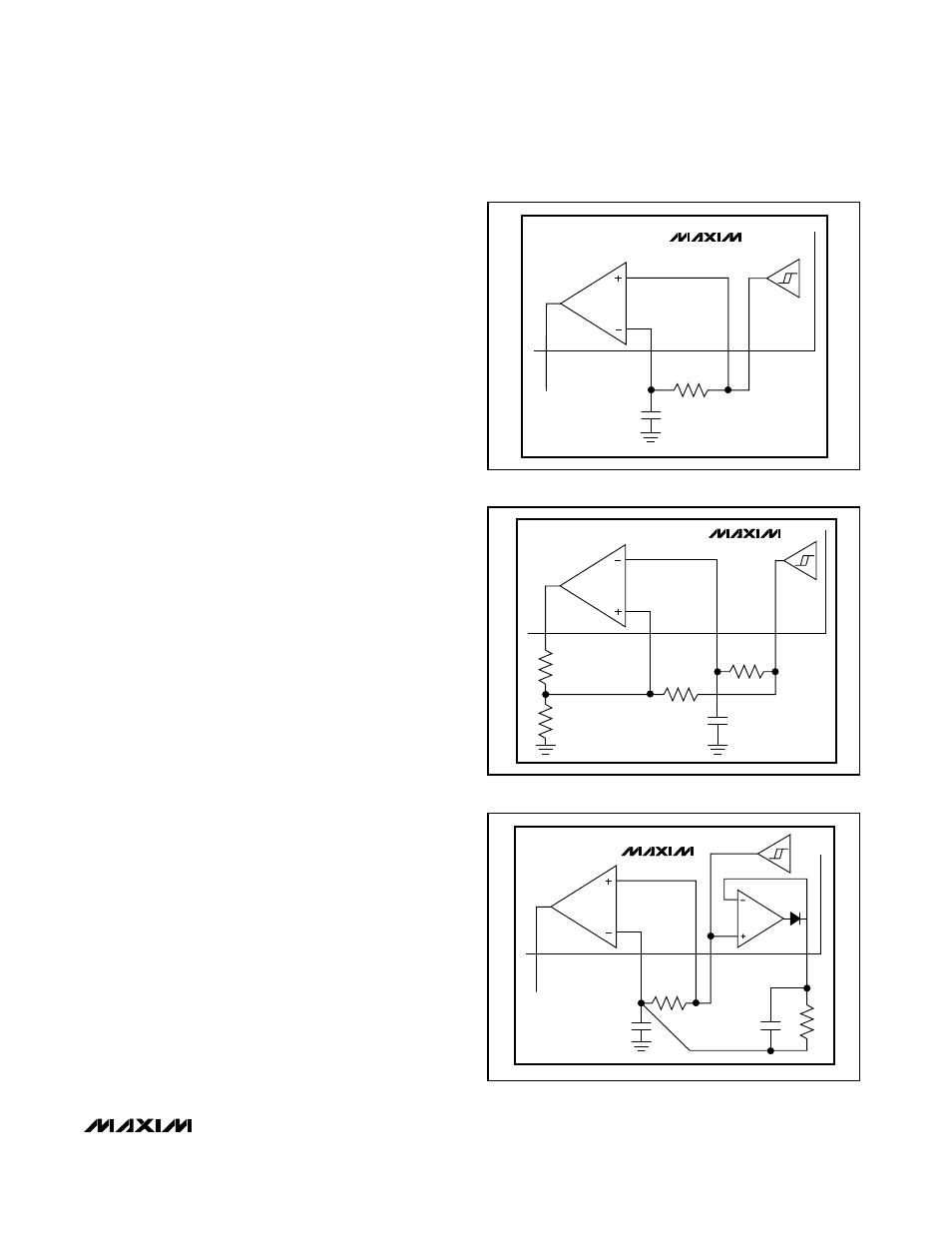
The suggested data slicer configuration uses a resistor
(R1) connected between DSN and DSP with a capaci-
tor (C4) from DSN to DGND (Figure 3). This configura-
tion averages the analog output of the filter and sets the
threshold to approximately 50% of that amplitude. With
this configuration, the threshold automatically adjusts
as the analog signal varies, minimizing the possibility
for errors in the digital data. The values of R1 and C4
affect how fast the threshold tracks to the analog ampli-
tude. Be sure to keep the corner frequency of the RC
circuit much lower than the lowest expected data rate.
Note that a long string of zeros or ones can cause the
threshold to drift. This configuration works best if a cod-
ing scheme, such as Manchester coding, which has an
equal number of zeros and ones, is used.
To prevent continuous toggling of DATAOUT in the
absence of an RF signal due to noise, add hysteresis to
the data slicer as shown in Figure 4.
Peak Detector
The peak-detector output (PDOUT), in conjunction with
an external RC filter, creates a DC output voltage equal
to the peak value of the data signal. The resistor pro-
vides a path for the capacitor to discharge, allowing the
peak detector to dynamically follow peak changes of
the data-filter output voltage. For faster data slicer
response, use the circuit shown in Figure 5.
Layout Considerations
A properly designed PC board is an essential part of
any RF/microwave circuit. On high-frequency inputs
and outputs, use controlled-impedance lines and keep
them as short as possible to minimize losses and radia-
tion. At high frequencies, trace lengths that are on the
order of
λ/10 or longer act as antennas.
Keeping the traces short also reduces parasitic induc-
tance. Generally, 1in of a PC board trace adds about
20nH of parasitic inductance. The parasitic inductance
can have a dramatic effect on the effective inductance
of a passive component. For example, a 0.5in trace
connecting a 100nH inductor adds an extra 10nH of
inductance or 10%.
To reduce the parasitic inductance, use wider traces
and a solid ground or power plane below the signal
traces. Also, use low-inductance connections to ground
on all GND pins, and place decoupling capacitors
close to all V
DD
connections.
MAX7033
315MHz/433MHz ASK Superheterodyne
Receiver with AGC Lock
______________________________________________________________________________________
13
DATA
SLICER
R1
25
DATAOUT
20
DSN
19
DFO
23
DSP
C4
MAX7033
Figure 3. Generating Data Slicer Threshold
DATA
SLICER
R3
R1
R2
R4
25
DATAOUT
*OPTIONAL
23
DSP
19
DFO
20
DSN
C4
MAX7033
Figure 4. Generating Data Slicer Hysteresis
DATA
SLICER
25k
Ω
25
DATAOUT
20
DSN
19
DFO
26
PDOUT
23
DSP
MAX7033
47nF
Figure 5. Using PDOUT for Faster Startup
