Isotopic pattern in mass spectra – HP Data Explorer 4 Series User Manual
Page 391
Isotopes
Data Explorer
™
Software User’s Guide
B-3
B
As the number of carbon atoms in a compound increases, the
possibility of the compound containing a
13
C instead of a
12
C
also increases. A compound with ten carbon atoms includes a
molecular ion M
+
and an isotopic ion (M+1)
+
one mass unit
greater than the molecular ion, which is approximately
11 percent of the abundance of the molecular ion. The
possibility of including two
13
C atoms in the same molecule
also increases with increasing number of carbon atoms.
Therefore, (M+2)
+
ions become more visible. In a compound
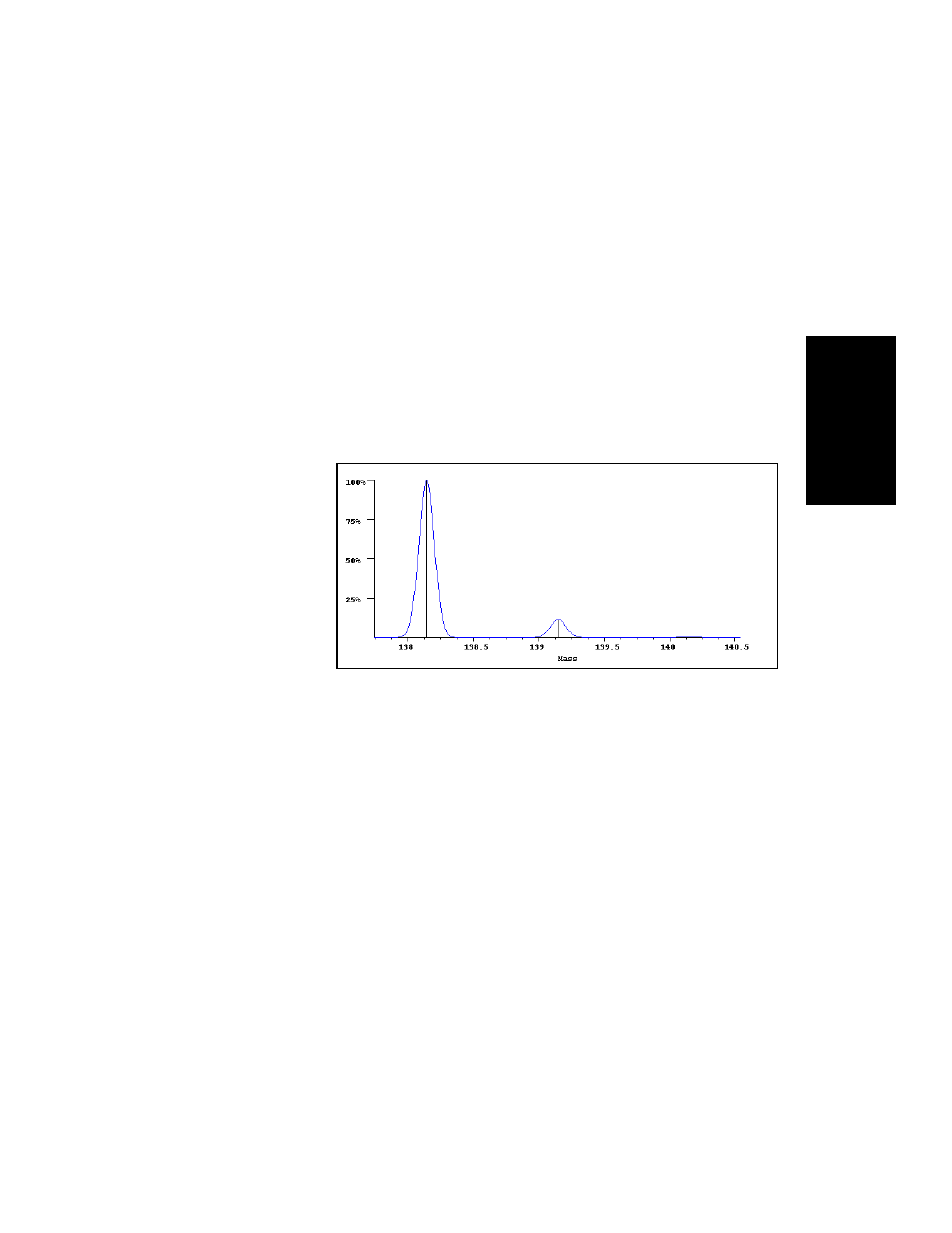
with ten carbon atoms such as decahydro naphthalene,
C
10
H
18
(Figure B-2), relative heights of M
+
, (M+1)
+
, and (M+2)
+
peaks are 100:11:0.5.
Figure B-2 Mass Spectrum of Decahydro Naphthalene
Isotopic pattern
in mass spectra
All compounds containing carbon include molecular ions and
isotopic ions that are 1 and 2 mass units higher than the
molecular ion. At higher masses, the isotopic pattern of a
mass spectrum is more pronounced as the relative abundance
of isotopes increases. In angiotensin I (Figure B-3) with a
molecular weight of 1,296 Da, (C
62
H
89
O
14
N
17
), a peak
containing one
13
C isotope is approximately 70 percent of the
pure
12
C peak.
M
+
(M+1)
+
(M+2)
+
