Figure2.1 lsi53c180 block diagram, 1 scsi a side and b side control blocks, Scsi a side and b side control blocks – Avago Technologies LSI53C180 User Manual
Page 20: Lsi53c180 block diagram
2-2
Functional Descriptions
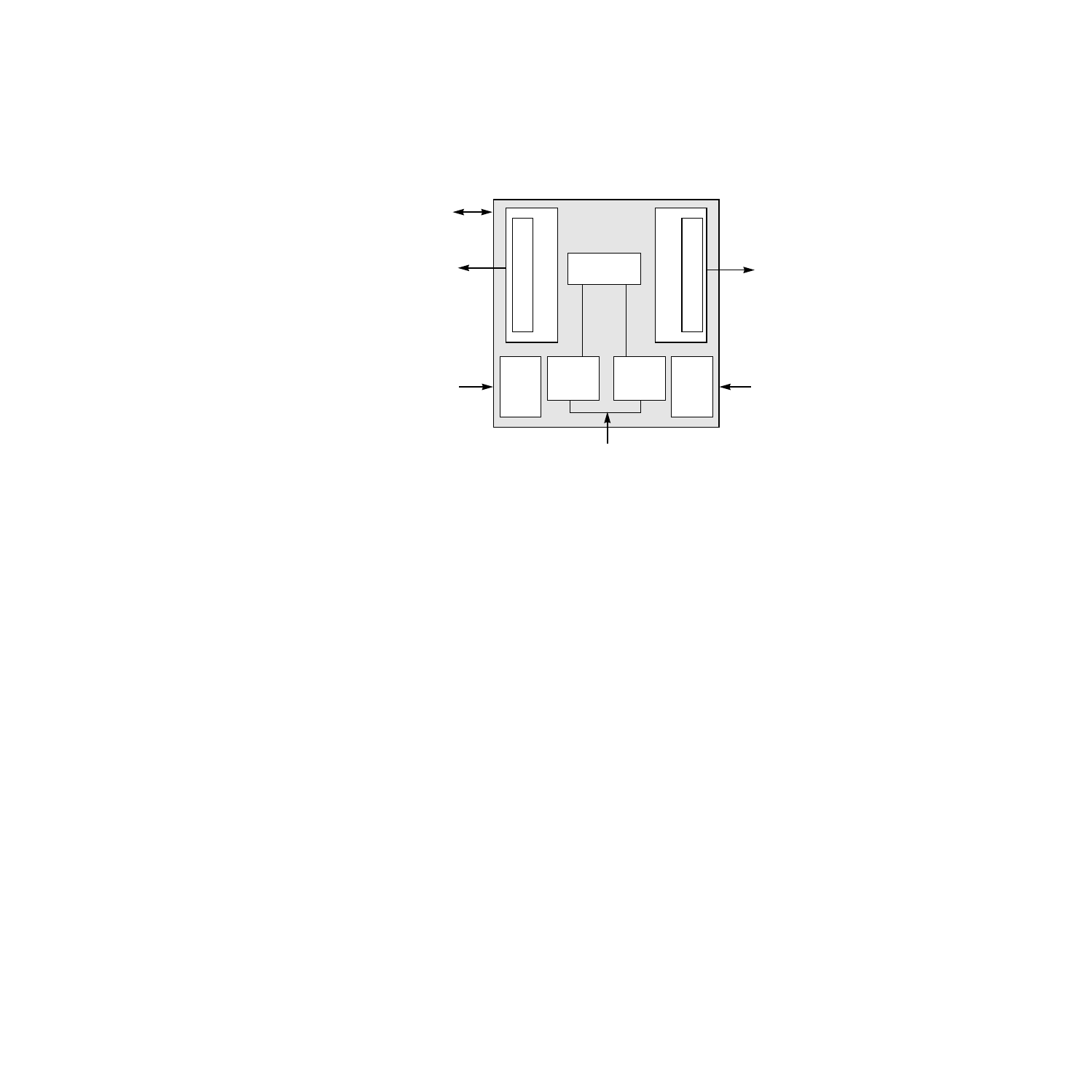
Figure 2.1
LSI53C180 Block Diagram
In its simplest form, the LSI53C180 passes data and parity from a source
bus to a load bus. The side asserting, deasserting, or releasing the SCSI
signals is the source side. The model of the LSI53C180 represents
pieces of wire that allow corresponding SCSI signals to flow from one
side to the other side. The LSI53C180 monitors arbitration and selection
by devices on the bus so it can enable the proper drivers to pass the
signals along. In addition, the LSI53C180 does signal retiming to
maintain the signal skew budget from the source bus to the load bus.
2.1.1 SCSI A Side and B Side Control Blocks
The SCSI A Side pins are connected internally to the corresponding
SCSI B Side pins, forming bidirectional connections to the SCSI bus.
In the LVD/LVD mode, the SCSI A Side and B Side control blocks
connect to both targets and initiators and accept any asynchronous or
synchronous data transfer rates up to the 160 Mbytes/s rate of Wide
Ultra160 SCSI. TolerANT
®
and LVD Link technologies are part of both
the A Side and B Side control blocks.
2.1.1.1 LSI53C180 Requirements for Synchronous Negotiation
The LSI53C180 builds a table of information regarding devices on the
bus in on-chip RAM. The PPR, SDTR, and WDTR information for each
Retiming
Logic
Precision
Delay
Control
State
Machine
Control
LV
D
DIFFSENS
Receiv
er
LVD
DIFFSENS
Receiv
er
SCSI Contr
ol Bloc
k
SCSI Contr
ol Bloc
k
LVD Link T
ransceiv
ers
LVD Link T
ransceiv
e
rs
Control
Signals
LVD, Single-ended,
Wide Ultra SCSI Bus
(A Side)
LVD, Single-ended
Wide Ultra SCSI Bus
(B Side)
A_DIFFSENS
B_DIFFSENS
40 MHz Clock Input
