6 grounding inverters, Installation 2.6 grounding inverters – Magnum Energy MS-PE Series User Manual
Page 29
Page 22
©
2013 Magnum Energy, Inc.
Installation
2.6 Grounding
Inverters
The inverter/charger should always be properly connected to a permanent, grounded wiring
system. A properly grounded system limits the risk of electrical shock, reduces radio frequency
noise from the inverter, and minimizes excessive surge voltages induced by lightning. Ensure
there is a well-defi ned, low-resistance path from the electrical system to the grounding system.
The low-resistance path helps stabilize the electrical system voltage with respect to ground and
carries fault currents directly to ground if the electrical system malfunctions. Review the following
terms to understand how the conductors in the electrical circuit connect to the system ground:
• Grounded Conductor (GC): The wire/cable in the electrical system that normally carries current
(usually AC neutral and/or DC negative), and is intentionally connected or “bonded” to the ground
system. This wire, or the ends of this wire, should be colored blue.
• Equipment Grounding Conductor (EGC): A wire/cable that does not normally carry current and is
used to connect the exposed metal parts of equipment—that might be accidentally energized—to the
grounding electrode system or to the grounded conductor. This wire, or the ends of this wire, should be
green or green w/yellow stripe; or this wire can be bare copper.
• Grounding Electrode Conductor (GEC): The wire/cable that does not normally carry current and
connects the grounded conductor and/or the equipment grounding conductor to the grounding electrode
at the service equipment.
• Grounding
Electrode
(GE): A ground rod or conducting element that establishes an electrical
connection to the earth.
• System Bonding Jumper (SBJ): The connection between the grounded circuit conductor in the
electrical system and the equipment grounding conductor at a separately derived system.
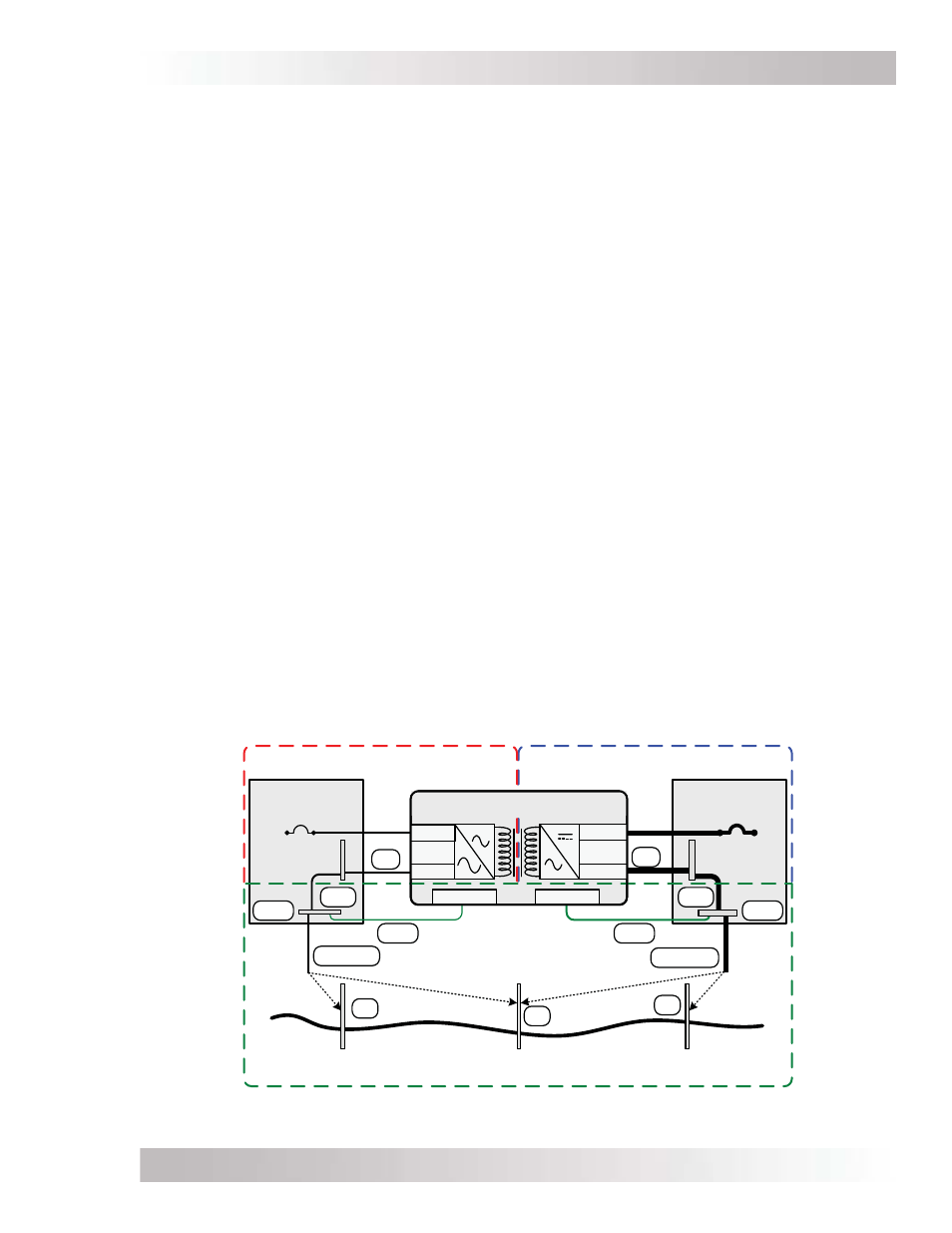
The MS-PE Series inverter/charger uses both AC and DC power; however, the AC electrical system
is isolated from the DC electrical system by an internal transformer. Although this inverter/charger
has two electrical systems, each electrical system must be properly grounded and connected to
a common earth reference (refer to Figure 2-10).
For proper grounding, each electrical system must connect all exposed metal parts of equipment
(via EGC) and one of the current carrying conductors (GC) together at a common point (ground
busbar – GBB), usually by a system bonding jumper (SBJ) in an electrical service disconnect panel.
The common point of each electrical system is then connected (via GEC) to the common ground
reference, such as a ground rod (GE). This connection to earth should only be made at one point
in each electrical system; otherwise, parallel paths will exist for the currents to fl ow. These parallel
current paths would represent a safety hazard and are to be avoided during installation.
Figure 2-10, Grounding System for MS-PE Series
AC
DC Service
Panel
AC Service
Panel
DC Electrical System
AC Electrical System
Neutral
Positive
Negative
DC
Grounding
System
Negative
SBJ
GC
GE
GEC-AC
EGC
AC Ground
DC Ground
SBJ
EGC
GC
Neutral
Hot
GEC-DC
GE
GE
GBB
GBB
Grounding Electrode
(AC and DC sides shared)
Grounding Electrode
(DC side dedicated)
Grounding Electrode
(AC side dedicated)
or
or
MS-PE Series Inverter/Charger
