Saving security logs into the security log file, Network requirements, Configuration considerations – H3C Technologies H3C SecBlade LB Cards User Manual
Page 40
31
NOTE:
Be aware of the following issues while editing file /etc/syslog.conf:
•
Comments must be on a separate line and must begin with a pound sign (#).
•
No redundant spaces are allowed after the file name.
•
The logging facility name and the information level specified in the /etc/syslog.conf file must be
identical to those configured on the LB by using the info-center loghost and info-center source
commands. Otherwise, the log information might not be output properly to the log host.
d.
Display the process ID of syslogd, kill the syslogd process, and then restart syslogd using the –r
option to make the new configuration take effect.
# ps -ae | grep syslogd
147
# kill -9 147
# syslogd -r &
Make sure the syslogd process is started with the -r option on a Linux log host.
Now, the system can record log information into the log file.
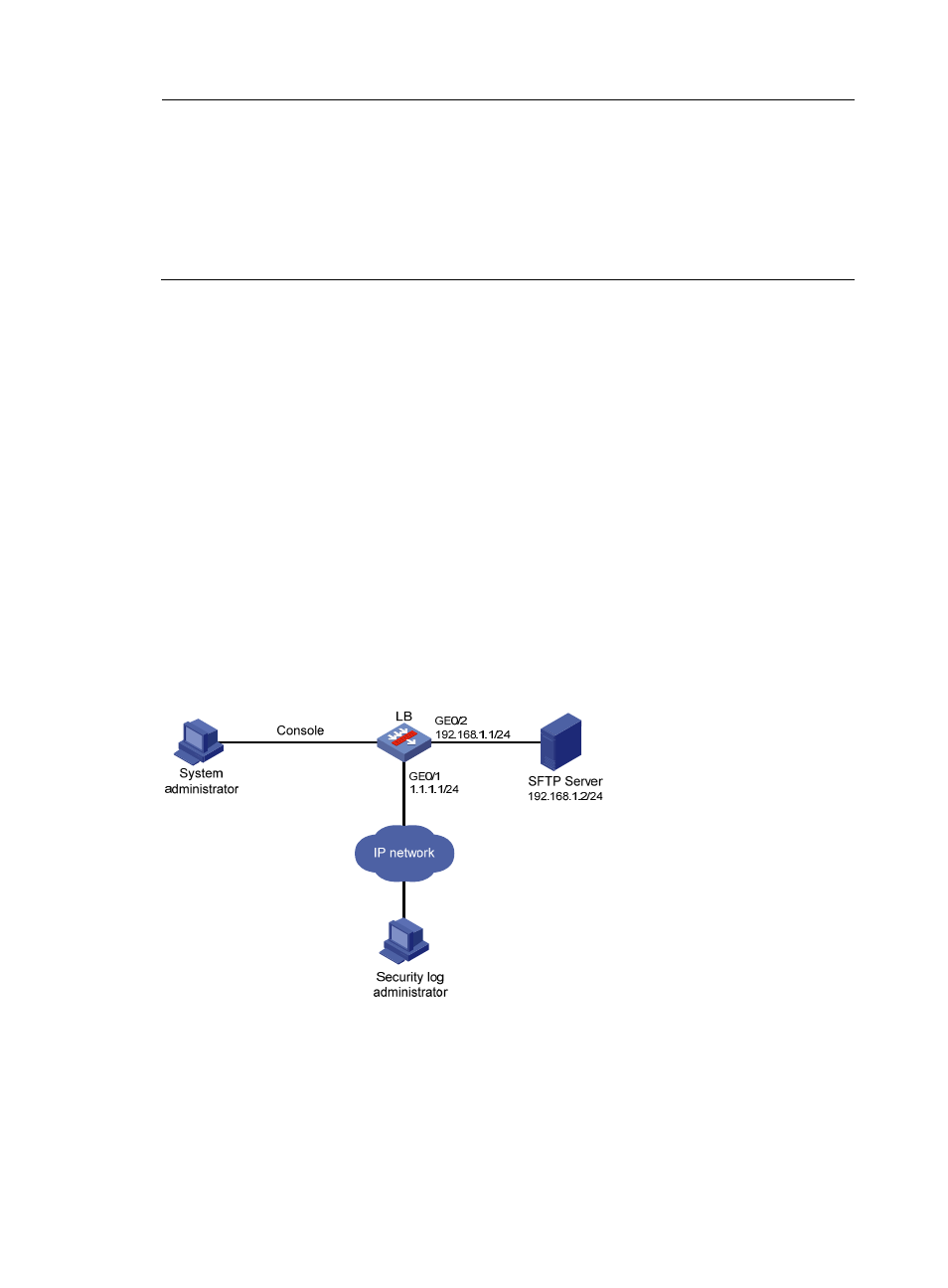
Saving security logs into the security log file
Network requirements
•
Save security logs into the security log file Flash0:/securitylog/seclog.log every one hour.
•
Only the security log administrator can view the contents of the security log file. No other logged-in
users can view, copy, or rename the security log file.
Figure 9 Network diagram
Configuration considerations
The configuration in this example includes two parts:
1.
Log in to the LB as the system administrator
{
Enable saving of security logs into the security log file and set the saving interval to one hour.
{
Create a local user seclog with the password 123123123123, and authorize this user as the
security log administrator. That is, use the authorization-attribute command to set the user
