Guralp Systems CMG-DM24 User Manual
Page 66
Operator’s Guide DM-24 Digitiser
Issue G January 2003
64
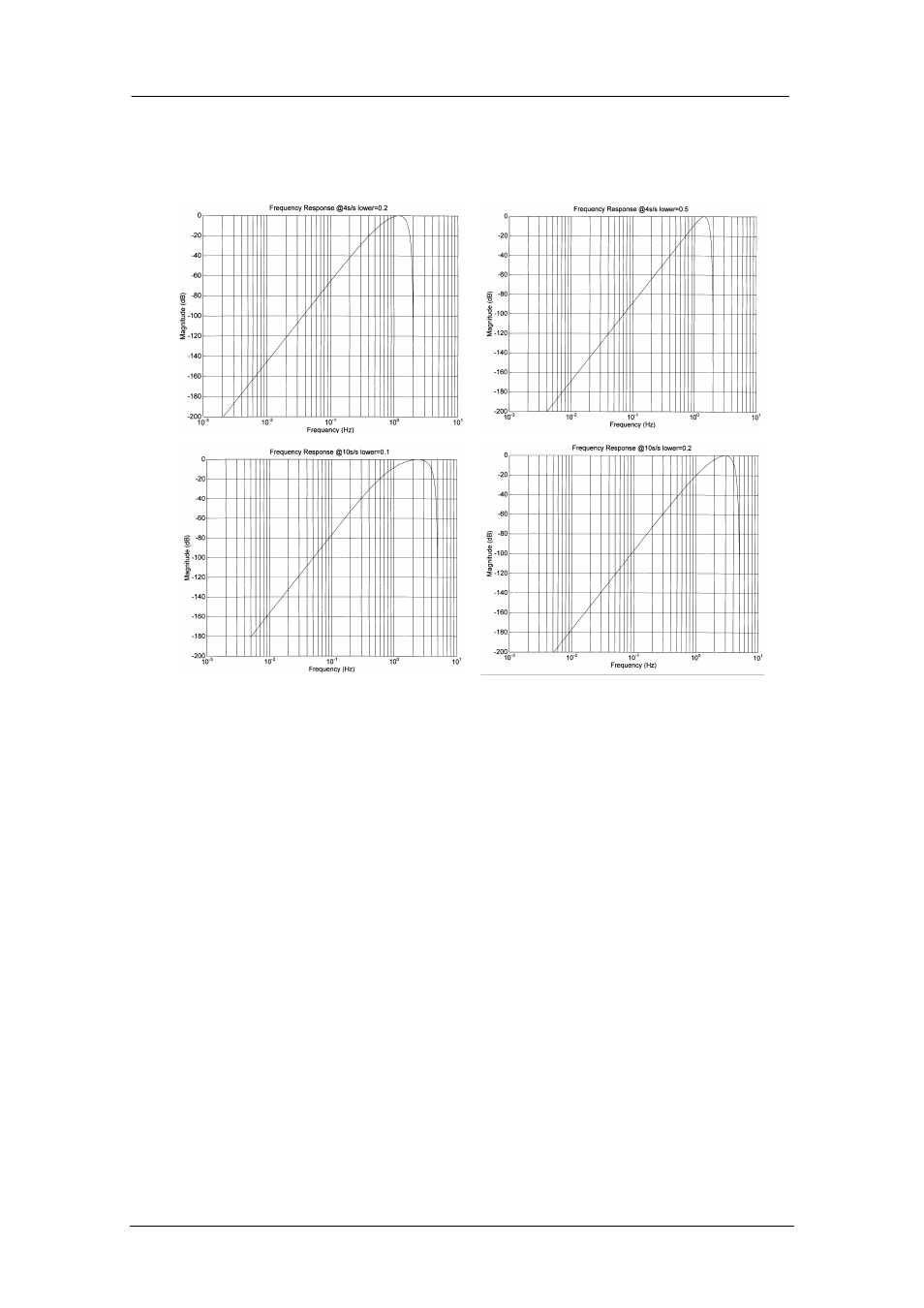
The spectral amplitudes for the various frequency responses available are shown in the
figures below.
TRIGGERING ALGORITHM
The triggering algorithm applied to the bandpass filtered data is a standard STA/LTA
ratio test. Averages of the modulus of signal amplitude are computed over two user
defined time periods, a short time average (STA) and a long time average (LTA), and
the ratio of the two at each sample point is computed (STA/LTA). If this ratio exceeds
a user-defined threshold, then a trigger is declared, and the system remains in a
triggered state until the ratio falls below the defined threshold. The trigger works by
identifying sections of an incoming data stream when the signal amplitude increases.
The purpose of taking a short term average, rather than triggering on signal amplitude
directly, is to reduce the probability of triggering on spurious spikes or short duration
transients, and to introduce some element of frequency selectivity into the triggering
process. As a rule of thumb, the short term average should be set to the dominant
frequency of the events the trigger is designed to catch. The purpose of the long term
average is to provide a measure of the variation in the background seismic noise, so it
should be set to some value longer than the period of the lowest frequency seismic
signal of interest. Obviously there is some element of trade-off in setting a value for the
trigger ratio. Too high a value will result in events being missed, while too low a value
will result in spurious non-seismic noise triggering the system producing false alarms.
Determining an apropriate value in any given situation which maximises the number of
seismic events detected while minimising the number of false alarms is a matter of
experiment.
