B.2.2 multicast routing, B.2.2 – Comtech EF Data CMR-8500 Manual User Manual
Page 80
CMR-8500 DVB IP ENCAPSULATOR
Revision 2
Appendix B. IP Routing Support
MN-CMR8500
Unicast is supported by the CMR-8500 as it would be in any routed network. A route is created and a
subnet mask is assigned to the route.
The CMR-8500 uses Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) notation in which a ‘slash’ followed by a
decimal number is used to represent the number of bits for the mask, e.g. /32 is 255.255.255.255 and /24
is 255.255.255.0.
As stated previously, part of the route configuration is a MAC address that is assigned for delivery of the
packet when it is encapsulated into MPE. The MAC address typically identifies the remote receiver
(physical device); e.g. satellite terminal, DTV terminal, or cable receiver.
B.2.2 Multicast Routing
Multicast routing provides point-to-multipoint delivery of IP datagrams. Routes for multicast IP packets
are configured according to the following:
• IP Addresses, which fall into class D (224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255)
• Medium Access Control (MAC) Addresses, which identify the frames as multicast. The least-
significant bit of the first byte of the six-byte MAC address is a ‘1’. For example, 0x01 00 5E 00 00
01 is a multicast address.
•
Broadcast frames are identified by the MAC Address, 0x FF FF FF FF FF FF.
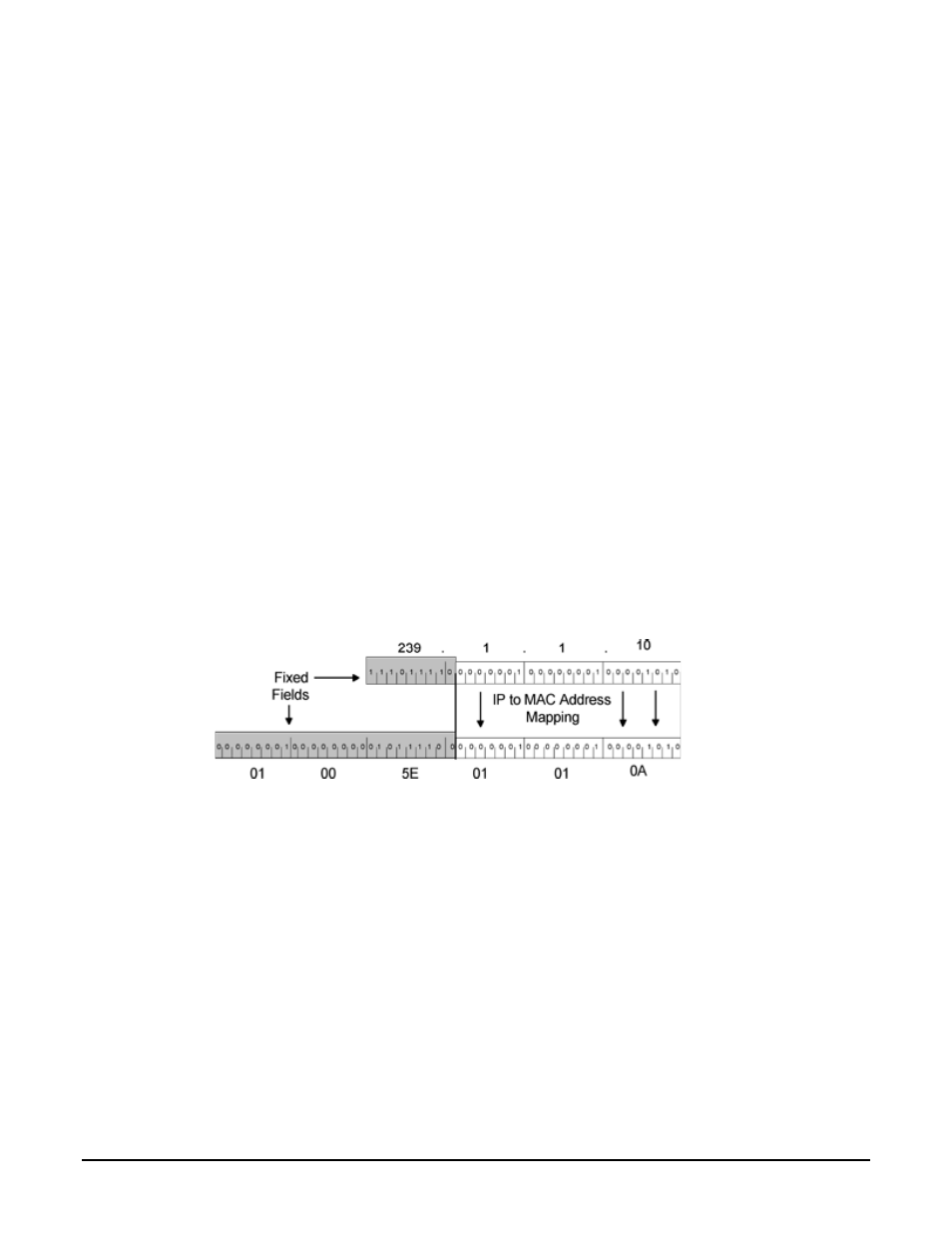
Multicast IP addresses are related to multicast MAC addresses as follows:
•
The lower 23 bits of the IP address are mapped into the lower 23 bits of the MAC address.
Figure B-1. Multicast Mapping (IP to MAC)
Several examples of the relationship are:
• Received IP: 239.1.1.10 = MAC: 0x01 00 5E 01 01 0A
• Received IP: 224.10.10.10 = MAC: 0x01 00 5E 0A 0A 0A
• Received IP: 228.63.10.10 = MAC: 0x01 00 5E 3F 0A 0A
Note that the upper 5 bits of the multicast IP address are ignored in the MAC so that 32 Multicast group
IP addresses map to a single MAC address. This implies further filtering is required at the end device.
B–2
