1 start of packet, 2 target address, 3 address delimiter – Comtech EF Data LPOD User Manual
Page 107
LPOD C-, X-, or Ku-Band Outdoor Amplifier / Block Up Converter (BUC)
MN-LPOD
Serial-based Remote Product Management
Revision 10
5–7
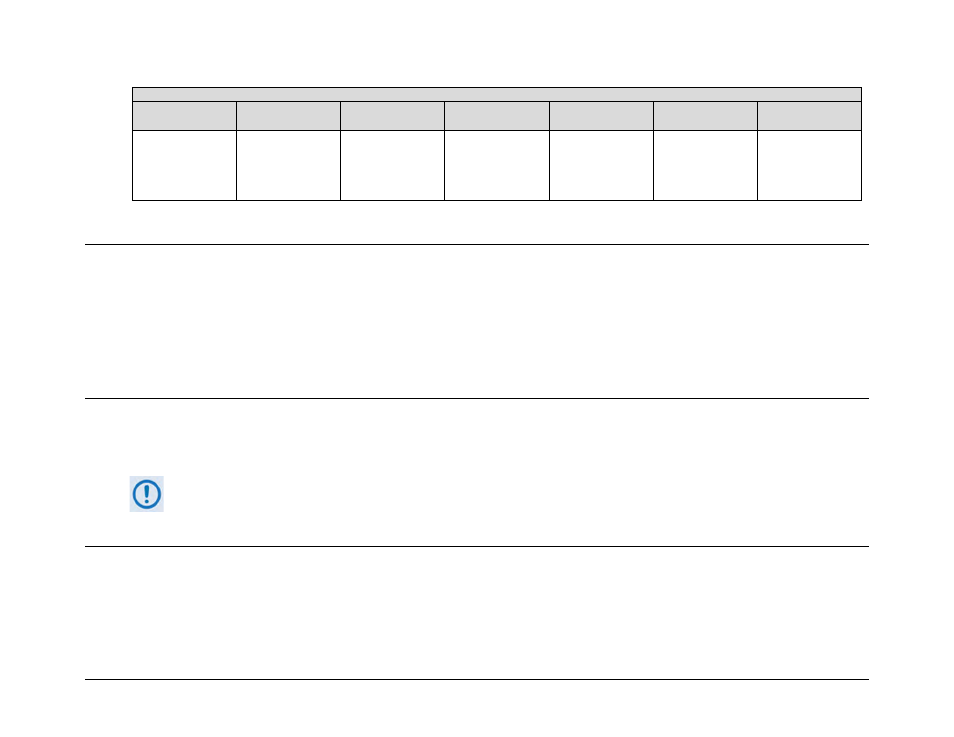
Target-to-Controller
Start of Packet
Target Address
Address Delimiter
Instruction Code
Code Qualifier
Optional
Arguments
End of Packet
>
ASCII code 62
(1 character)
0-9
ASCII codes 48-57
(4 characters)
/
ASCII code 47
(1 character)
A-Z, a-z
ASCII codes 65-90,
97-122
(3 characters)
=, ?, !, or *
ASCII codes
61,63,33 or 42
(1 character)
(From 0 to n
characters)
Carriage Return,
Line Feed
ASCII codes
13,10
(2 characters)
Example: >0412/MUT=1{CR}{LF}
5.1.4.1 Start of Packet
Because this is used to provide a reliable indication of the start of packet, these two characters may not appear anywhere else within the
body of the message:
• Controller-to-Target: This is ‘less-than’ the character '<' (ASCII code 60).
• Target-to-Controller: This is the ‘greater-than’ character '>' (ASCII code 62).
5.1.4.2 Target Address
Up to 9,999 devices can be uniquely addressed. In EIA-232 applications this value is set to 0. In EIA-485 applications, the permissible
range of values is 1 to 9999.
The Controller sends a packet with the address of a Target – the destination of the packet. When the Target responds, the
address used is the same address, to indicate to the Controller the source of the packet. The Controller does not have its
own address.
6B
5.1.4.3 Address Delimiter
This is the ‘forward slash’ character ' / ' (ASCII code 47).
