K-bus modes, Freerun mode, K-bus cycle – BECKHOFF BK3xx0 User Manual
Page 51: Slow freerun (default setting)
Notes on the Documentation
Fieldbus Components
49
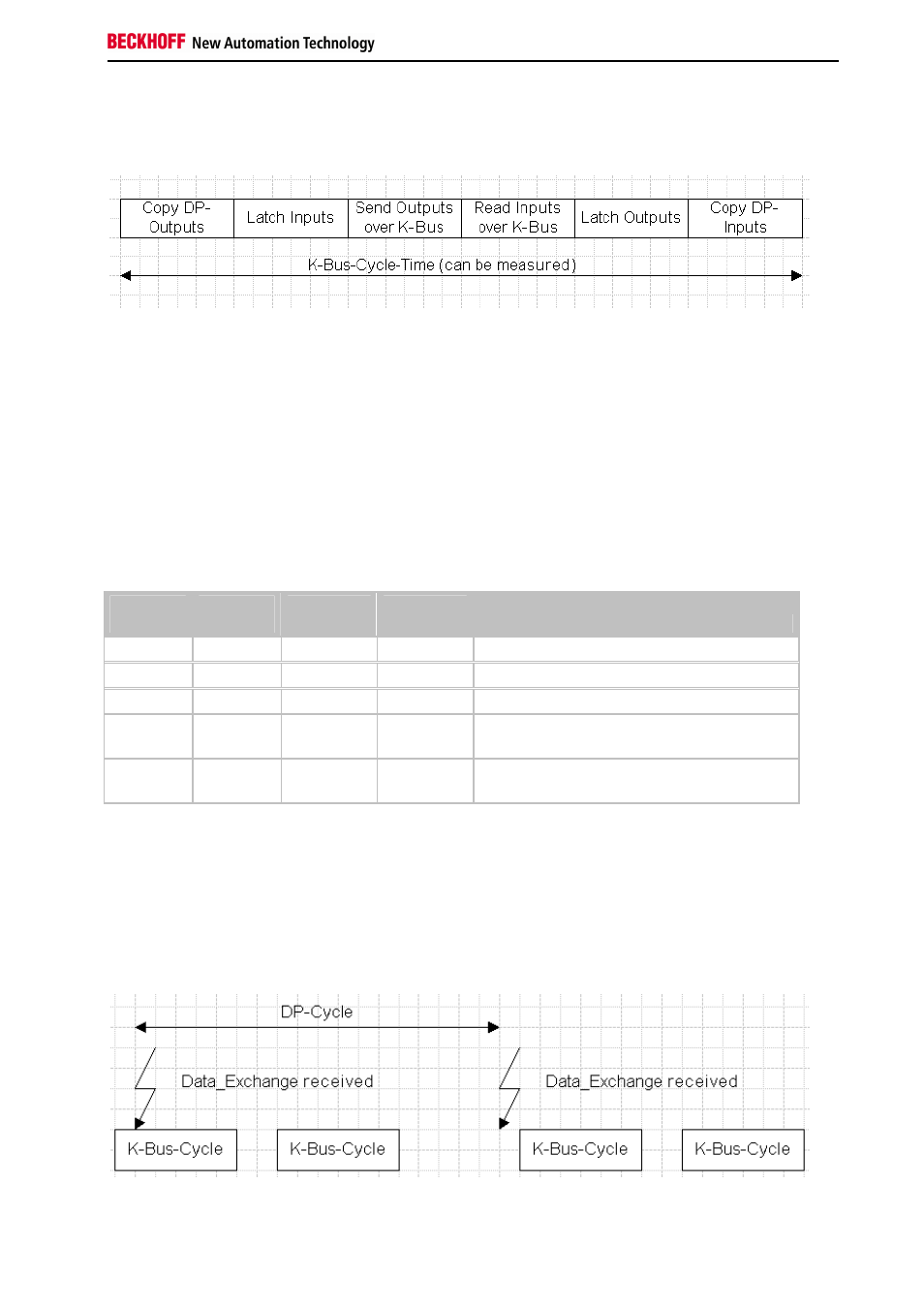
K-Bus Cycle
The K-Bus cycle can be set to run freely (FreeRun mode) or synchronously (synchronous mode) with respect to the
DP cycle. The K-Bus cycle for the DP coupler consists of the following parts:
The K-Bus cycle time can be calculated to a precision of approximately 10% by means of the following formula (4-
channel terminals or terminals with more than 6 bytes of data (exception: ASI terminal KL6201, which has more than
12 bytes of data) require two or more K-Bus cycles. The number of K-Bus cycles is in register ?? of table 90):
Tcyc (in µs) = number of K-Bus cycles x (600
+
number of
digital channels x 2.5 + number of analog
input channels x 32 +
number of analog output channels x 42)
The K-Bus cycle time can be read via DPV1. If TwinCAT is used, this is possible on the "Beckhoff" tab of
the DP coupler in the System Manager.
K-Bus modes
The K-Bus mode (the type of synchronisation between the K-Bus cycles and the DP cycle) is set via the
UserPrmData:
Byte 9, bit
4
Byte 9, bit
6
Byte 12, bit
0
Byte 12, bit
1
K-Bus mode
0
bin
1
bin
0
bin
0
bin
Slow FreeRun
1
bin
1
bin
0
bin
0
bin
Fast FreeRun
0
bin
0
bin
0
bin
0
bin
Synchronous
0
bin
0
bin
1
bin
0
bin
Synchronous with optimised input update, one
cycle
0
bin
0
bin
0
bin
1
bin
Synchronous with optimised input update, two
cycles
FreeRun mode
Slow FreeRun (default setting)
In the FreeRun mode there is no synchronisation between the K-Bus cycle and the DP cycle. It is a
characteristic feature of the Slow FreeRun mode that the K-Bus cycle is called from the main task. Acyclic
communication or events result in heavy jitter in the K-Bus cycle (KS2000, DPV1, terminal diagnosis,
etc.), because all of these functions are also called from the main task.
