Altera Active Serial Memory Interface User Manual
Page 31
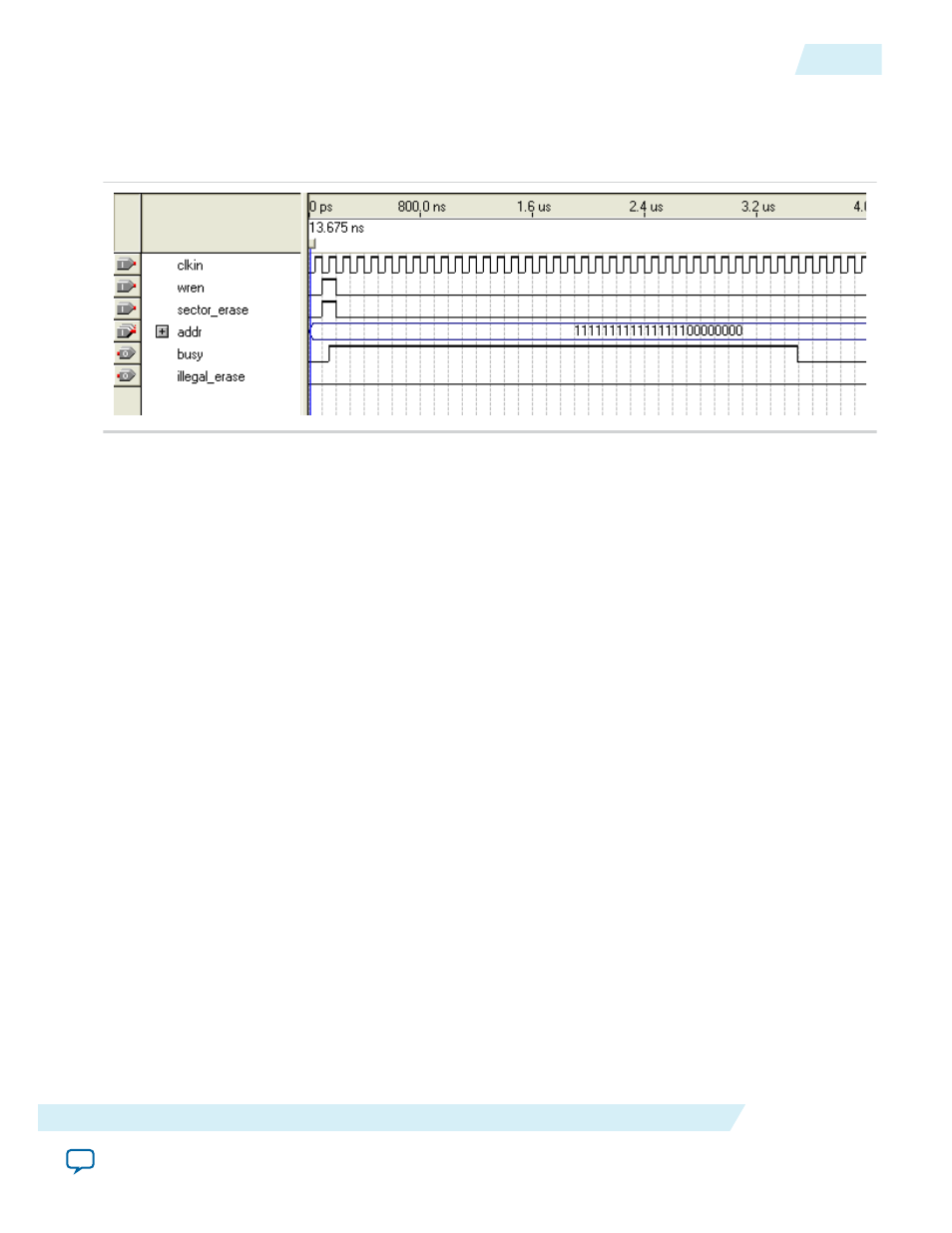
Figure 15: Erasing Memory in a Specified Sector
This figure shows an example of the latency when the Altera ASMI Parallel IP core is executing the erase
memory command. The latency shown does not correctly reflect the true processing time. It shows the
command only.
The IP core registers the
sector_erase
signal on the rising edge of the clkin signal. The address
placed on the
addr[23..0]
signal is a valid address in the sector that you can erase.
Ensure that the memory address to be erased appears on the
addr[23..0]
signal before setting
the wren and
sector_erase
signals to a value of one. After the IP core receives the sector erase
command, the IP core asserts the
busy
signal when erasing the sector.
If
wren
signal has a value of zero, then the sector erase operation is carried out, and the
busy
signal remains deasserted.
If the memory region is protected (specified in the EPCS/EPCQ/EPCQ-L status register), the
erase operation cannot proceed, and the
busy
signal is deasserted. The
illegal_erase
port is
then asserted for two clock cycles to indicate that the erase operation has been cancelled.
If you keep the
wren
and
sector_erase
signals asserted while the
busy
signal is deasserted after
the IP core has finished erasing the memory, the IP core re-registers the
wren
and
sector_erase
signals as a value of one and carries out another sector erase operation. Therefore, before the IP
core deasserts the
busy
signal, you must deassert the
wren
and
sector_erase
signals.
Note: For EPCQ256/EPCQ_L256 or larger devices, the width of the
addr
and
read_address
signals is 32 bit.
Erase Memory in Bulk on the EPCS/EPCQ/EPCQ-L256 Device
Use the
bulk_erase
signal to instruct the IP core to erase memory in bulk on the EPCS/EPCQ/
EPCQ_L256 device.
UG-ALT1005
2014.12.15
Erase Memory in Bulk on the EPCS/EPCQ/EPCQ-L256 Device
31
Altera ASMI Parallel IP Core User Guide
Altera Corporation
