Settings for iso & bsi methods, Astm treatment for acid and sulfur, Calculations – Parr Instrument 6100 User Manual
Page 51
Calculations
6100
B
w w w . p a r r i n s t . c o m
49
When the Acid Correction is set to Fixed Total the
value is considered a final value and the operator is
not prompted for an acid value when reporting the
results.
Entered Total: The Acid Correction represents the
total base required to titrate the bomb washings
(in milliliters). This includes both nitric and sulfuric
acid. The correction is entered by the operator when
reporting the results.
The calculation is the same as the Fixed Total above.
The value listed on the Acid Correction button is
used for preliminary calculations. When finalizing
the report the operator will be prompted for the acid
value.
Calculated HNO
3
: In ASTM D5865 there are provi-
sions for calculating the nitric acid contribution.
For test samples that contain no nitrogen, the
quantity of nitric acid formed during the combustion
process is a function of the volume of the bomb, the
oxygen filling pressure, and the quantity of energy
released.
For the calculated nitric acid method:
e1 = (nitric acid factor/1000)(Energy Equivalent)
(corrected temperature rise)
Example: For a test run with energy equivalent of
2425.07 and a corrected temperature rise of 2.6348
would result:
e1 = (1.58/1000)(2425.07)(2.6348)
e1 = 10.10 calories
The calculated nitric acid method can be applied
to samples containing up to 2% nitrogen without
introducing a significant error in the resulting heat
of combustion value.
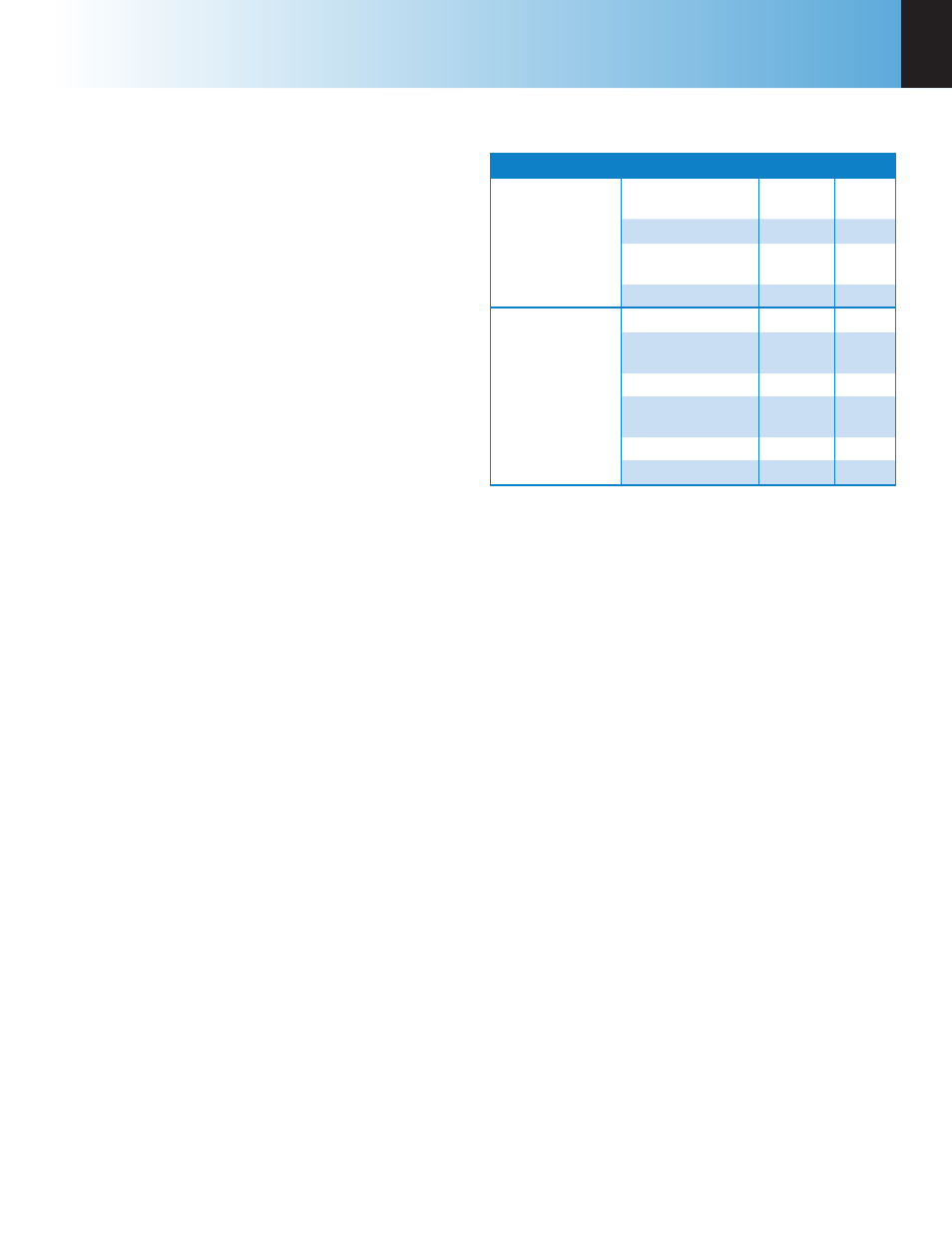
Table B-1
Settings for ISO & BSI Methods
Page
Line
Setting Value
Thermochemical
Corrections
Acid Correction
(STD)
Entered
HNO
3
13
Fixed Sulfur STD
Off
7
Acid Correction
(DET)
Entered
HNO
3
13
Fixed Sulfur DET
Off
7
Calculations
Factors
Acid Multiplier
0.154
Sulfur Value is
Percent
Off
Sulfur Multiplier
0.1
Use Offset
Correction
On
Offset Value
-43.5
Offset Value
-43.5
ASTM Treatment for Acid and Sulfur
In the ASTM treatment, the correction for acid
formation assumes that all the acid titrated is nitric
acid. Obviously, if sulfur is present in the sample,
which in turn produces sulfuric acid, part of the
correction for the sulfuric acid formed is already
included in the ASTM nitric acid correction (e1). This
is adjusted by a separate computation based upon
the sulfur content of the sample. An additional cor-
rection of 1.37 kcal must be applied for each gram
of sulfur converted to sulfuric from sulfur dioxide.
This is based upon the heat of formation of sulfuric
acid, from sulfur dioxide, under bomb conditions,
which is -72.2 kcal per mole or -36.1 calories per
milliequivalent. But remember, a correction of 14.1
calories per milliequivalent of sulfuric acid is already
included in the ASTM nitric acid correction (e1).
Therefore the additional correction which must be
applied for sulfur will be the difference between 36.1
and 14.1 or 22.0 calories per milliequivalent (44.0
Kcal per mole). For convenience, this is expressed,
in the ASTM e2 formula, as 13.7 calories (44.0/32.06)
for each percentage point of sulfur per gram of
sample.
