6 extra clock jumper, Extra clock jumper – CANOGA PERKINS 2240 Fiber Optic Modem User Manual
Page 25
Chapter 2 Installation and Setup
Setup
25
In the NORM position the 2240 samples TXD at the clock edge corresponding to the appropriate
standards, i.e., the 2240 samples TXD at the SCT A lead FALLING edge.
In the INV (invert) position the 2240 samples TXD at the clock edge opposite of the appropriate
standards, i.e., the 2240 samples TXD at the SCT A lead RISING edge.
Factory setting: NORM
2.1.6 EXTRA CLOCK Jumper
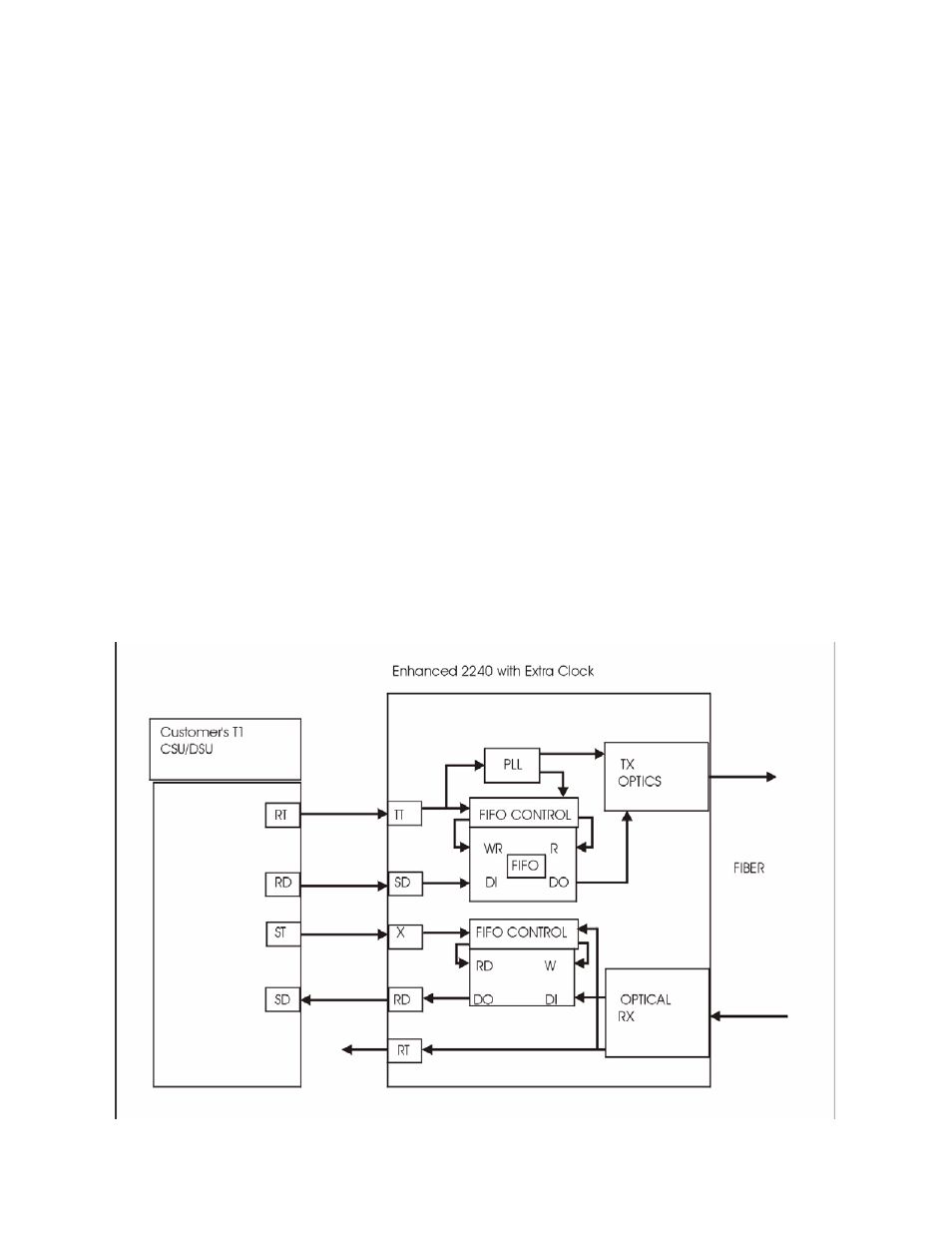
This two-pin jumper (W26, labeled XTCLK), in conjunction with the enhanced interfaces (- 422, -
436 and - 430), allows the 2240 to accept BOTH customer clocks for tail circuit applications.
Refer to the RS-449/422, V.35 and RS-530 interface sections for more information on the
enhanced interfaces. This jumper causes the 2240 to shift data out (RXD) from the 2240 in sync
with either the 2240's SCR (present operation) or the extra clock pins on enhanced interfaces. In
the case of the RS-530 interface there are no unused pins, so a switch on the RS-530 interface is
used to select the direction of the SCT leads (refer to the RS-530 interface section). In a typical
application (see Figure 2-3) these extra clock pins would be cabled to the customer's T1 CSU/
DSU's SCT (ST) pins (keep in mind that the 2240s are acting as a tail circuit). This feature is also
necessary if older "gapped clock" CSU/DSUs are used.
With the jumper OFF, the 2240 shifts data out (RXD) in sync with its SCR signal.
With the jumper ON, the 2240 shifts data out (RXD) in sync with the extra clock signal.
Factory setting: OFF
Figure 2-3 illustrates the use of extra clock pins in a tail circuit application at the clock source
end.
