ClearCube R-Series Data Center Products User Manual
Page 71
R-Series Data Center Products User’s Guide
Chassis and Blade Installation • 47
RMMs can only be installed in R4300 chassis. A BSBP without an RMC installed can
perform C/Port Switching, Admin Switching, and Sparing under the control of an
RMC or an RMM.
Each RMM in an R4300 series chassis provides an Ethernet connection, allowing it to
control a chain of as many as 14 chassis. If an RMM is not connected to Ethernet, it
does not auto-negotiate, and provides control and monitoring only for the chassis in
which it is installed.
The RMM has three auto-negotiation modes:
•
Primary (including jumper-strapped Primary)
•
Secondary
•
Standby
The model for auto-negotiation assumes that a given network contains a mix of R4300
chassis, and legacy BSBPs and DCBPs.
The R4300 Remote Management Module uses the following auto-negotiation rules:
•
An RMM must be active (that is, powered up and functioning correctly) to assert
its status as Primary or other.
•
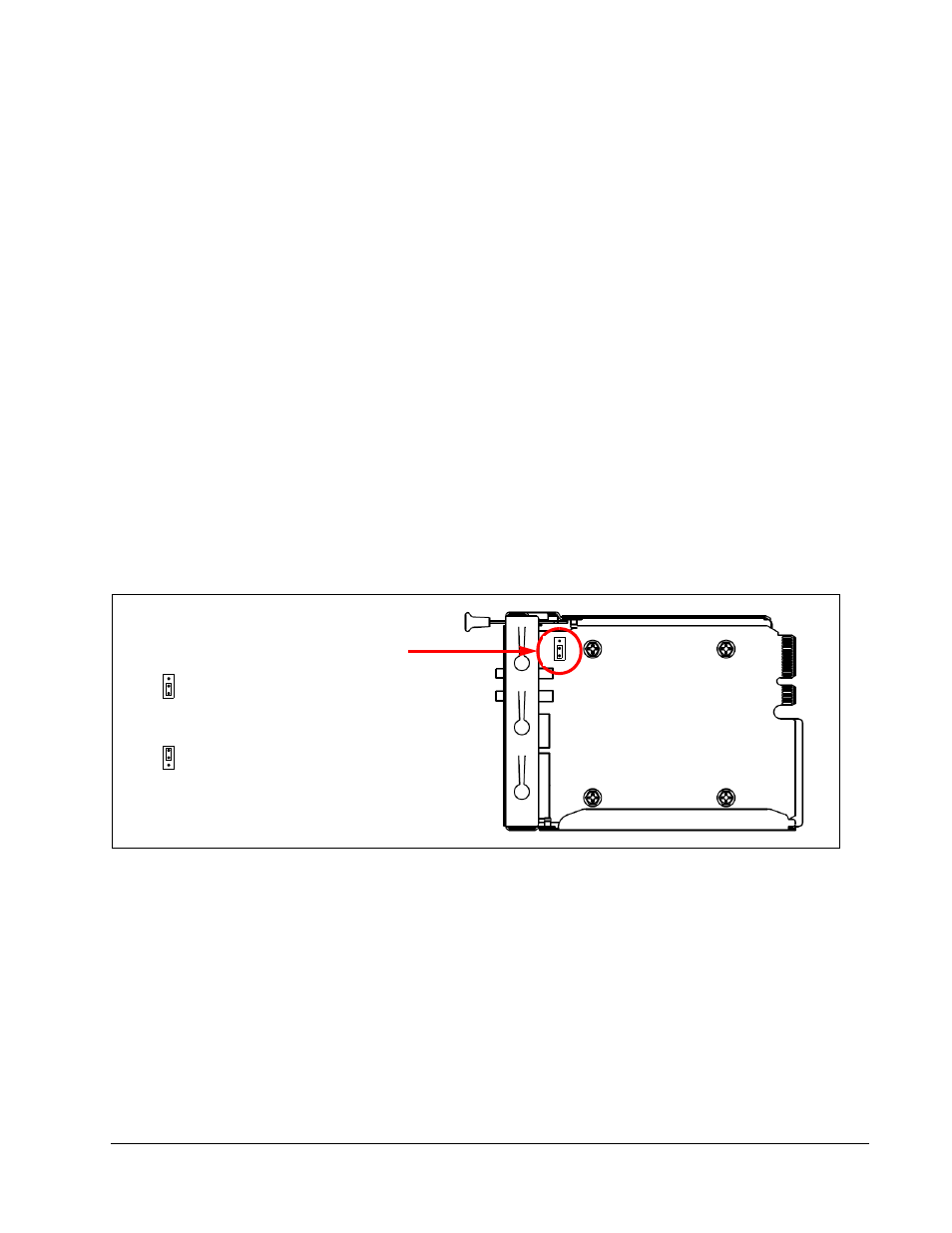
If a jumper-configured RMM is present in a chain, that RMM is always Primary,
as shown in Figure 28.
•
Never jumper-configure an RMM in a Control Chain that also contains an RMC.
Figure 28 RMM Jumper Location
The RMC (in a BSBP or DCBP) uses the following rules for auto-negotiating a
Primary RMC in a Control Chain:
•
An RMC must be active (that is, powered up and functioning correctly) to assert
its status as Primary.
If an RMC is present in a chain, that RMC must always be the Primary.
For best results, follow these guidelines for configuring your Control Chains:
RMM (Bottom View)
JP1
– Leave JP1 jumpered on pins 2 and 3
– Jumper Pins 1 and 2 to force Primary
for auto-negotiation (Default shown)
JP
1
or remove jumper entirely
