Epeaters, Wds), Important notes – Weidmuller WI-MOD-945-E: 900Mhz Wireless Ethernet & Device Server v2.16 User Manual
Page 53: 16 - repeaters (wds)
Weidmuller Wireless Ethernet Modem & Device Server WI-MOD-945-E User Manual
Page 53
www.weidmuller.com
Rev 2.136
3.16 -
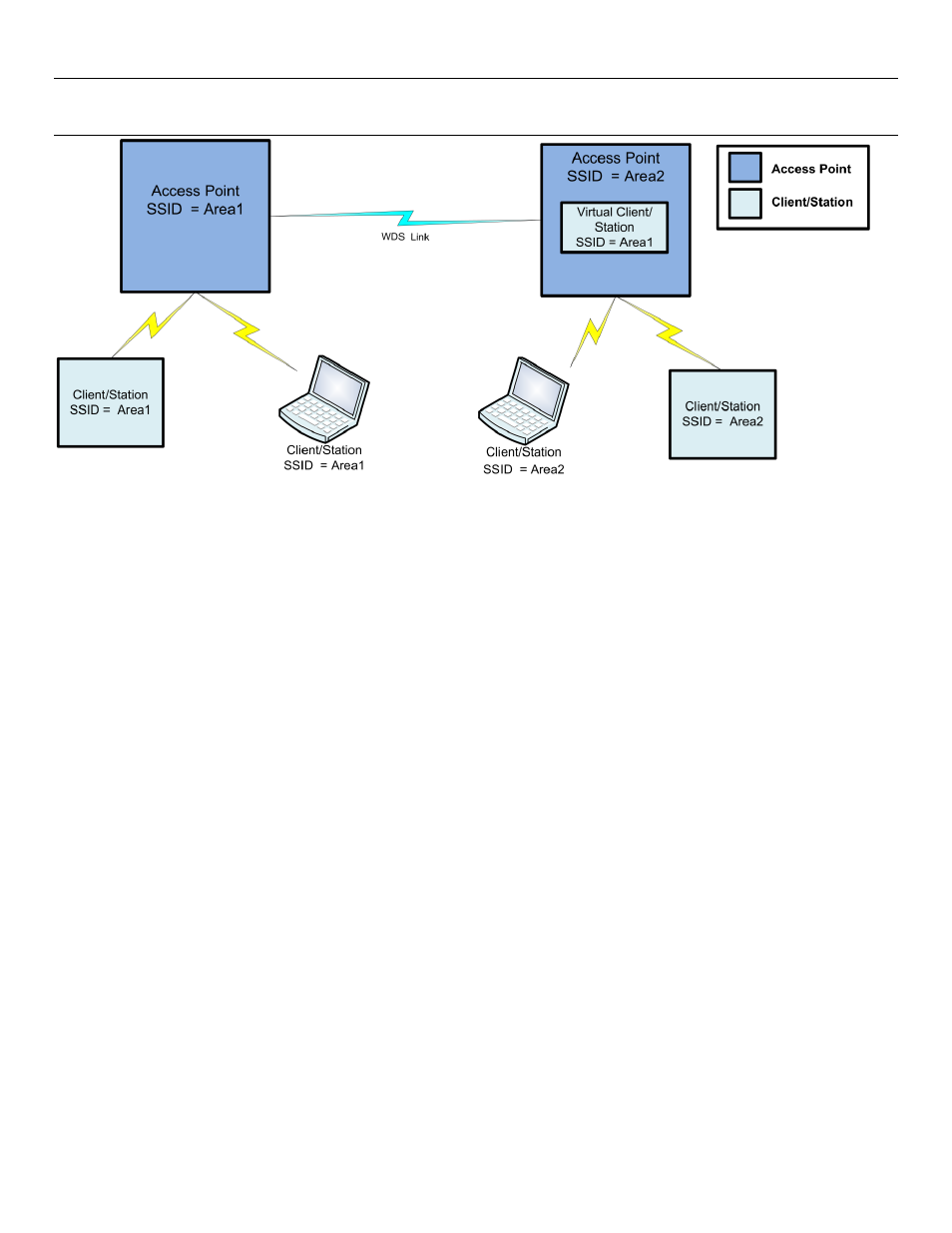
Repeaters (WDS)
The range of a wireless network can be extended by allowing Access Points to behave as repeaters and forward traffic to
other Access Points. Access Point to Access Point communications is also known as Wireless Distribution System
(WDS). The WI-MOD-945-E offers very powerful WDS configuration, allowing for a mesh network with self-healing
functionality. Alternatively, fixed AP to AP links can be configured for optimized throughput.
Each WI-MOD-945-E Access Point supports up to 10 separate interfaces for WDS links to other devices.
Each WDS interface can be either a bridge or router interface (refer section 1.0 -
“Network Topology” for more
information on bridge vs router). If you need a simple repeater network, use a bridge interface.
A WDS bridge interface allows traffic to be bridged to another Access Point on the same IP network. WDS bridge
interfaces do not require additional IP Address configuration, as they are bridged with the standard wireless interface that
is used for connections to associated clients. All of the WDS interfaces on the one Access Point may be bridged if
required.
WDS bridge interfaces have the advantage that redundant paths are permitted when using the bridge Spanning Tree
Protocol (see section 3.5 - Spanning Tree Algorithm ), thus behaving as a self-healing mesh network. Bridged networks
are also not as configuration intensive as routed networks. Since WDS bridge interfaces generally do not require IP
address configuration (they inherit the IP address of the standard wireless interface).
A WDS router interface allows traffic to be routed to an Access Point on a different network, and therefore requires
configuration of an IP address to reflect the network address of the destination network. WDS router interfaces cannot
provide the redundancy of bridge interfaces, but can be used to reduce radio bandwidth requirements because the router
can determine the destination based on IP address, whereas the bridge must go through a learning phase where all
broadcast traffic must be retransmitted on each interface. Routed networks may also be used in some cases to avoid the
overhead introduced by the bridge Spanning Tree Protocol when network loops exist.
Important Notes:
All Access Points must be configured on the same fixed radio channel. Auto Channel selection must not
be selected (See “Radio Configuration” page for details on configuring the channel.)
Figure 33 - WDS Repeaters
