Etwork, Onfiguration, 4 - network configuration – Weidmuller WI-MOD-945-E: 900Mhz Wireless Ethernet & Device Server v2.16 User Manual
Page 30
Weidmuller Wireless Ethernet Modem & Device Server WI-MOD-945-E User Manual
Page 30
www.weidmuller.com
Rev 2.136
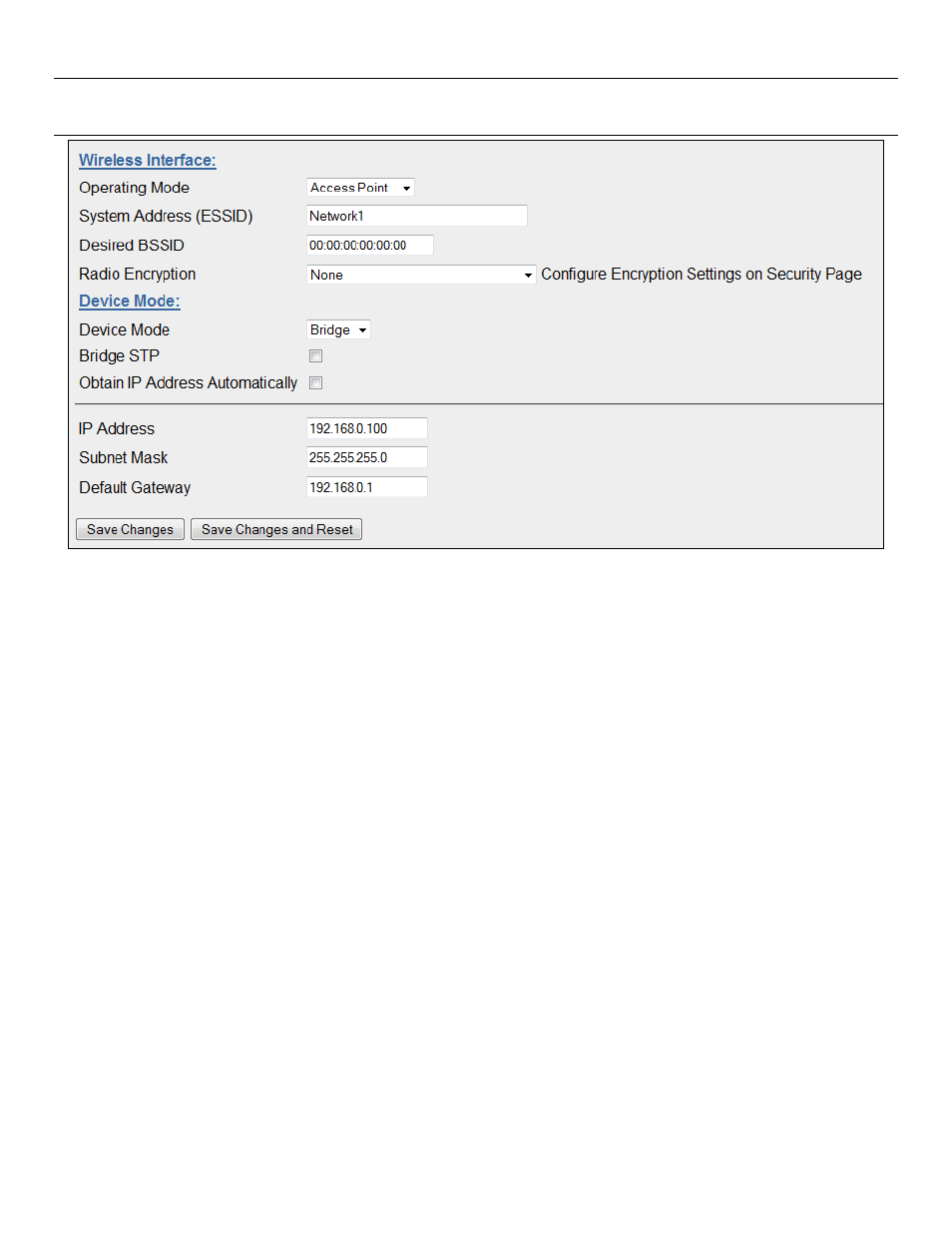
3.4 - Network Configuration
Figure 16 - Network
You can view or modify Ethernet network parameters by selecting the “Network” menu. When prompted for username and
password,
enter “user” as the username, and “user” as the password in the password field (This is the factory default –
See section 3.23 -
“Module Information Configuration” to change). If you have forgotten the IP address or password, the
Factory Default switch may be used to access the existing configuration. Refer to previous section above for this
procedure.
The Network Configuration page allows configuration of parameters related to the wired and wireless Ethernet interfaces.
In general, IP address selection will be dependent upon the connected wired Ethernet device(s)
– before connecting to an
existing LAN consult the network administrator.
Default configuration of the module will be Client and Bridge. When in Bridged Mode the modules wired and wireless IP
address will be the same, meaning only one IP Address is required. If the Device Mode is changed to Router the page will
display two IP addresses, one for Ethernet and one for Wireless. For more information on Bridging Networks see section
3.17 -
If the module has been configured for VLAN the page will show Device Mode as VLAN Bridge and the Ethernet IP and
netmask will no longer be editable. See Section 3.22 -
“VLAN” for more details on VLAN configuration.
A system of WI-MOD-945-E
’s must have at least one Access Point configured as a master with one or more Clients. All
WI-MOD-945-E
’s should be given the same System Address (ESSID) and Radio Encryption settings. For further
information and examples on wireless network topologies refer section 1.0 -
“Network Topology” above.
The WI-MOD-945-E supports several different radio encryption schemes. If utilising any form of encryption, all modules in
the system that communicate with each other will need the same encryption method and encryption keys. The available
encryption methods are listed below.
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) encryption is the weakest encryption method, defined by the original IEEE802.11
standard and uses a 40bit or 104bit key with a 24bit initialization vector to give a 64bit and 128bit WEP encryption level.
WEP is not considered an effective security scheme, and should only be used if it is necessary to interoperate with other
equipment which does not support more modern encryption methods.
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) is a subset of the IEEE802.11i Security Enhancements specification.
