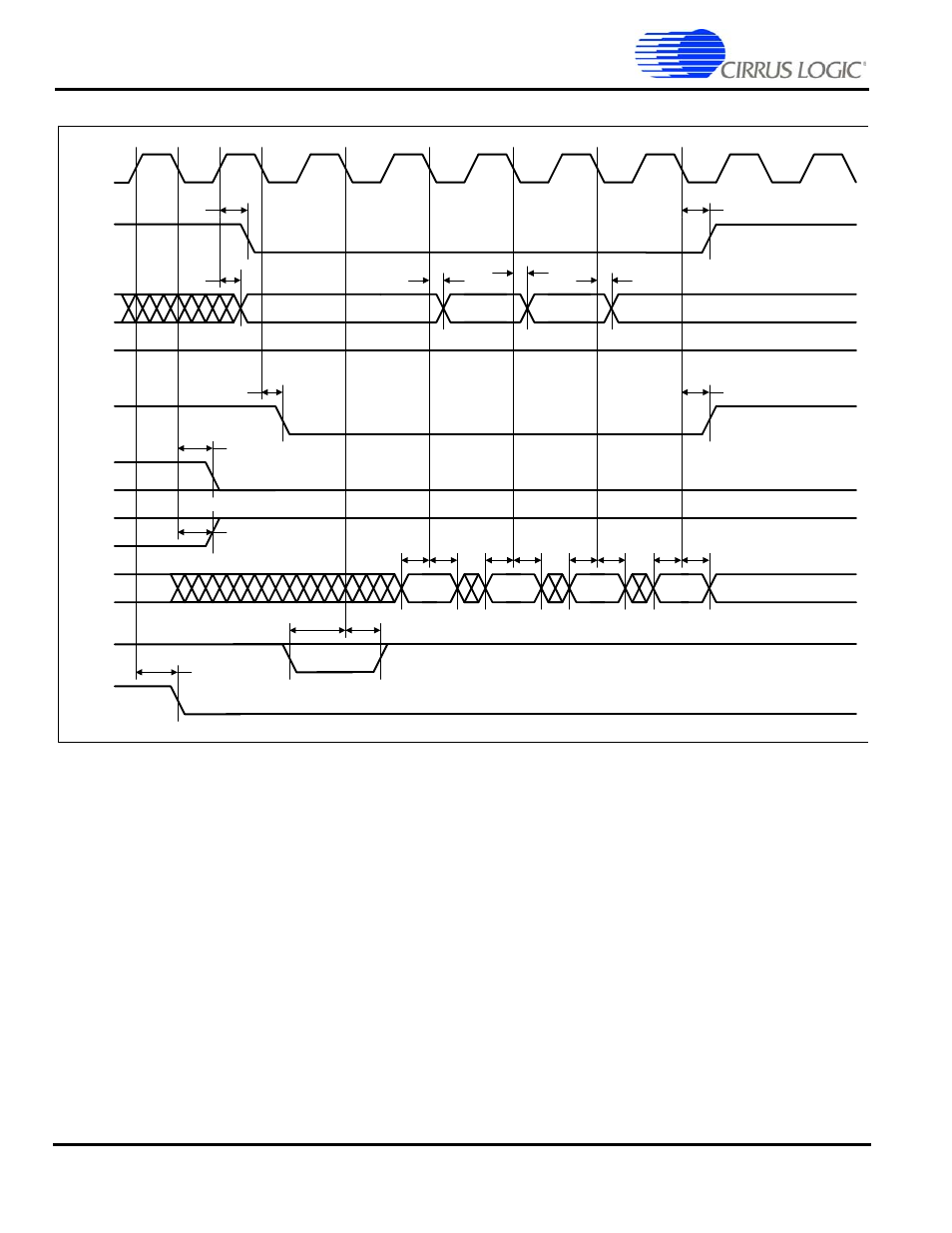
Static memory burst read cycle – Cirrus Logic EP7309 User Manual
Page 18
18
Copyright Cirrus Logic, Inc. 2011
(All Rights Reserved)
DS507F2
EP7309
High-Performance, Low-Power System on Chip
Static Memory Burst Read Cycle
Note: 1. Four cycles are shown in the above diagram (minimum wait states, 1-0-0-0). This is the maximum number of consecutive
cycles that can be driven. The number of consecutive cycles can be programmed from 2 to 4, inclusively.
2. The cycle time can be extended by integer multiples of the clock period (22 ns at 45 MHz, 27 ns at 36 MHz, 54 ns at
18.432 MHz, and 77 ns at 13 MHz), by either driving EXPRDY low and/or by programming a number of wait states. EXPRDY is
sampled on the falling edge of EXPCLK before the data transfer. If low at this point, the transfer is delayed by one clock period
where EXPRDY is sampled again. EXPCLK need not be referenced when driving EXPRDY, but is shown for clarity.
3. Consecutive reads with sequential access enabled are identical except that the sequential access wait state field is used to
determine the number of wait states, and no idle cycles are inserted between successive non-sequential ROM/expansion
cycles. This improves performance so the SQAEN bit should always be set where possible.
4. Address, Halfword, Word, and Write hold state until next cycle.
EXPCLK
nCS
A
nM OE
HALF
W ORD
W ORD
D
nM W E
EXPRDY
W RITE
t
CSd
t
Ad
t
Ah
t
Ah
t
Ah
t
CSh
t
M OEh
t
M OEd
t
EXs
t
EXh
t
Ds
t
Dh
t
Ds
t
Ds
t
Ds
t
Dh
t
Dh
t
Dh
t
W Rd
t
HW d
t
W Dd
Figure 5. Static Memory Burst Read Cycle Timing Measurement
