4 types of calibration and compensations, An366 – Cirrus Logic AN366 User Manual
Page 6
AN366
6
AN366REV2
Use Equation 5 to convert the hexadecimal value to a decimal ratio value:
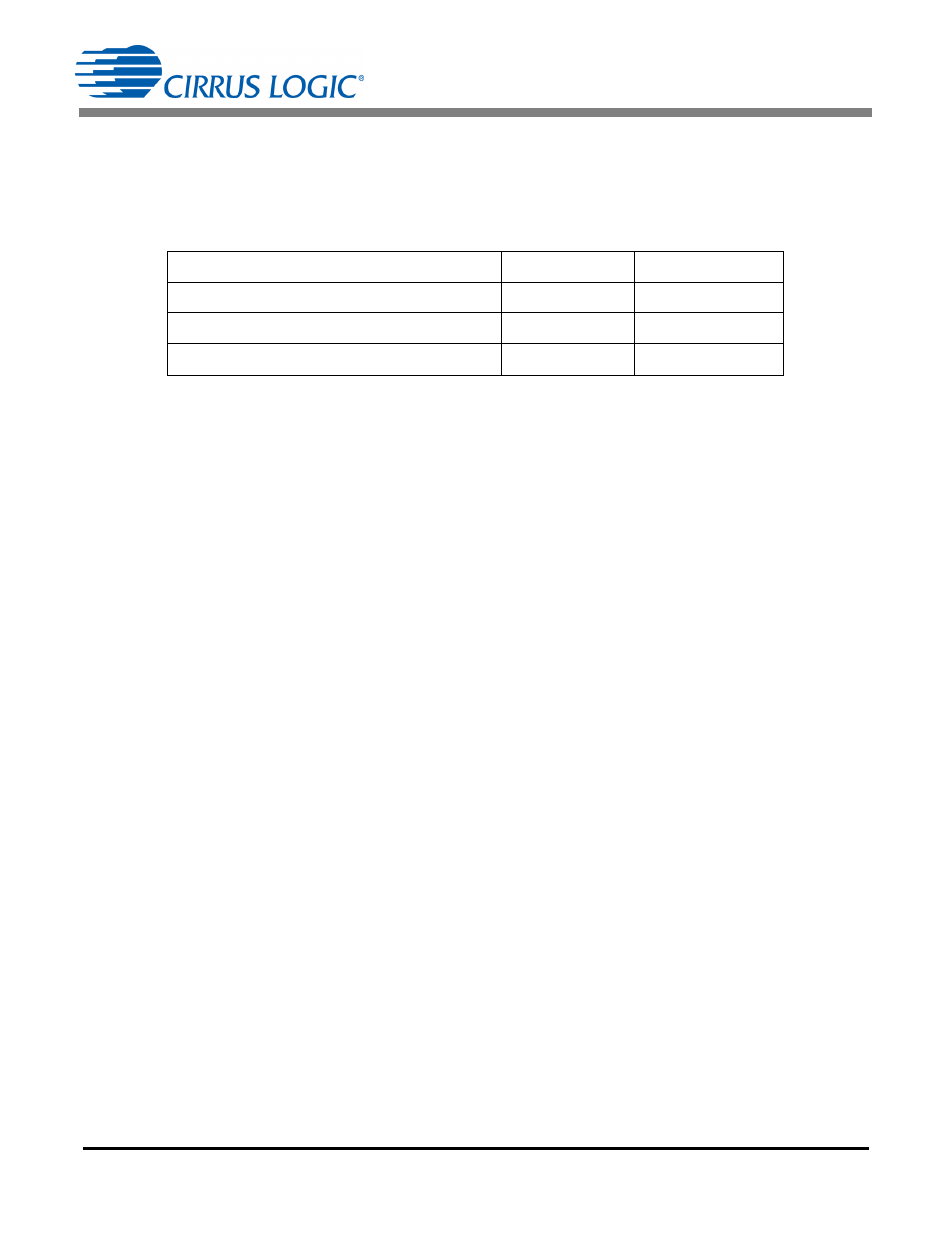
Using Equation 5, the following table identifies the key values.
4 Types of Calibration and Compensations
Calibration is self-contained within the CS5480/84/90, and all calculations are performed by the device and
stored in internal registers. Compensations require that the MCU perform some of the calculations and then
store the results back into the CS5480/84/90 registers. Since the CS5480/84/90 does not have non-volatile
memory (NVM), permanent storage of calibration and compensation must be placed in the MCU NVM and re-
loaded after any AFE reset condition.
In general, each calibration and compensation requires the following steps:
1. Configure the CS5480/84/90 initial conditions
2. Apply the analog input with stimulus from an accurate source
3. Enable the desired calibration
4. Execute calibration
5. Read the results
6. Calculate the new register values for compensations
7. Store the results in the AFE and NVM
It is common to perform calibration and compensation simultaneously. For example, since an AC gain calibration
and a phase compensation require a similar input signal to be applied to the current and voltage channels, cal-
ibration and compensation are performed simultaneously.
Key Power Register Values Range (-1 to 1)
Decimal Value
Register Value
Maximum Power Register
1
0x7FFFFF
Maximum Power Input
0.36
0x2E147B
No Load Input
0
0x000000
VALUE
Decimal
MSB
–
1
2
23
1
–
------------------ hex2dec VALUE
Hexidecimal
=
[Eq: 5]
