1 dilution water supply, 2 neat polymer supply, 3 polymer mixing chamber – Pulsafeeder Polyfeeder EN User Manual
Page 5
5
The activated solution exits the system for immediate use or aging, depending on the needs of
the user and/or process.
2.1 Dilution
Water
Supply
Dilution water must be supplied from a water supply system capable of meeting the maximum flow
requirements of the system. For pipe connection sizes, see the table in Section 5.4. Supply water must
be in the temperature range of 40F – 104F (4.4C - 40C). If using non-potable water, installation of a
strainer is recommended to prevent particulate from accumulating in system components. Dilution
water quality has a direct effect on polymer solution quality, which can result in higher than normal
polymer usages.
2.2
Neat Polymer Supply
The neat polymer supply tank or tote must be positioned to provide a positive suction pressure (head) to
the feed pump. Generally this requirement is satisfied as long as the lowest possible liquid level in the
tank or tote is maintained above the center line of the pump and the suction line diameter is large
enough to avoid excessive frictional losses in the piping or hose.
Ensure that no dilution water comes in contact with the neat polymer solution prior the polymer’s
entry into the mixing chamber. Neat polymers should also be within the appropriate viscosity range
for the type of polymer feed pump being used for proper operation. Refer to Table 2-1 for polymer
feed pump types and viscosity ranges
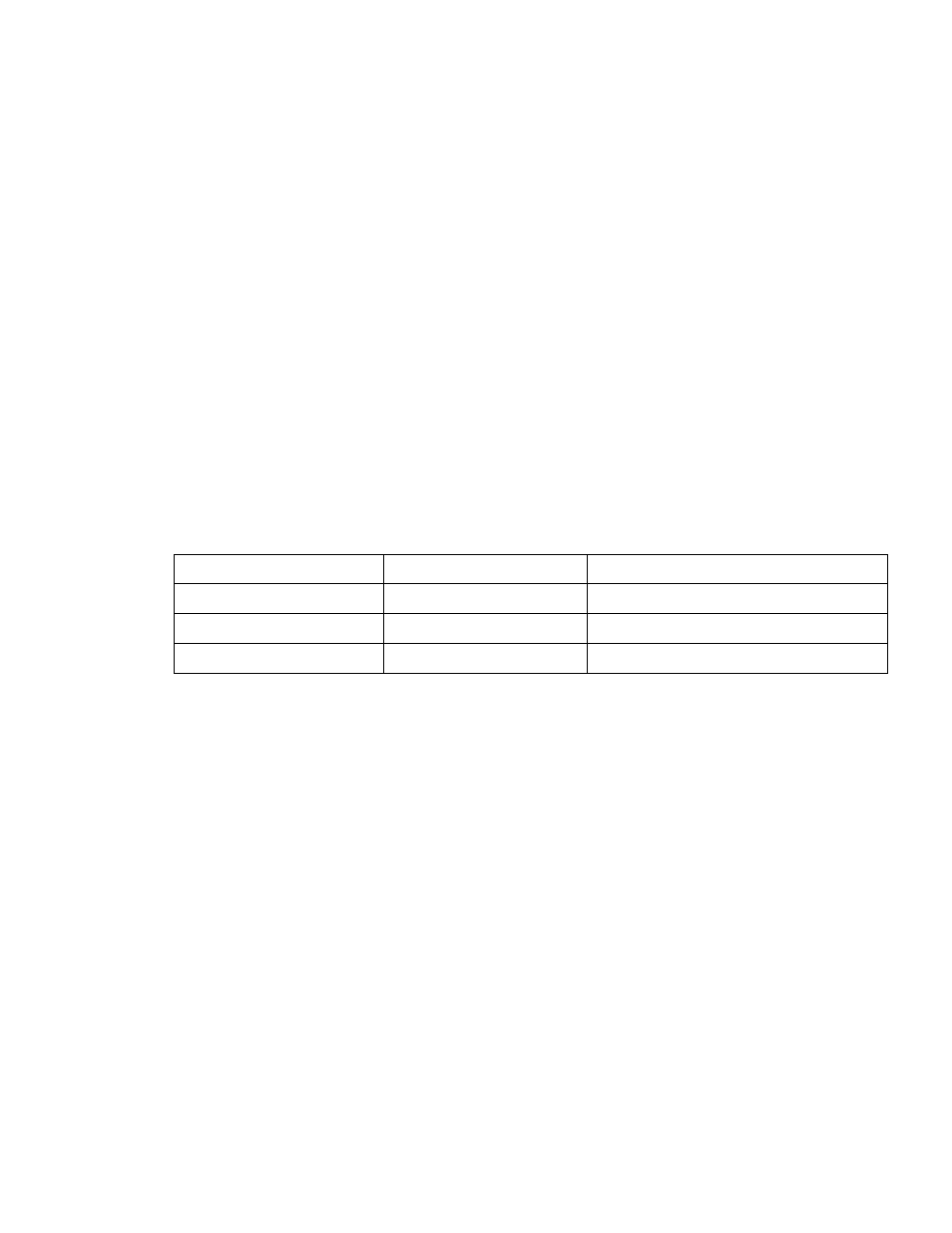
Polymer feed pump type
Viscosity range
Maximum acceptable viscosity
Solenoid
0 - 10,000 cps
3,000 cps
Gear 500
-
20,000
cps
7,000
cps
Progressing Cavity
500 - 20,000 cps
10,000 + cps
Table 2-2 Polymer Feed Pump Viscosity Ranges
2.3 Polymer
Mixing
Chamber
Neat polymer is combined with dilution water in the Polymer Mixing Chamber, beginning the actual
polymer make-down process. The neat polymer is injected into the primary dilution stream at the
inlet if the chamber, where it encounters the motorized dispersion disc which provides rapid
dispersion and hydration of the polymer. The stream is then directed around a series of baffles which
provide full expansion of the polymer molecules exiting the mixing chamber for use. It should be
noted that although the system polymer is highly activated upon exiting the system, further activation
is possible through tank aging. Aging is especially useful in high use or continuous use application as
a means to reduce chemical usage and increase polymer efficiency.
