Agilent Technologies Agilent 4396B User Manual
Page 98
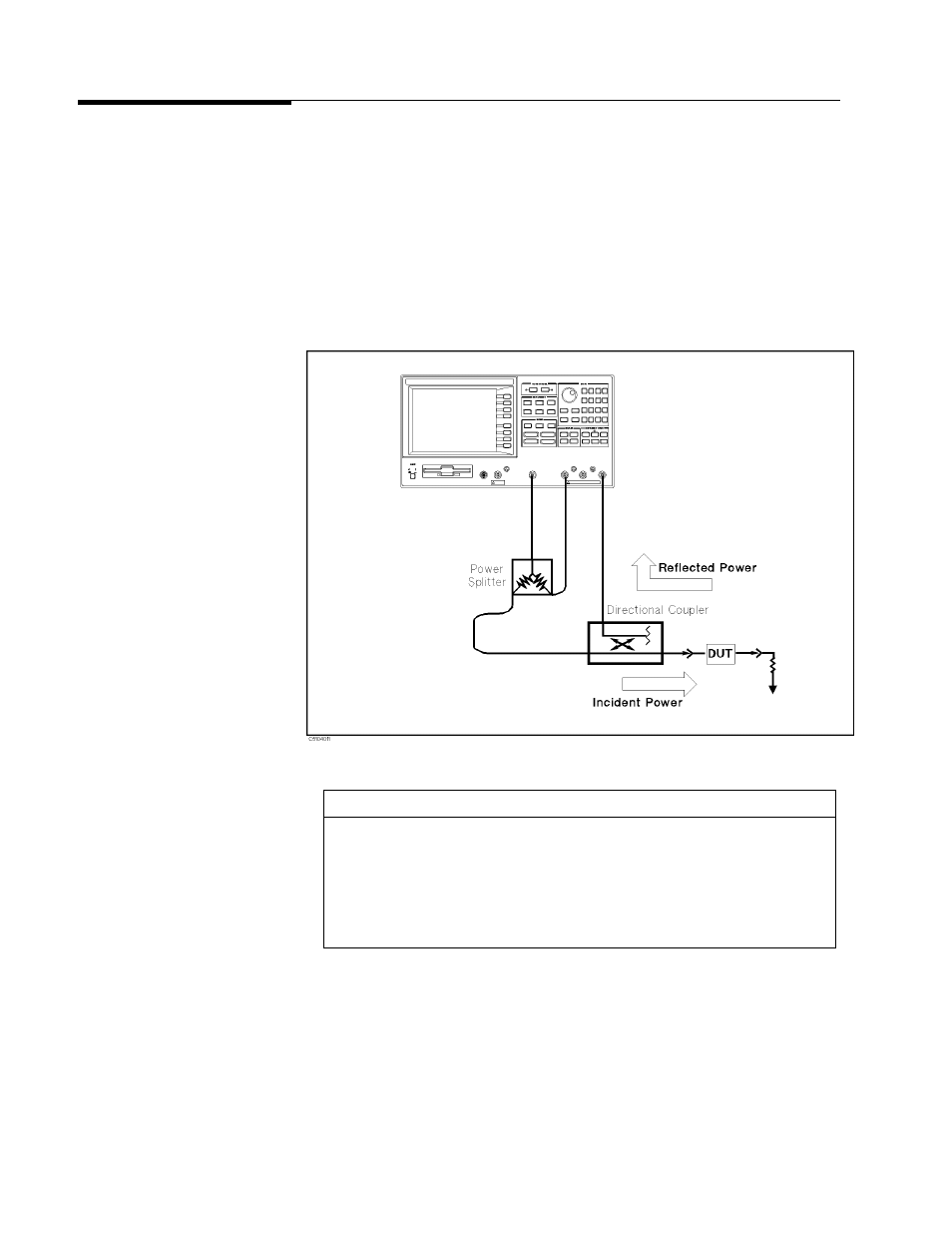
Re ection
Measurement
When
making
a
re ection
measurement,
the
analyzer
monitors
the
signal
going
to
the
DUT
and
uses
it
as
the
reference
.
It
compares
the
re ected
signal
from
the
DUT
to
the
reference
signal.
The
ratio
of
the
incident
and
re ected
signals
is
the
re ection
coecient
of
the
DUT
or
,
when
expressed
in
decibels
,
the
return
loss
.
Re ection
measurements
require
the
connection
of
a
directional
device
,
such
as
a
directional
coupler
,
to
separate
the
power
re ected
from
the
DUT
.
This
separation
is
necessary
so
that
it
can
be
measured
independently
of
the
incident
power
(see
the
following
gure).
Figure
5-11.
Re ection
Measurement
Multi-P
ort
T
est
Devices
When
the
device
has
more
than
one
port,
connect
high-quality
terminations
(loads)
to
all
unused
DUT
ports
to
terminate
them
into
their
characteristic
impedance
(usually
50
or
75
).
If
this
is
not
done
,
re ections
o
the
unused
ports
will
cause
measurement
errors
.
The
S-parameter
test
set
automatically
switches
the
termination
at
the
unused
port
for
each
S-parameter
measurement.
When
using
a
transmission/re ection
test
set,
terminate
the
unused
input
port
of
the
analyzer
with
a
high
quality
load.
The
signal
re ected
from
the
DUT
is
measured
as
a
ratio
with
the
incident
signal.
It
can
be
expressed
as
a
re ection
coecient,
a
return
loss
,
or
as
SWR.
These
measurements
are
mathematically
dened
as:
5-12
Network
Measurement
Examples
