HP XP Racks User Manual
Page 190
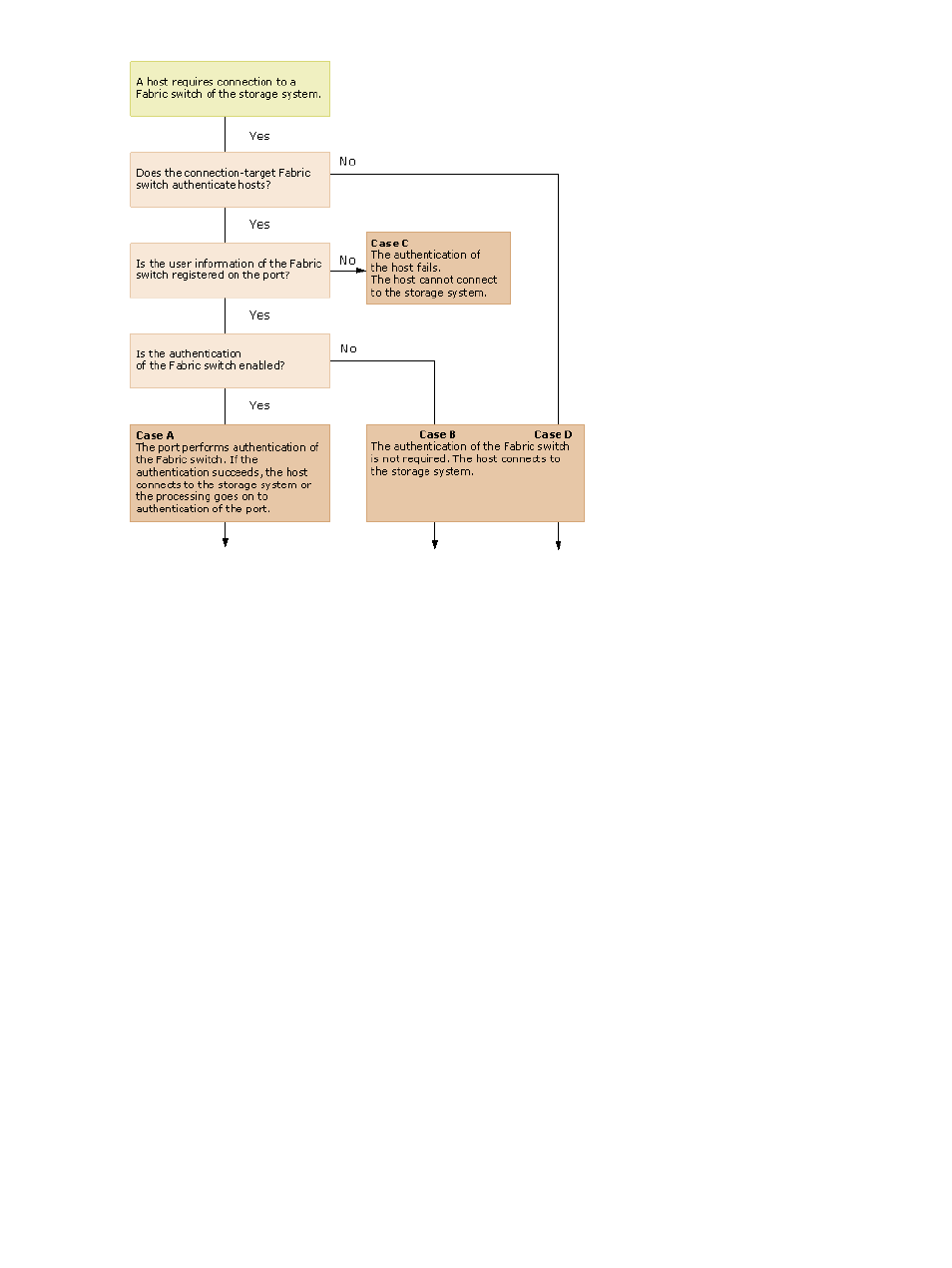
Authenticating fabric switches by ports (Cases A, B, and C)
•
If the user information of the fabric switch is registered on the port, and authentication of the
fabric switch is enabled (Case A)
Each port authenticates the fabric switch. If the authentication of the fabric switch ends
successfully, either of the following actions occurs:
◦
When the fabric switch is configured for mutual authentication, processing continues to
authentication of the port.
◦
When the fabric switch is not configured for mutual authentication, the fabric switch
connects to the storage system.
If the fabric switch of the port is not configured for authentication with CHAP, the authentication
fails and the fabric switch cannot connect to the storage system.
•
If the user information of the fabric switch is registered on the port, but authentication of the
fabric switch is disabled (Case B)
Each port does not perform authentication of the fabric switch. The fabric switch connects to
the storage system without authentication regardless of whether the fabric switch is configured
for authentication with CHAP.
•
If the user information of the fabric switch is not registered on the port (Case C)
Regardless of the setting on the fabric switch, the port performs authentication of the fabric
switch, but results in failure. The fabric switch cannot connect to the storage system.
Not authenticating fabric switches by ports (Case D)
The fabric switch connects to the storage system without authentication of the host regardless of
whether the fabric switch is configured for authentication with CHAP. In this case, though you need
not register the user information of the fabric switch on the port, you can register it.
190 Managing logical volumes
