Formatted pool capacity, Rebalancing the usage level among parity groups – HP XP Racks User Manual
Page 108
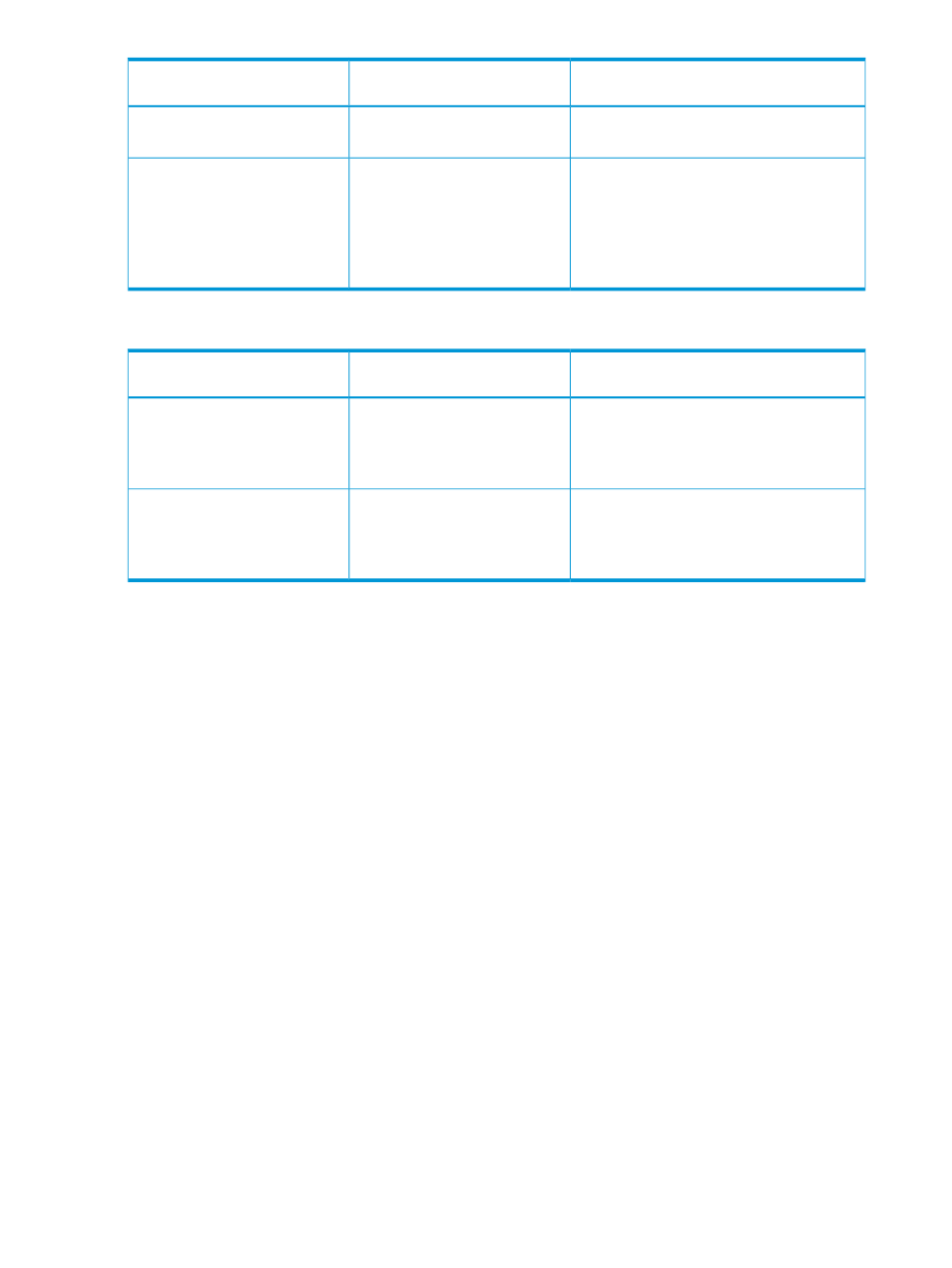
Description
Order in which pages are
allocated to tiers
Tier of deleted pool-VOLs
If there is no free space in Tier 1 and Tier 2,
pages are allocated to Tier 3.
If there is free space in Tier 3, pages are
allocated to Tier 3.
Tier 3, Tier 2, and Tier 1
Tier 3
If there is no free space in Tier 3, pages are
allocated to Tier 2.
If there is no free space in Tier 2 and Tier 3,
pages are allocated to Tier 1.
The following table describes page allocation in a 2-tier configuration.
Description
Order in which pages are
allocated to tiers
Tier of deleted pool-VOLs
If there is free space in Tier 1, pages are
allocated to Tier 1.
Tier 1 and Tier 2
Tier 1
If there is no free space in Tier 1, pages are
allocated to Tier 2.
If there is free space in Tier 2, pages are
allocated to Tier 2.
Tier 2 and Tier 1
Tier 2
If there is no free space in Tier 2, pages are
allocated to Tier 1.
Formatted pool capacity
The formatted pool capacity is the capacity of initialized free space in the pool, not the capacity
of all the free space in the pool. The free space of the pool is monitored by a storage system.
Space is formatted automatically if needed. You can confirm the formatted pool capacity in the
View Pool Management Status window (see
“View Pool Management Status window” (page 375)
).
Dependent on the load of the storage system, the format speed of the free space of the pool is
adjusted.
New pages are allocated, then initialized, during data write operations to the V-VOL. If a significant
number of new pages are allocated, initialization might be delayed as a result of conflicts between
data write and new page initialization processes. Such conflicts could occur, for example, when
you create a file system of new THP-VOLs from the host. You can initialize the free space of a pool
in advance to prevent delays in data write operations.
If you want to change the method of performing the function to format the free space of a pool,
contact HP Technical Support.
Rebalancing the usage level among parity groups
If multiple parity groups that contain LDEVs used as pool-VOLs exist, rebalancing can improve
biased usage rates in parity groups. Rebalancing is performed as if each parity group were a
single pool-VOL. After rebalancing, the usage rates of LDEVs in a parity group may not be balanced,
but the usage rate in the entire pool is balanced.
The usage level among parity groups is automatically rebalanced when these operations are in
progress:
•
Expanding pool capacity
•
Shrinking pool capacity
•
Reclaiming zero pages
108 Configuring thin provisioning
