Deployment modes, Deployment scenarios, Deployment modes deployment scenarios – HP Smart Update Manager (User Guide) User Manual
Page 11
Deployment modes
The following key terms are used when using HP SUM to deploy updates:
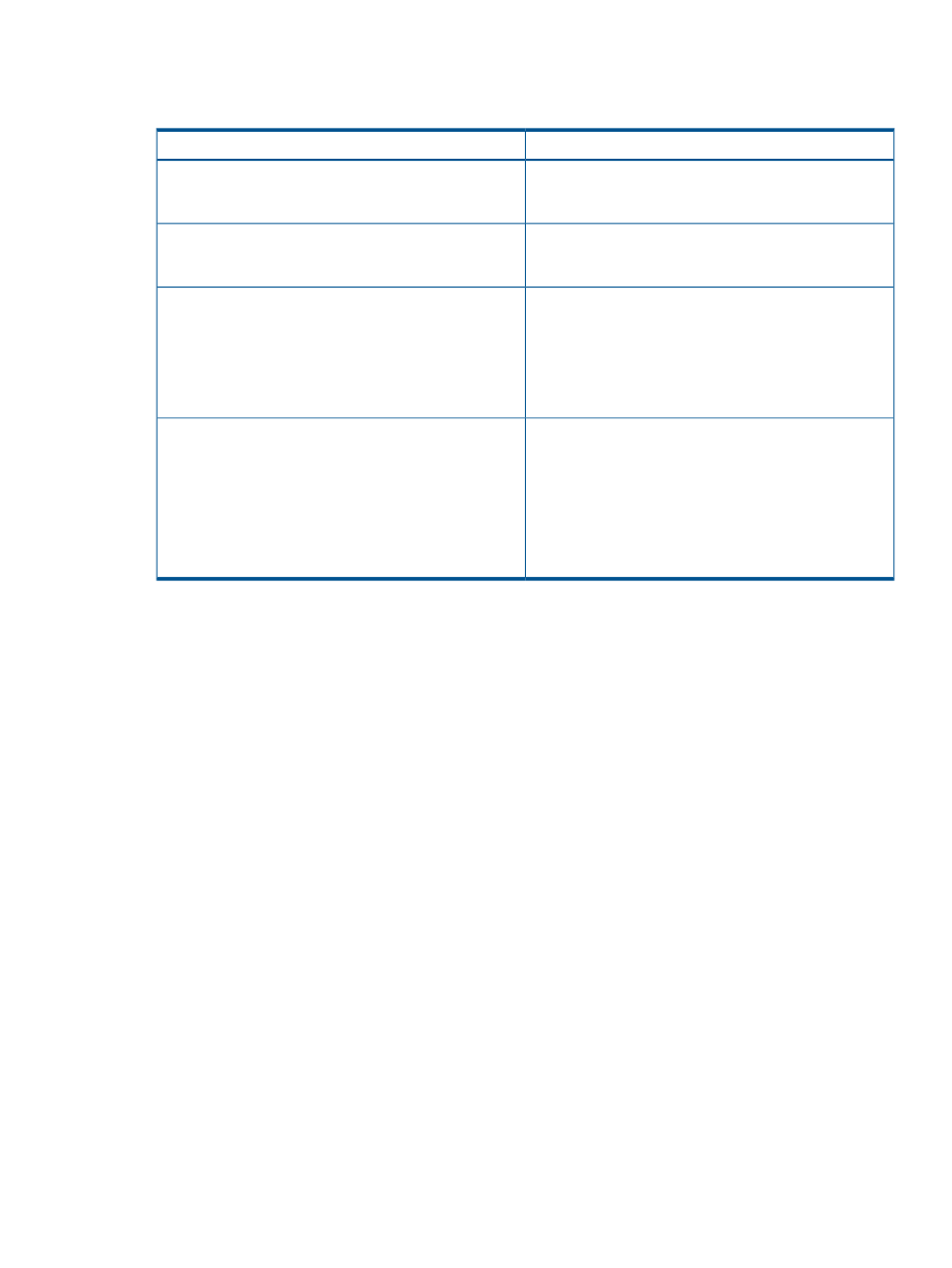
Definition
Term
The installation runs on the physical hardware you are
updating. For example, running a utility on a server to
update the server's system ROM.
Local
The installation runs on one system, but updates other
physical targets. For example, updating the OA firmware
across a network through a web browser.
Remote
The installation occurs while the host processor is running
in the normal server environment. For example, if the server
Online
runs Microsoft Windows Server 2008, the update occurs
under this environment. The update does not require you
to boot to a special environment to update the firmware.
You might need to reboot the target to activate the
firmware.
In offline mode, the HP SUM boots a small Linux kernel
and enables updates to occur on a single server.
Offline
•
Only updates the local system
•
Only uses a single repository
NOTE:
Some features of HP SUM that require the
regular local host operating systems are not supported
in offline mode.
These terms can be used in combination to designate the type of environment required for updates
to occur, such as local-online or remote-online.
Offline mode does not support the following functions:
•
Proxy Server details
•
Configure components
•
Filter repository contents
•
Use multiple repositories
•
Add repository
•
Edit repository
•
Remove repository
•
Configure components
•
Abort installation
•
Last updated field
•
Associated targets
Deployment scenarios
HP SUM deploys updates from a local host or one or more remote hosts. If the host running HP
SUM is using Windows, you can update Windows, Linux, VMware, or HP–UX targets. You can
also update remote HP ProLiant or HP Integrity iLO, OA, and VC targets.
Deploying HP SUM
11
