Using the spi interface, Spi interface — master mode, Spi interface — slave mode – Analog Devices ADuC812 User Manual
Page 27: Aduc812
REV. B
ADuC812
–27–
Table XII. SPICON SFR Bit Designations (continued)
Bit
Name
Description
1
SPR1
SPI Bit-Rate Select Bits.
0
SPR0
These bits select the SCLOCK rate (bit-rate) in Master Mode as follows:
SPR1
SPR0
Selected Bit Rate
0
0
f
OSC
/4
0
1
f
OSC
/8
1
0
f
OSC
/32
1
1
fosc/64
In SPI Slave Mode, i.e., SPIM = 0, the logic level on the external
SS pin (Pin #12)
can be read via the SPR0 bit.
NOTE
The CPOL and CPHA bits should both contain the same values for master and slave devices.
SPIDAT
SPI Data Register
Function
The SPIDAT SFR is written by the
user to transmit data over the SPI
interface or read by user code to
read data just received by the SPI
interface.
SFR Address
F7H
Power-On Default Value
00H
Bit Addressable
No
Using the SPI Interface
Depending on the configuration of the bits in the SPICON SFR
shown in Table XII, the ADuC812 SPI interface will transmit
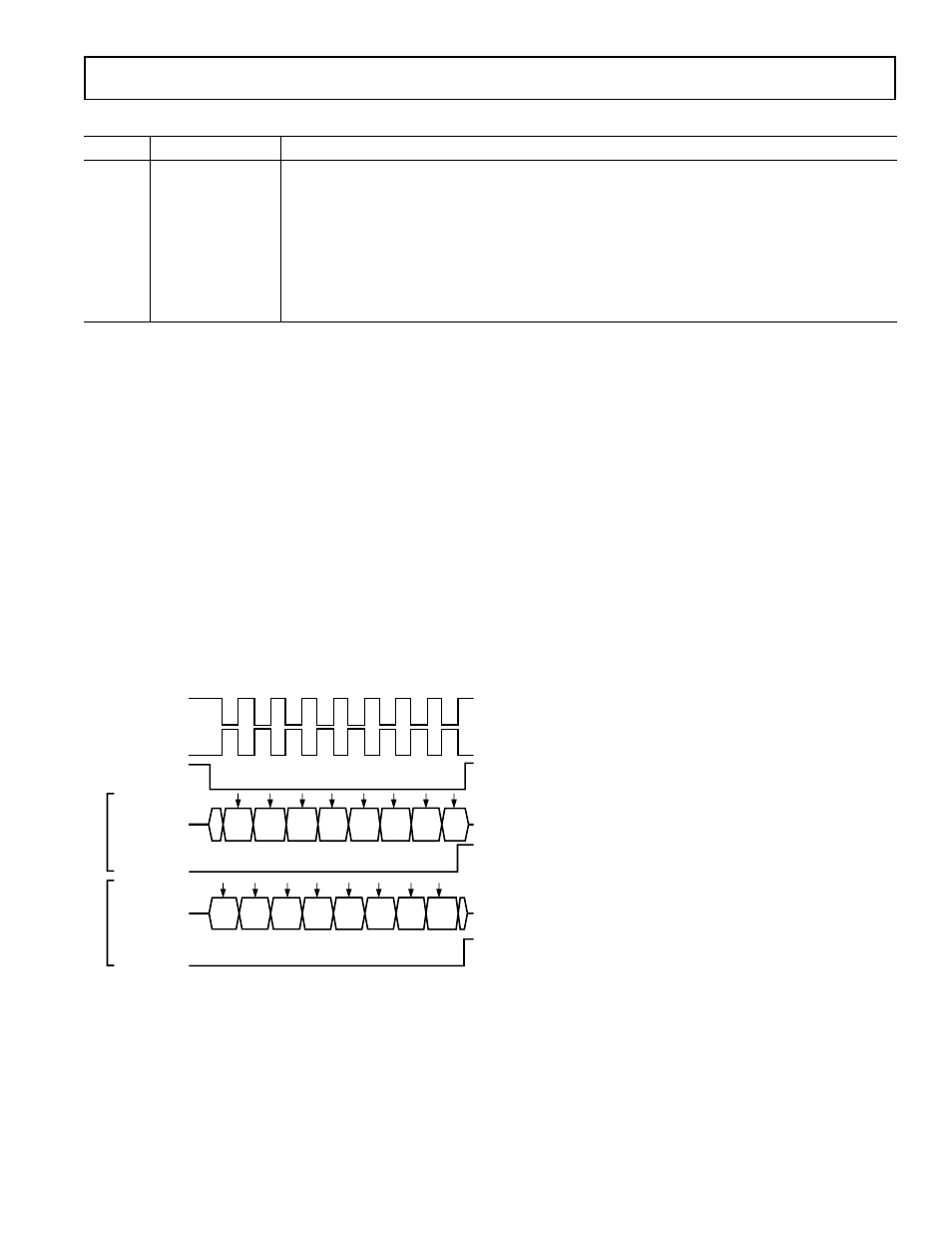
or receive data in a number of possible modes. Figure 26 shows
all possible ADuC812 SPI configurations and the timing rela-
tionships and synchronization between the signals involved.
Also shown in this figure is the SPI interrupt bit (ISPI) and how
it is triggered at the end of each byte-wide communication.
MSB
BIT 6
BIT 5
BIT 4
BIT 3
BIT 2
BIT 1 LSB
?
MSB
BIT 6
BIT 5
BIT 4 BIT 3
BIT 2 BIT 1
LSB ?
SCLOCK
(CPOL = 1)
SCLOCK
(CPOL = 0)
SS
SAMPLE INPUT
DATA OUTPUT
ISPI FLAG
SAMPLE INPUT
DATA OUTPUT
ISPI FLAG
(CPHA = 1)
(CPHA = 0)
Figure 25. SPI Timing, All Modes
SPI Interface—Master Mode
In master mode, the SCLOCK pin is always an output and gener-
ates a burst of eight clocks whenever user code writes to the
SPIDAT register. The SCLOCK bit rate is determined by
SPR0 and SPR1 in SPICON. It should also be noted that the
SS pin is not used in master mode. If the ADuC812 needs to
assert the
SS pin on an external slave device, a Port digital output
pin should be used.
In master mode a byte transmission or reception is initiated
by a write to SPIDAT. Eight clock periods are generated via the
SCLOCK pin and the SPIDAT byte being transmitted via MOSI.
With each SCLOCK period a data bit is also sampled via MISO.
After eight clocks, the transmitted byte will have been completely
transmitted and the input byte will be waiting in the input shift
register. The ISPI flag will be set automatically and an interrupt
will occur if enabled. The value in the shift register will be latched
into SPIDAT.
SPI Interface—Slave Mode
In slave mode the SCLOCK is an input. The
SS pin must
also be driven low externally during the byte communication.
Transmission is also initiated by a write to SPIDAT. In slave
mode, a data bit is transmitted via MISO and a data bit is received
via MOSI through each input SCLOCK period. After eight clocks,
the transmitted byte will have been completely transmitted and the
input byte will be waiting in the input shift register. The ISPI flag
will be set automatically and an interrupt will occur if enabled.
The value in the shift register will be latched into SPIDAT only
when the transmission/reception of a byte has been completed.
The end of transmission occurs after the eighth clock has been
received if CPHA = 1, or when
SS returns high if CPHA = 0.
