Dwyer MTL5045 User Manual
Page 28
6.24
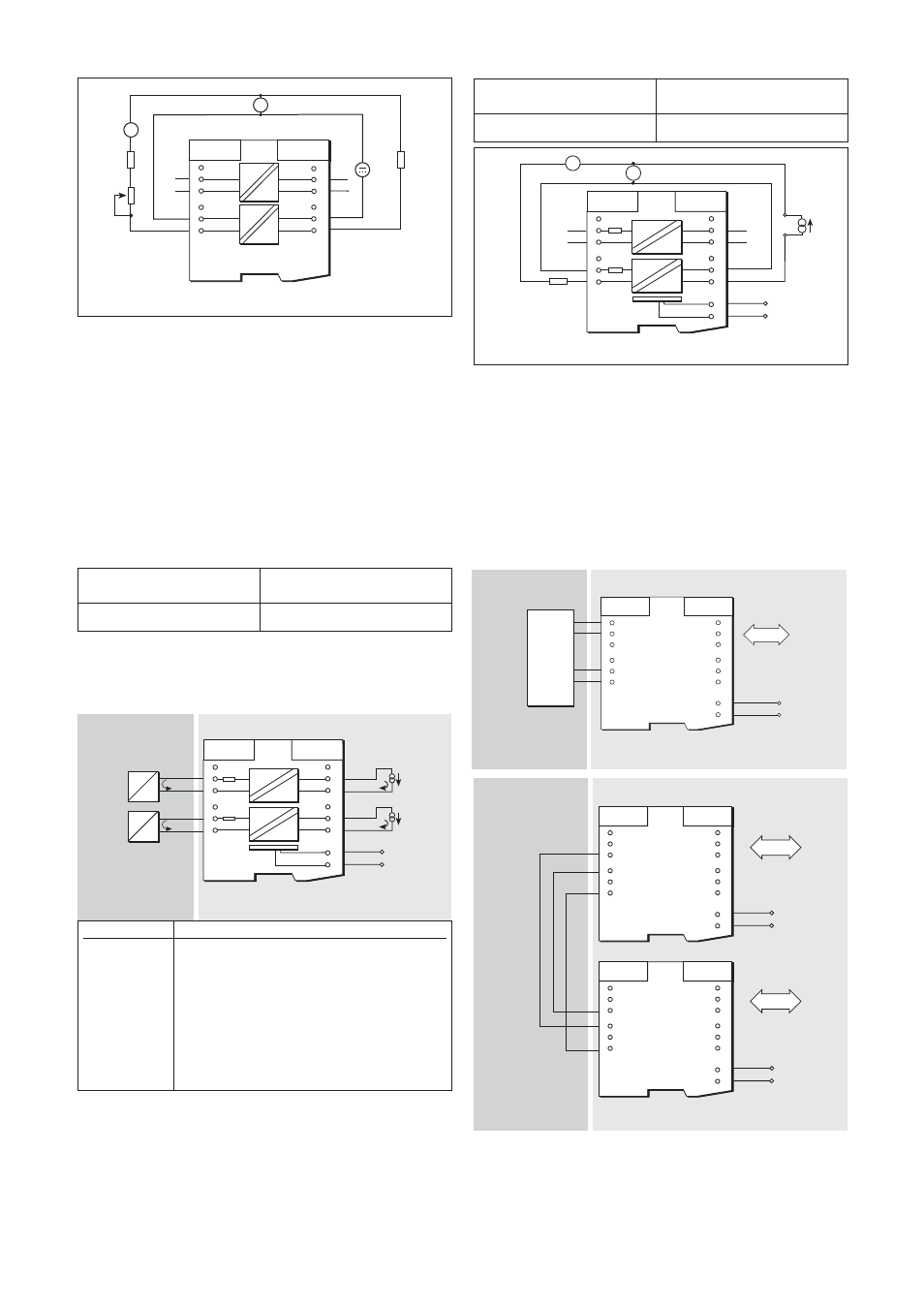
MTL5051 serial data comms isolator
The MTL5051provides either bi-directional serial data communications
from a computer system in a safe area to instrumentation in a hazardous
area or data communications across a hazardous area. It is used to
provide a fully floating dc supply for, and serial data communications to
MTL640 text displays and MTL650 series text and graphics terminals or
to other IS and non-IS instrumentation and keyboards.
6.24 .1
Wiring connections
See figures 6.52 and 6.53 and the terminal specifications in tables 6.11
and 6.12 for wiring connections. See also section 6.22.2 on hazardous-
area interfacing.
6.24.2
Hazardous-area interfacing
Displays/terminals: For details of interfacing with MTL640 and
MTL650 series displays/terminals (as an alternative to the MTL696
communications interface) see the appropriate product instruction
manual.
24
INM5000-6 Jul 2010
from either. For smart two–wire transmitters it provides bi-directional
communication signals superimposed on the 4/20mA signal. The
MTL5048 can also be used for isolating and passing a 4/20mA
signal from the safe area to the hazardous-area. The transmitter can
be interrogated either from the operator station or by a hand-held
communicator (HHC) for both the channels.The MTL5049 isolates and
passes on two 4 to 20mA signals from a controller located in a safe area
to two loads in a hazardous area.
6.22.1
Wiring connections
See figure 6.48 for wiring connections.
6.22.2
Testing
Make the safe- and hazardous-area connections shown in figure 6.49
and, using RV1 to vary the output current, carry out the following checks,
first on channel 1 and then on channel 2.
6.23
MTL5049 two-channel isolating driver
The MTL5049 isolates and passes on two 4 to 20mA signals from a
controller located in a safe area to two loads in a hazardous area.
6.23.1
Wiring connections
See figure 6.50 for wiring connections.
6.23.2
Testing
Make the safe- and hazardous-area connections shown in figure 6.51
and, using the current source to vary the output current, carry out the
following checks, first on channel 1 and then on channel 2.
6
5
4
3
2
1
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Vs
Vs+
20 to 35V dc
RS232, TTL
or RS422
Rx
Tx
5V or 12V supply
Common
Tx
Rx
Supply
Common
Figure 6.52: MTL5051 wiring diagram (to a hazardous area)
Hazardous area
Safe area
Output
Current
current
reading (A1)
4 to 20mA
<±20
μA
6
5
4
3
2
1
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
I
I
I
I
Vs
Vs+
20 to 35V dc
A1
A2
+
Current
source
470W
+
+
+
Ch1
Ch2
Ch1
Ch2
Figure 6.51: Test circuit for MTL5049
RS232, or
RS422
RS232, or
RS422
6
5
4
3
2
1
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
6
5
4
3
2
1
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Vs
Vs+
20 to 35V dc
Vs
Vs+
20 to 35V dc
Safe area
Hazardous area
Figure 6.53: MTL5051 wiring diagram (across a hazardous area)
Output
Current
current (A2)
reading (A1)
4 to 20mA
<±80
μA
6
5
4
3
2
1
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
I
I
I
I
P
I
4/20mA
+
P
I
4/20mA
+
+
4/20mA
+
4/20mA
Vs
Vs+
20 to 35V dc
Ch 1
Ch 2
Ch 1
Ch 2
Figure 6.50: MTL5049 wiring diagram and connections
Hazardous area
Safe area
Terminal
Function
1
Output –ve (Ch 1)
2
Output +ve (Ch 1)
4
Output -ve (Ch 2)
5
Output +ve (Ch 2)
8
Input -ve (Ch 2)
9
Input +ve (Ch 2)
11
Input –ve (Ch 1)
12
Input +ve (Ch 1)
13
Supply –ve
14
Supply +ve
6
5
4
3
2
1
7
8
9
10
11
12
I
I
I
I
Ch 2
+
+
Ch 2
24V
+
A1
A2
Ch 1
180W
2k
RV1
W
+
+
240W
Figure 6.49: Test circuit for MTL5048
