Dwyer MTL5045 User Manual
Page 27
6.20.2
Testing
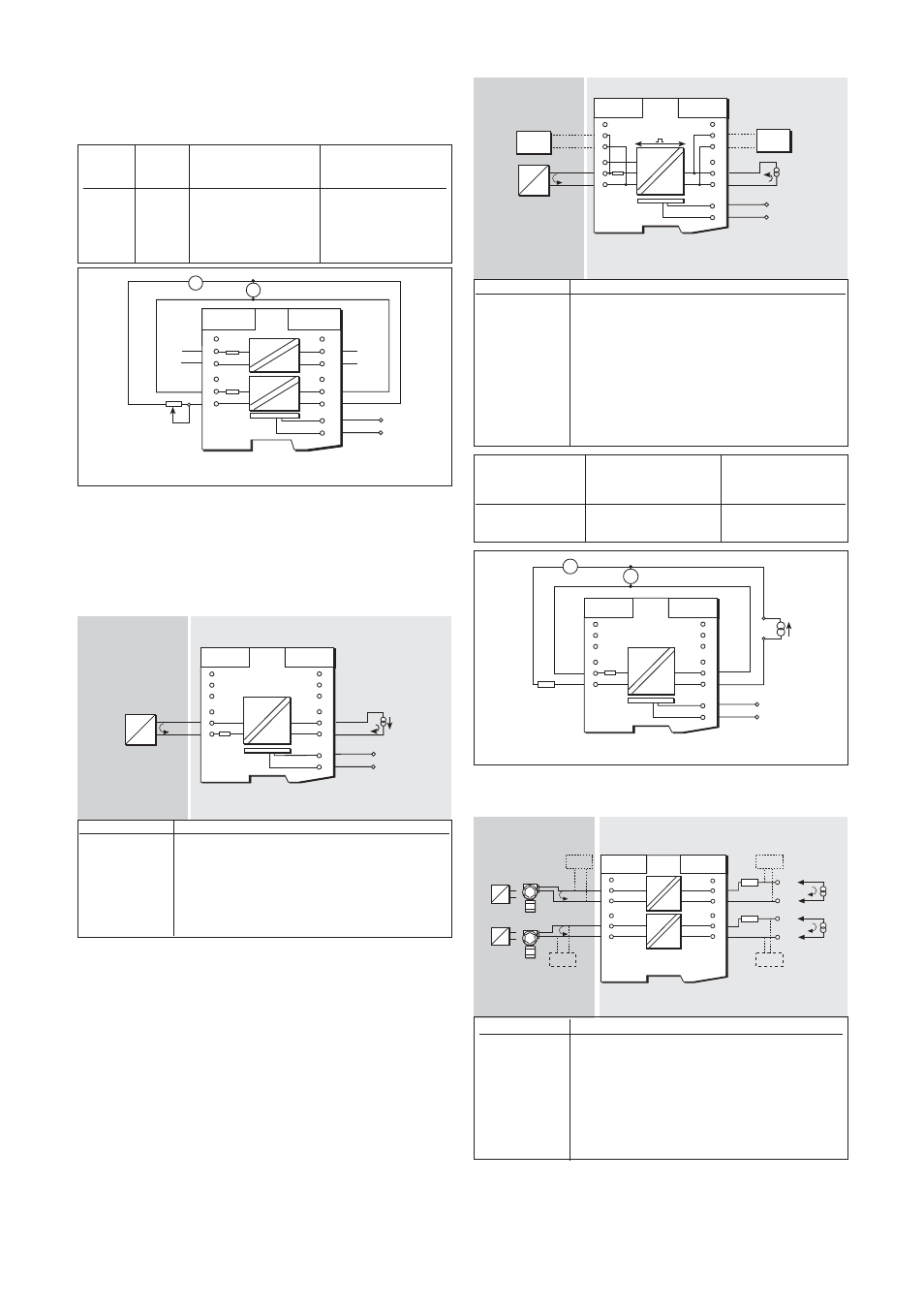
Make the safe- and hazardous-area connections shown in figure 6.44
and, using RV1 to vary the output current, carry out the following checks,
first on channel 1 and then on channel 2:
6.21
MTL5045/46 isolating drivers
The MTL5045/46 isolate and pass on a 4 to 20mA signal from a
controller located in a safe area to a load in a hazardous area. The
MTL5046 also permits bi-directional transmission of 'smart' digital
communication signals superimposed on the 4 to 20mA signal, and is
provided with line fault detection (LFD).
6.21.1
Wiring connections
See figures 6.45 and 6.46 for wiring connections (MTL5045 and
MTL5046 respectively).
6.21.2
Line fault detection (LFD) (MTL5046 only)
(See section 3.1.4 for definition of a line fault)
Line fault detection is signalled by an impedance change in the safe-area
loop. When a line fault occurs, the impedance between terminals 11
and 12 is >100k
Ω.
6.22.1
Testing
Make the safe and hazardous-area connections shown in figure 6.47
and, using the current source to vary the output current, carry out the
checks shown in the table above figure 6.47.
6.22
MTL5048 analogue input/output, loop-
powered isolator
The MTL5048 is a dual channel analogue input/output loop-powered
isolator being powered from the safe area side. The same current
flows in both hazardous and safe-area circuits and can be controlled
23
INM5000-6 Jul 2010
7
8
9
6
5
4
3
2
1
13
14
10
11
12
I
I
I
I
+
+
Ch 1
10kW lin
RV1
A1
A2
Ch 1
Ch 2
Ch 2
Vs
Vs+
20 to 35V dc
+
+
Figure 6.44: Test circuit for MTL5044
6
5
4
3
2
1
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Vs
Vs+
20 to 35V dc
+
4/20mA
P
I
4/20mA
+
I
I
Hazardous area
Safe area
Figure 6.45: MTL5045 wiring diagram and connections
Hazardous area
Safe area
6
5
4
3
2
1
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Vs
Vs+
20 to 35V dc
+
4/20mA
HHC*
HHC*
* Hand-held communicator
P
I
4/20mA
+
I
I
Hazardous area
Safe area
Figure 6.46: MTL5046 wiring diagram and connections
Output
Current
Voltage channel 1
Voltage channel 2
current
reading
(terminal 2 with
(terminal 5 with
(A2)
(A1)
respect to terminal 1)
respect to terminal 4)
4 to 20mA
<±20µA
–
–
20ma
–
>16.5V
–
20ma
–
–
>16.5V
Output
Current reading
Current reading
current
(A1)
(A1)
(A2)
(MTL5045)
(MTL5046)
4 to 20mA
<±20µA
<±10µA
6
5
4
3
2
1
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
I
I
Vs
Vs+
20 to 35V dc
+
A1
A2
+
Current
source
680W
+
Figure 6.47: Test circuit for MTL5045/46
Terminal
Function
1
Output –ve
2
Output +ve
4
Optional HHC -ve
5
Optional HHC +ve
8
Optional HHC -ve
9
Optional HHC +ve
11
Input –ve
12
Input +ve
13
Supply –ve
14
Supply +ve
6
5
4
3
2
1
7
8
9
10
11
12
I
I
I
I
Ch 2
+
Ch 1
+
22
35V
dc
Ch 2
Ch 1
+
4/20mA
4/20mA
HHC
HHC
4/20
+
HHC
HHC
P
I
P
I
4/20
22
35V
dc
Figure 6.48: MTL5048 wiring diagram and connections
Terminal
Function
1
Tx– or input connection –ve (Ch 1)
2
Tx+ or input connection +ve (Ch 1)
4
Tx– or input connection –ve (Ch 2)
5
Tx+ or input connection +ve (Ch 2)
8
Output –ve or input +ve (Ch 2)
9
Output +ve or Tx supply +ve (Ch 2)
11
Output –ve or input +ve (Ch 1)
12
Output +ve or Tx supply +ve (Ch 1)
Terminal
Function
1
Output –ve
2
Output +ve
11
Input –ve
12
Input +ve
13
Supply –ve
14
Supply +ve
