Dwyer MTL5045 User Manual
Page 24
20
INM5000-6 Jul 2010
6.15.2 Testing
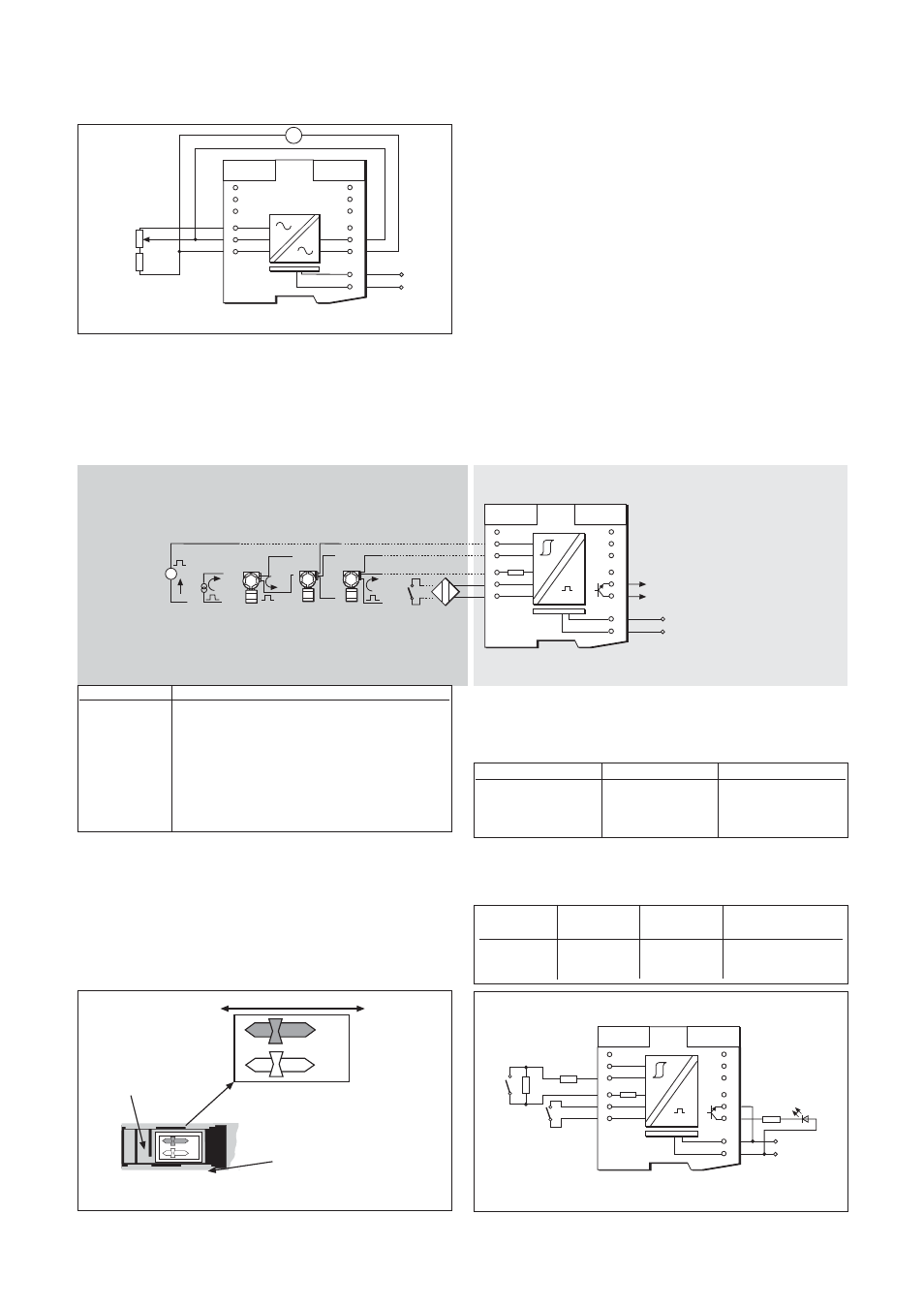
Make the safe- and hazardous-area connection shown in figure 6.31.
Measure the voltage on terminal 3 with respect to terminal 1; this should
be >19V. Vary the potentiometer setting and check that the reading on
voltmeter V varies by no more than ±100mV.
6.16
MTL5032 pulse isolator
The MTL5032 isolates pulses from a switch, proximity detector, current
pulse transmitter or voltage pulse transmitter located in the hazardous area.
6.16.1. Wiring connections
See figure 6.32 for wiring connections.
*Note: When connected to a circuit which requires an external voltage
or current input, the output may be connected in parallel with that input
in conjunction with a pull-up resistor wired to terminal 12 and connected
to an appropriate voltage source. The zero volt of the same voltage
source should be referenced back to terminal 11. (Maximum current is
50mA; e.g. resistor value of 510
Ω
at 24V.)
6.16.2 Voltage pulse settings
The threshold voltage for the voltage pulse input is set by two switches
located on the base of the unit. Referring to figure 6.33, these are set
as follows:
6.16.3
Testing
Make the safe- and hazardous-area connections shown in figure 6.34
and carry out the following checks:
O
N
2
1
OFF
ON
SW1
SW2
Label face
Base of unit
Figure 6.33: Pulse voltage selection switches
Threshold
SW1
SW2
3V
On
On
6V
On
Off
12V
Off
Off
Vs
Vs+
20 to 35V dc
V
100W
1kW
V
T
Sig
0V
6
5
4
3
2
1
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Figure 6.31: Test circuit for MTL5031
V
Vs
Vs+
20 to 35V dc
Voltage
pulse
Current
pulse
2-wire
current
pulse
3-wire
current
pulse
3-wire
voltage
pulse
+
4/20
mA
4/20
mA
4/20
mA
6
5
4
3
2
1
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
+
+
+
+
Figure 6.32: MTL5032 wiring diagram and connections
Hazardous Area
Safe Area
Vs
Vs+
20 to 35V dc
+
SW1
2.2kW
2.2kW
SW2
4.7kW
TEST
6
5
4
3
2
1
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
+
+
Figure 6.34: Test circuit for MTL5032
Status
Test LED
SW1
SW2
LED
(terminal 14)
Closed
Open
On
On
Open
Closed
On
On
Terminal
Function
1
Common -ve
2
Proximity detector +ve
3
Current +ve
4
Transmitter +ve
5
Voltage +ve
11
Output –ve
12
Output +ve
13
Supply –ve
14
Supply +ve
