Badger Meter Model IOG User Manual
Page 21
NOTE:
N
If the number of linear points is set to 1 the ER-500 assumes the user is entering the maximum frequency and
coefficient Further the meter assumes that the implied first point is at a frequency of 0 (zero) Hz and a coefficient
of 0 (zero)
Frequency
Press the ENTER button once and the first linear point’s frequency input Freq#1 begins to flash Enter the frequency for
the first linear point using
▲
arrow button to increment the numerical values and the ► arrow button to change the
position of the number being entered When the frequency value input is complete, press the ENTER button once again
to change to the coefficient value Coef#1 for the first linear point
Coefficient
The coefficient is the value applied to the nominal K factor to correct it to the exact K factor for that point The coefficient
is calculated by dividing the actual K factor for that point by the average (Nominal) K factor for the flow meter
Linear Coefficient =
Actual K factor
Nominal K factor
Linear coefficient calculation
At the coefficient Coef#1 prompt, enter the coefficient that corresponds to the frequency value previously entered Press
the ENTER button once to move to the scaling point
Continue entering pairs of frequency and coefficient points until all data has been entered Press the ENTER button to
move to the next parameter
NOTE:
N
The frequency values must be entered in ascending order If a lower frequency value is entered after a higher value
the ER-500 flashes Limit followed by the minimum frequency value acceptable to the display
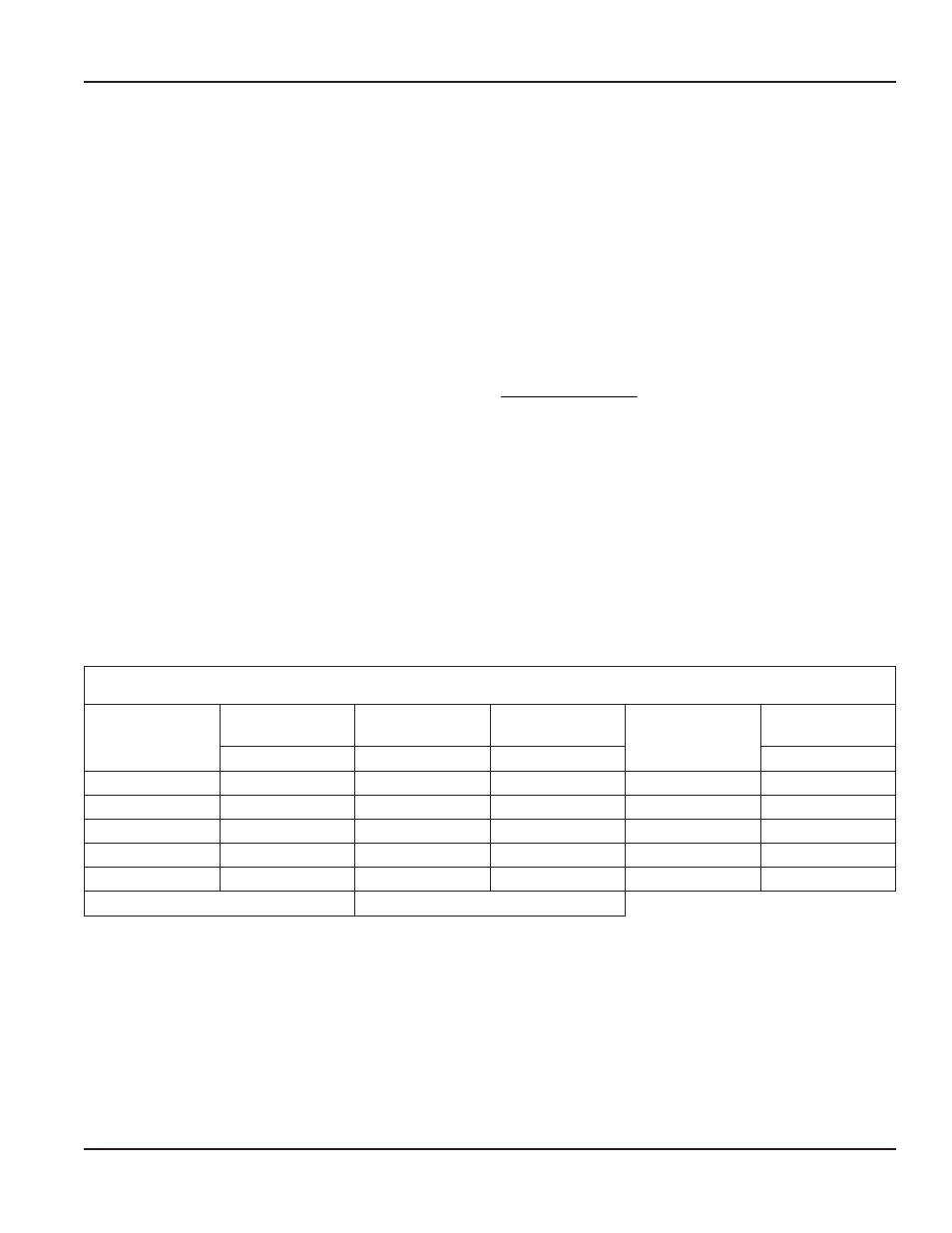
Example:
The following is actual data taken from a 1 inch turbine flow sensor calibrated with water
Unit Under Test (UUT) Calibration Data Table In GPM
Actual
GPM
UUT
Frequency
UUT Actual
K factor
(Hz x 60)
Nominal K
Linear
Coefficient
Raw Error
Hz
Counts/Gallon
GPM
% Rate
50 02
755 900
906 72
49 72
1 0060
0 59
28 12
426 000
908 96
28 02
1 0035
0 35
15 80
240 500
913 29
15 82
0 9987
-0 13
8 88
135 800
917 57
8 93
0 9941
-0 59
4 95
75 100
910 30
4 94
1 0020
0 20
Nominal K (NK)
912 144
Table 3: Sample linearization data
In this example the linear coefficient has already been calculated by the calibration program so all that is required is to enter 5
into the number of linear points Lin Pts parameter and then enter, in order, the five frequency, linear coefficient data pairs
User Manual
Page 21
August 2013
