Commissioning / operation, 1 configuration of cyclic data transfer, 2 cyclic data – KROHNE MFC 400 Profibus User Manual
Page 24: 1 input data, Float format
4
COMMISSIONING / OPERATION
24
MFC 400
www.krohne.com
06/2013 - 4002835301 - AD MFC 400 PROFIBUS R01 en
4.1 Configuration of cyclic data transfer
During network configuration the user has to select which function block input/output data shall
be transferred between the PROFIBUS master and the PROFIBUS slave. Network configuration
will be done using one of the GSD files described before. During configuration a functional
module - describing a valid configuration of a single function block and defined in the GSD file
selected - has to be assigned to each slot of the device in order to select which data has to be
transferred for the corresponding function blocks.
The cyclic layout (have a look at chapter "Ident. Number selector") shows which type of
functional module is valid for each slot.
The order of transmission of the data always remains the same. If an "Empty Module" is
assigned to a slot no data will be sent for the corresponding function block and all function block
data following this empty module will move up one position.
4.2 Cyclic data
In a PROFIBUS network cyclic data is described from the point of view of the master. Therefore
input data is transferred from the slave to the master while output data is transferred from the
master to the slave.
4.2.1 Input data
Input data is transferred from the PROFIBUS device to the master for the measuring value and
the totalizer values. The format is the same for both. If input data transfer is configured 5 bytes
are transferred for the corresponding slot:
• 4 byte float value (Float Format according to IEEE Standard 754 Short Real Number)
• 1 byte status value
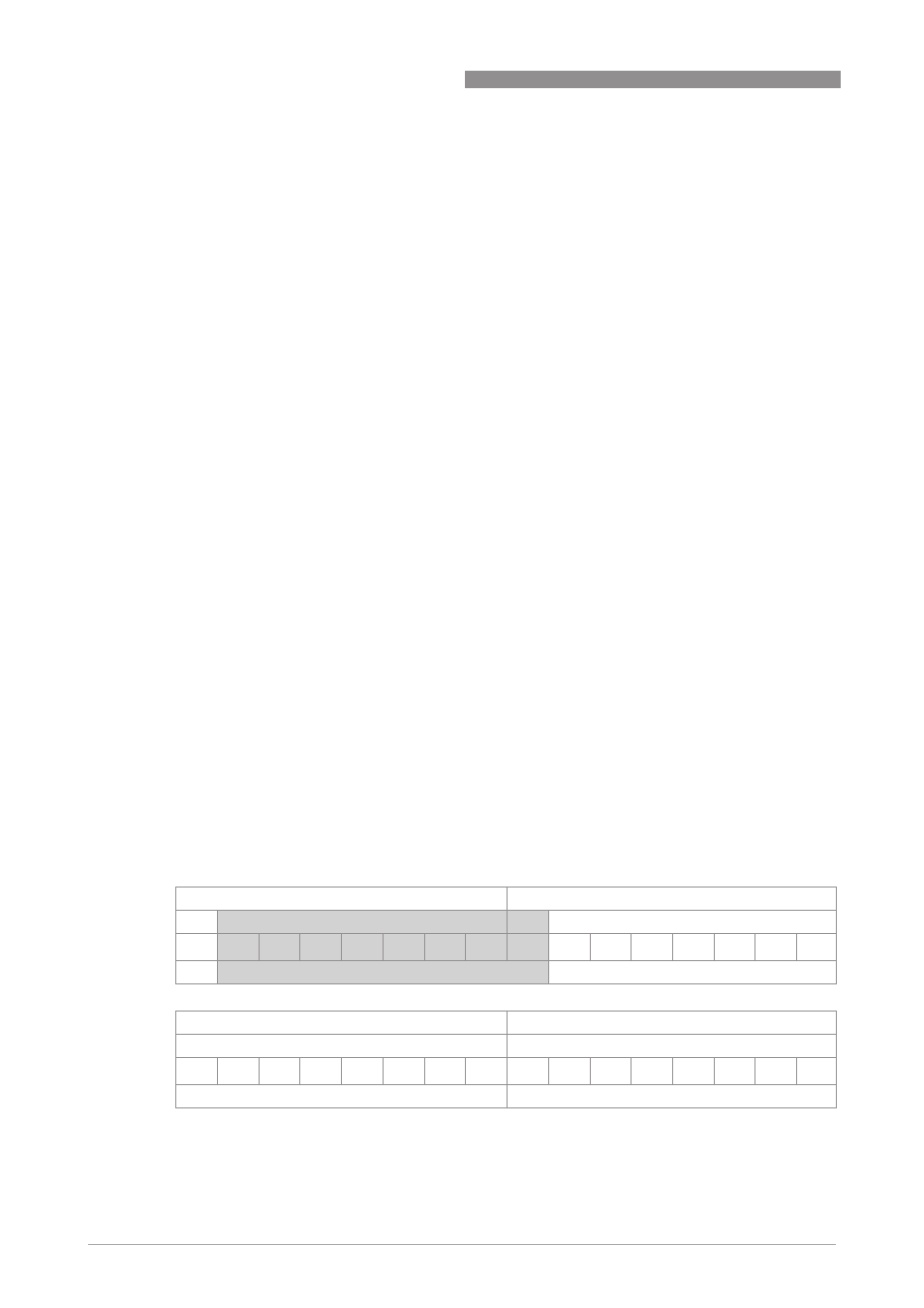
Float value
Float value
Float value
Float value
The following example describes the format of the float value according to IEEE Standard 754
Short Real Number:
Float format
Example (binary): 40 F0 00 00 (hex) = 0100 0000 1111 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
Byte n
Byte n+1
Bit7
Bit6
Bit7
Bit6
VZ
2
7
2
6
2
5
2
4
2
3
2
2
2
1
2
0
2
-1
2
-2
2
-3
2
-4
2
-5
2
-6
2
-7
Exponent
Mantissa
Byte n+2
Byte n+3
Bit7
Bit7
2
-8
2
-9
2
-10
2
-11
2
-12
2
-13
2
-14
2
-15
2
-16
2
-17
2
-18
2
-19
2
-20
2
-21
2
-22
2
-23
Mantissa
Mantissa
