Ipdact module - introduction, Client, Alarm receiver center – Fire-Lite IPDACT Installation Manual User Manual
Page 5
IPDACT Module - Introduction
I-2
Doc.Dm373-I
Rev.2.0
The communication protocol varies depending on the manufacturers who
usually tend to use their own solutions. The IPDACT supports Contact-ID
protocol.
The CP is placed as the first connection element to the PSTN so that it can
prioritize the customer’s telephone line.
Public Telephony
Switched Network
Alarm
Control Panel
Client
Alarm Receiver
Sur-Gard/Radionics
Automation SW
IBS/ MAS/ MicroKey
Fax
Alarm Receiver Center
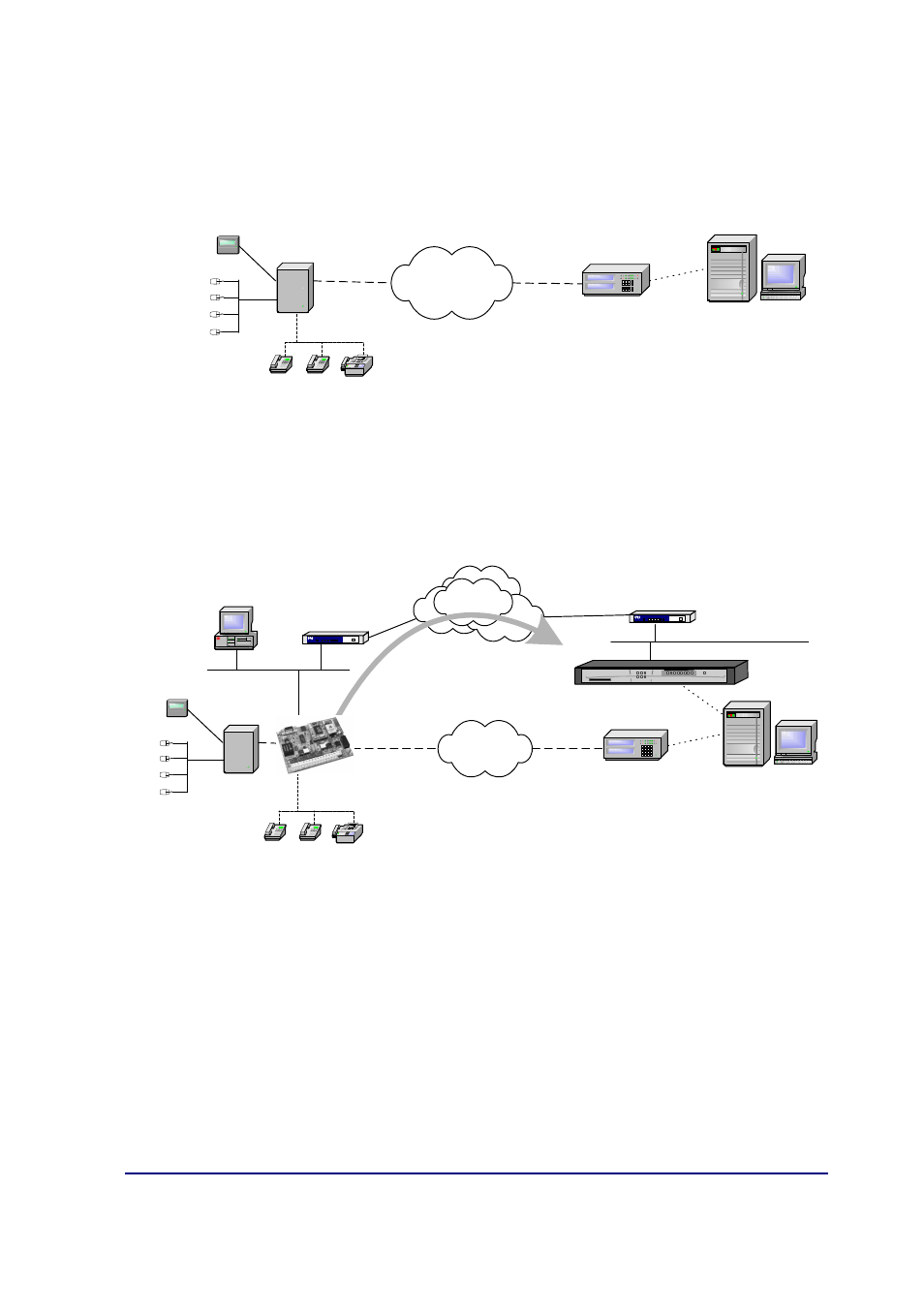
Figure 1. Traditional security scenario
Within the general user scenario, the IPDACT device is located in the client
area, next to the control panel, intercepting the telephone line. This is
displayed in Figure 2. The arrow in the figure demonstrates the preferred
path to send alarms from the CP; here the telephone line is used as a backup
in case there is a communication malfunction in the IP network.
Public Telephony
Switched
Network
Alarm
Control Panel
Client
hecho por M.A. Berrojo
Teldat
C
Intenet
router
router
Eth 10 Mbps
Eth 10 Mbps
Alarm Receiver
Sur-Gard/Radionics
Visor Alarm
Automation SW
IBS/ MAS/ MicroKey
hecho por M.A. Berrojo
Teldat
C
Fax
M I P
Alarm Receiver Center
hecho por M.A. Berrojo
hecho por M.A. Berrojo
@
T e l d a t
Visor
Alarm
Figure 2. Teldat VisorALARM and IPDACT operating scenario
From firmware release 2.2 onwards, the IPDACT has a new functionality
incorporated giving rise to a third possible scenario: network backup. In the
previous scenario, where communication fails between the device and the
ARC, the IPDACT hands over the communications to the control panel. With
the new functionality, the IPDACT tries to open communications with a second
device, the backup VisorALARM. Only in cases where there are problems
with this second device does the control panel take over. Meanwhile, even in
this state, the IPDACT continues to try and communicate with the ARC until
one of the VisorALARMs responds.
