Configuring an extended ipv6 acl, Figure 7-5, Acl configuration - standard ipv6 – LevelOne GTL-2690 User Manual
Page 169
Access Control Lists
7-8
7
• Source Prefix-Length – A decimal value indicating how many contiguous bits
(from the left) of the address comprise the prefix (i.e., the network portion of the
address).
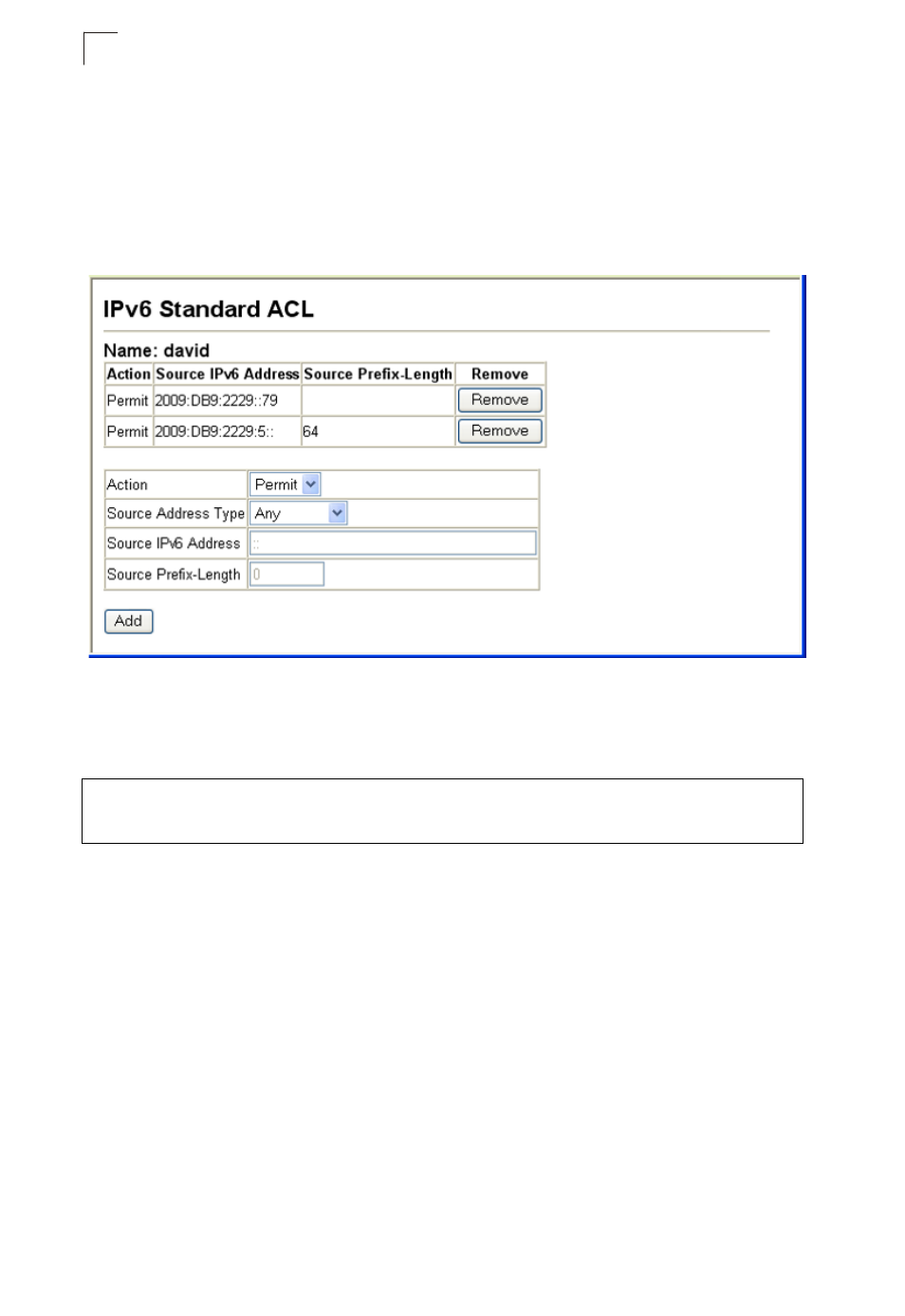
Web – Specify the action (i.e., Permit or Deny). Select the address type (Any, Host,
or IPv6-prefix). If you select “Host,” enter a specific address. If you select
“IPv6-prefix,” enter a subnet address and the prefix length. Then click Add.
Figure 7-5 ACL Configuration - Standard IPv6
CLI – This example configures one permit rule for the specific address
2009:DB9:2229::79 and another rule for addresses with the network prefix
2009:DB9:2229:5::/64.
Configuring an Extended IPv6 ACL
Command Attributes
• Action – An ACL can contain any combination of permit or deny rules.
• Destination Address Type – Specifies the destination IP address. Use “Any” to
include all possible addresses, or “IPv6-prefix” to specify a range of addresses.
(Options: Any, IPv6-prefix; Default: Any)
• Destination IP Address – The address must be formatted according to RFC 2373
“IPv6 Addressing Architecture,” using 8 colon-separated 16-bit hexadecimal
values. One double colon may be used in the address to indicate the appropriate
number of zeros required to fill the undefined fields. (The switch only checks the
first 64 bits of the destination address.)
Console(config-std-ipv6-acl)#permit host 2009:DB9:2229::79
Console(config-std-ipv6-acl)#permit 2009:DB9:2229:5::/64
Console(config-std-ipv6-acl)#
