Experiment 9: michelson interferometer, Equipment needed, Introduction – PASCO WA-9316A Complete Microwave Optics System User Manual
Page 25: Purpose, Procedure, Equipment needed: introduction
013-13906B
Experiment 9: Michelson Interferometer
25
Experiment 9: Michelson Interferometer
Equipment Needed:
Introduction
Like the Fabry-Perot interferometer, the Michelson interferometer splits a single wave, then brings the constituent waves back
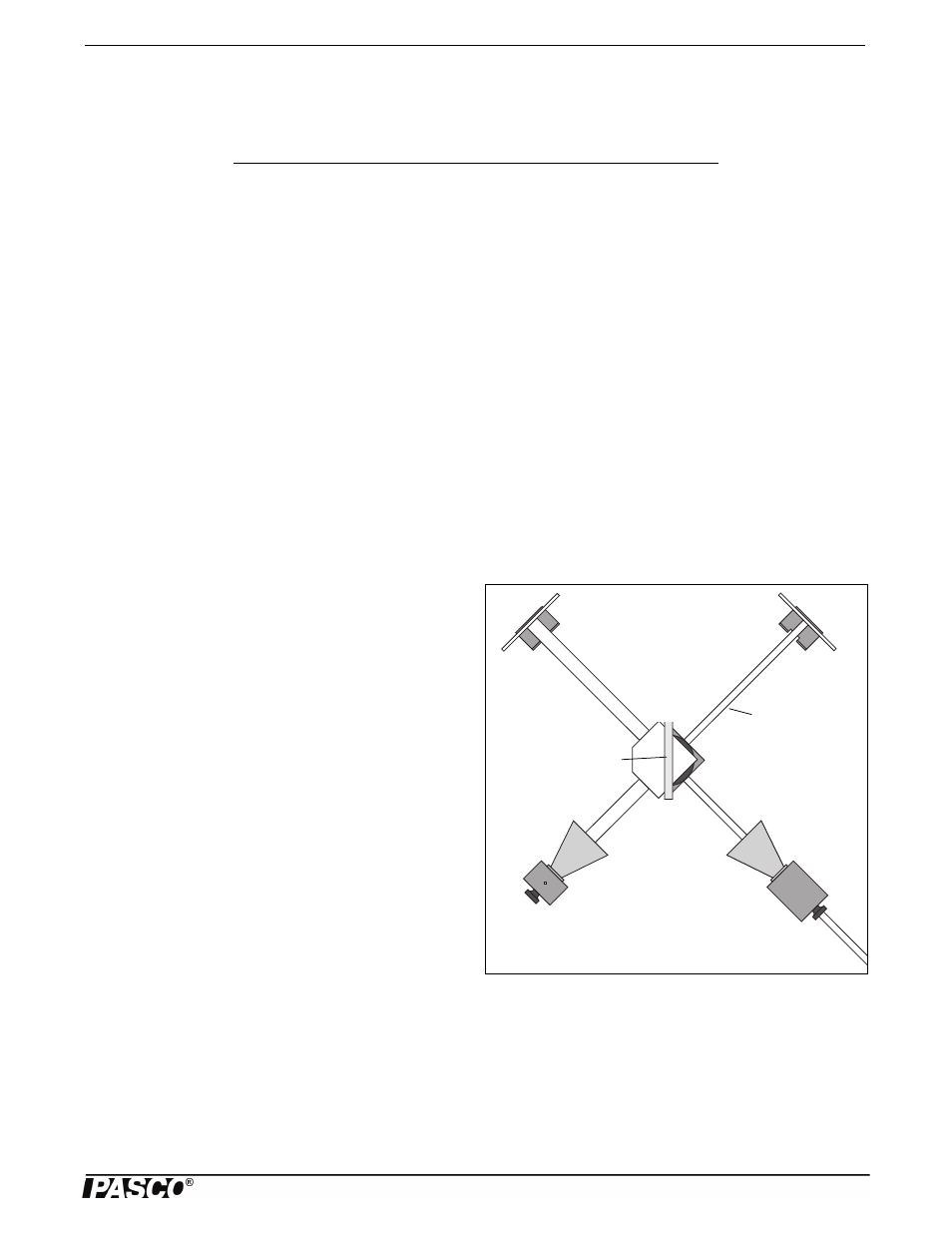
together so that they superpose, forming an interference pattern. Figure 9.1 shows the setup for the Michelson interferometer.
A and B are Reflectors and C is a Partial Reflector. Microwaves travel from the Transmitter to the Receiver over two different
paths. In one path, the wave passes directly through C, reflects back to C from A, and then is reflected from C into the
Receiver. In the other path, the wave reflects from C into B, and then back through C into the Receiver.
If the two waves are in phase when they reach the Receiver, a maximum signal is detected. By moving one of the Reflectors,
the path length of one of the waves changes, thereby changing its phase at the Receiver so a maxima is no longer detected.
Since each wave passes twice between a Reflector and the Partial Reflector, moving a Reflector a distance
/2 will cause a
complete 360-degree change in the phase of one wave at the Receiver. This causes the meter reading to pass through a mini-
mum and return to a maximum.
Purpose
In this experiment you will investigate the Michelson Interferometer.
Procedure
Figure 9.1: Equipment Setup
Partial
Reflector
A
B
C
Goniometer
1. Arrange the equipment as shown in Figure 9.1. Plug in the
equipment and adjust the Receiver for an easily readable
signal.
2. Slide Reflector A along the Goniometer arm and observe
the relative maxima and minima of the meter deflections.
3. Set Reflector A to a position which produces a maximum
meter reading. Record, x
1
, the position of the Reflector on
the Goniometer arm.
•
x
1
= _________________________.
4. While watching the meter, slowly move Reflector A away
from the Partial Reflector. Move the Reflector until the
meter reading has passed through at least 10 minima and
returned to a maximum. Record the number of minima
that were traversed. Also record x
2
, the new position of
Reflector A on the Goniometer arm.
•
Minima traversed = _________________________.
•
x
2
= _________________________.
5. Use your data to calculate
, the wavelength of the microwave radiation.
•
= _________________________.
6. Repeat your measurements, beginning with a different position for Reflector A.
•
x
1
= _________________________.
Item
Item
Transmitter
Goniometer
Receiver
Component Holders (2)
Partial Reflectors (1)
Reflectors (2)
Fixed Arm Assembly
Rotating Component Holder
