Teacher's guide, Exp 1: introduction to ray optics, Exp 2: the law of reflection – PASCO OS-8500 INTRODUCTORY OPTICS SYSTEM User Manual
Page 59
012-02744K
Introductory Optics System
®
53
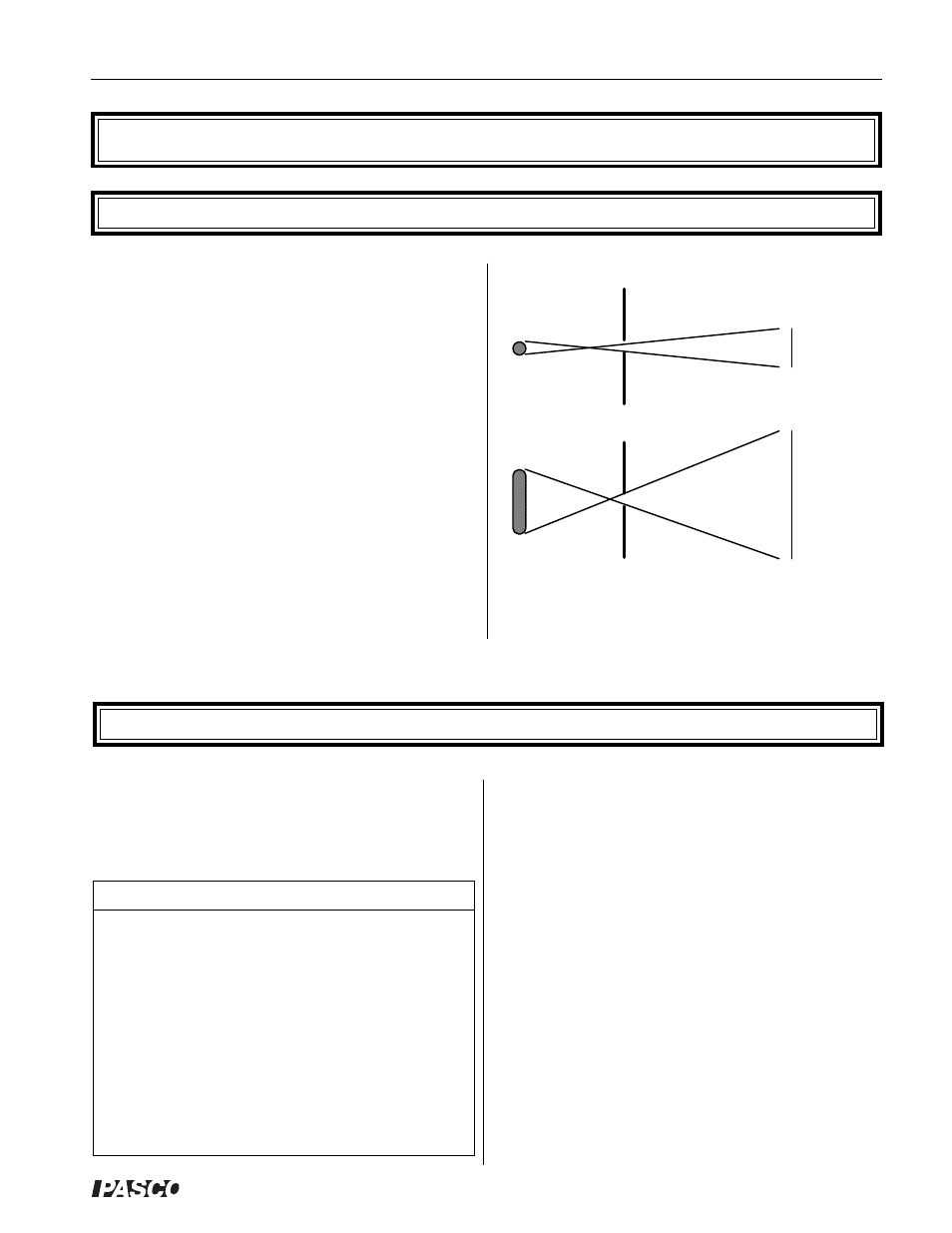
Straight-Line Propagation of Light
The rays are straight, originating from the lamp filament.
Because of this, they widen and become less distinct as
the distance to the filament increases.
As the slit plate is rotated from vertical, the slit images
become wider and less distinct. This is caused by the
greater angle subtended by the filament on the slit.
Image width
Slits aligned with filament
Slit
Filament
Slit
Filament
Image width
Slits perpendicular to filament
Exp 1: Introduction to Ray Optics
Teacher's Guide
Ray Tracing: Locating the Filament
The measurements in steps 1 and 2 should agree very
closely. (within a few millimeters)
➀
The two trials are essentially the same, with a slight
deviation due to improper alignment of the mirror.
➁
The incident ray, reflected ray, and the normal are
all on the ray table, which is a plane.
➂
The two are equal. (This experimental trial shows a
slight deviation due to improper alignment of the
mirror.)
Answers to – Questions
➀
The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflec-
tion.
The incident ray, normal, and reflected ray are all
in the same plane.
➁
It doubles any error, thus allowing us to see any
error more accurately.
➂
(answers may vary)
Exp 2: The Law of Reflection
Suggestions on – Procedure
Make sure that the mirror is set up exactly on the
“component” line. Any deviation will affect the
accuracy of your results.
angle of:
Incidence
Reflection 1 Reflection 2
0
0
0
10
10
10
20
20
20
30
30
30
40
41
41
50
51
51
60
61
61
70
71
71
80
81
80
90
90
90
