PASCO OS-8500 INTRODUCTORY OPTICS SYSTEM User Manual
Page 34
Introductory Optics System
012-02744K
®
28
Place the convex side of the Ray Optics Mirror so that its focal point is coincident with the point where
the rays cross, as in Figure 11.2b. Of course, with the mirror in this position, the rays are reflected and
don’t actually cross. The point where the rays did cross, though, can be used as a virtual object.
➂ Describe the reflected rays when a virtual object is positioned at the focal point of the convex mirror.
Image Location
Remove the Parallel Ray Lens. Slide the Slit Plate, Ray Table, and mirror along the Optics Bench, as far
as possible from the Light Source. Orient the mirror as in Figure 11.1.
➀ Where is the image of the light bulb filament formed? ______________________________.
➁ How is image location affected as you move the mirror closer to the filament? ____________
_________________________________________________________________________.
➂ Is an image still formed when the distance between the filament and mirror is less than the focal length of
the mirror? If so, what kind? _____________________________________.
➃ Using the convex side of the mirror, can you obtain a real image of the Light Source filament? If so,
how? _______________________________________________________________.
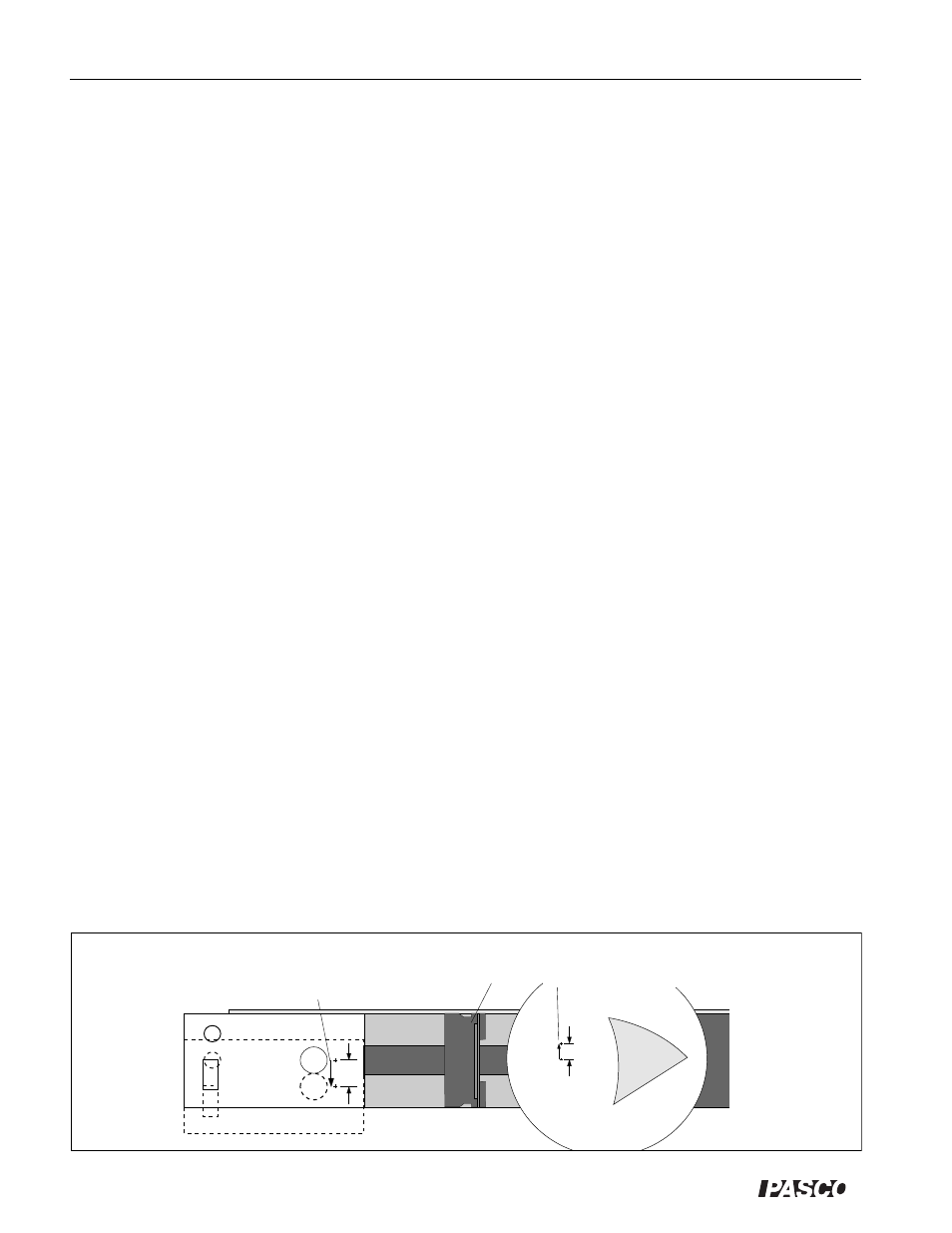
Magnification and Inversion
In the plane of the Ray Table, the filament of the Light Source acts as a point source. To observe magnification
and inversion, an extended source is needed. As shown in Figure 11.3, two positions of the Light Source
filament can be used to define an imaginary arrow, of height h
o
.
Position the filament of the Light Source first at the tail of the imaginary arrow, then at the tip. For each position,
locate the image. The magnification is determined by dividing h
i
, the height of the image arrow, by h
o
, the
height of the object arrow.
Measure the magnification for several different distances between the light source and the mirror.
➀ Qualitatively, how does the degree of magnification depend on the distance between the object and the mirror?
____________________________________________________________.
➁ Is the image inverted? Does image inversion depend on object location? ____________________.
________________________________________________________________________________.
Cylindrical Aberration
Cylindrical aberration is the distortion of the reflected image caused by imperfect focusing of the re-
flected rays. Place a blank sheet of paper over the Ray Table. Arrange the equipment so all the light
rays are reflected from the concave surface of the mirror. Block all but two rays and mark the point of
intersection. Do this for several pairs of rays.
➀ Are all the rays focused at precisely the same point?________________________________.
➁ How would you alter the shape of the cylindrical lens to reduce the amount of cylindrical aberra-
tion?________________________________________________________________.
Figure 11.3 Magnification and Inversion
h
0
h
i
Slit Plate
Two positions of the light
source filament define an
imaginary arrow.
For each position of the light source
filament, an image is formed, defining
the image of the imaginary arrow.
