Experiment 15: the diffraction grating, Introduction, Procedure – PASCO OS-8500 INTRODUCTORY OPTICS SYSTEM User Manual
Page 41
012-02744K
Introductory Optics System
®
35
EQUIPMENT NEEDED:
-Optics Bench
-Light Source
-Ray Table Base
-Component Holder
-Diffraction Scale
-Diffraction Plate
-Diffraction Grating
-Slit Mask
-Color Filter (any color). Perform in a well lighted room.
Experiment 15: The Diffraction Grating
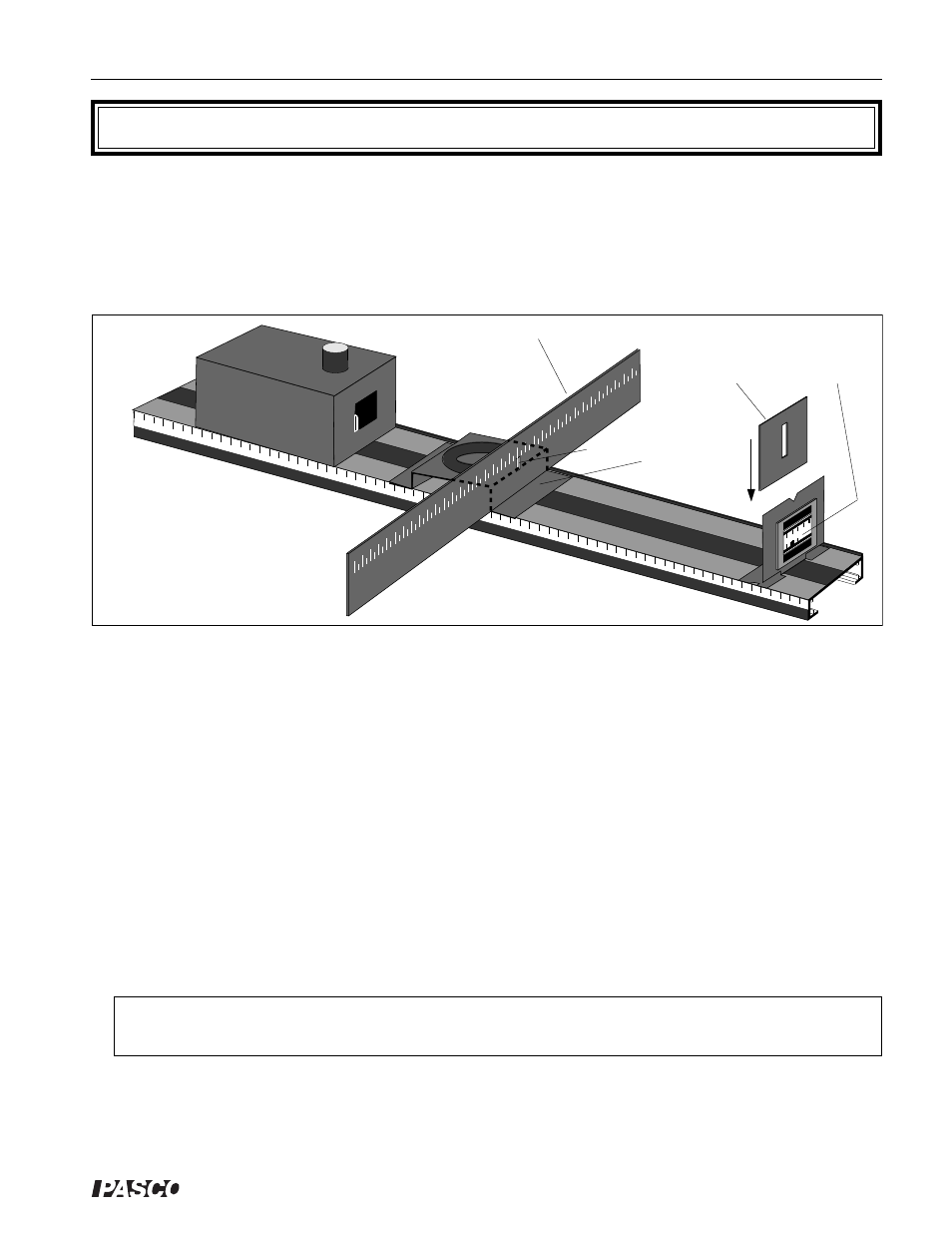
Figure 15.1 Equipment Setup
Introduction
Diffraction gratings are used to make very accurate measurements of the wavelength of light. In theory,
they function much the same as two slit apertures (see Experiment 9). However, a diffraction grating has
many slits, rather than two, and the slits are very closely spaced. By using closely spaced slits, the light
is diffracted to large angles, and measurements can be made more accurately. In spreading out the
available light to large angles, however, brightness is lost. By using many slits, many sources of light are
provided, and brightness is preserved.
In this experiment you will use a diffraction grating to determine the range of wavelengths for each of
the colors in the visible spectrum.
Procedure
Arrange the equipment as shown in Figure 15.1. When looking through the Diffraction Plate window,
the filament of the Light Source must be directly visible through the slot in the Diffraction Plate. Look
through each of the double slit patterns (Patterns D, E, and F) of the Diffraction Plate at the filament of
the Light Source. Qualitatively, compare the spacing of the interference maxima for the different pat-
terns.
➤NOTE: You may find that a blue/green color filter placed behind the Slit Mask will make it easier
to distinguish the details of the diffraction patterns.
➀ How does the spacing of the maxima relate to the spacing of the slits on the Diffraction Plate (compare
patterns of equal slit width, but different slit spacing)?
__________________________________________________________.
➁ Look through the 10-slit pattern (Pattern G) at the filament. What effect does the larger number of slits
have on the diffraction pattern?_________________________________.
. . . . .
. . ..
. . . . ..
. .
. . . . .. .
. . .
. . . . .
. . ..
. . . . ..
. .
. . . . .. .
. . .
. . . . .
. . ..
. . . . ..
. .
. . . . .. .
. . .
. . . . .
. . ..
. . . . ..
. .
. . . . .. .
. . .
. . . . .
. . ..
. . . . ..
. .
. . . . .. .
. . .
....
......
......
....
.
.........
....
.......
.
.........
....
....
....
....
......
.......
....
....
......
......
....
.
.........
....
.......
.
....
......
......
....
.
.........
....
....
....
.........
....
.......
.
....
.....
....
....
....
....
......
......
.....
......
....
......
....
.
DIF
FR
AC
TI
ON
P
LA
TE
A
B
C
D
E
DIF
FR
AC
TIO
N P
LAT
E
J
I
H
G
F
Diffraction Scale
Slot
Ray Table
Base
Diffraction
Plate
Window
Slit Mask
